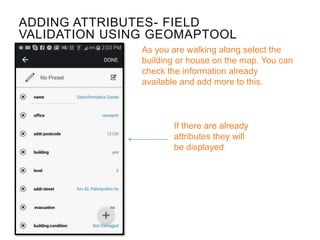
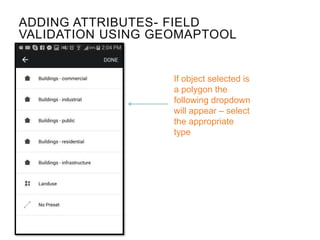
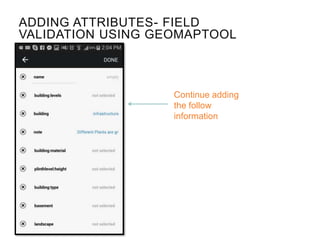
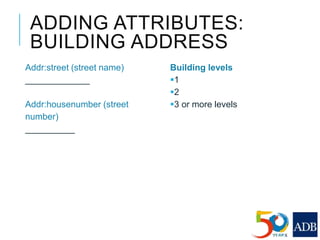
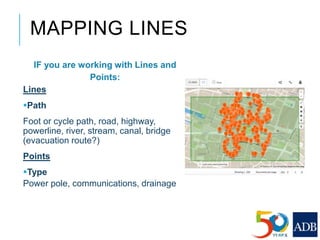
This document provides guidance on conducting field validation using mobile applications to collect building and infrastructure attribute data. It outlines the steps including: choosing a mobile app; designing a field validation survey to align with OSM tags and values; practicing adding attributes to buildings and infrastructure in the field; and checking uploaded data. The goal is to efficiently create an exposure database for disaster preparedness and resilience by quantifying vulnerable locations and buildings. Good practices like charging phones, having a mapping plan, and respecting privacy are also covered.

















![APPLICATION
[**DESIGN YOUR
POWERPOINT DEPENDING
ON THE MOBILE
APPLICATION CHOSEN**]
The following is an example ppt.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02fieldvalidationcc-170918030625/85/Lesson-2-Field-Validation-21-320.jpg)