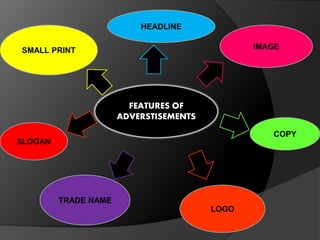
The document outlines the key features of advertisements, focusing on elements such as headlines, images, copy, logos, trade names, slogans, and small print. It explains how these components work together to attract and persuade the target audience through visual appeal, emotive language, and strategic messaging. Additionally, it highlights the importance of branding and legal disclaimers in advertisements.