The study employs quantum chemical and molecular dynamics simulations to assess the corrosion inhibition capabilities of various thiazole and thiadiazole derivatives against iron corrosion. The research calculates key quantum chemical parameters and binding energies to understand the interactions between these compounds and the iron surface, revealing theoretical predictions that align with previous experimental results. The findings underscore the significance of organic compounds with π-bonds and heteroatoms in developing effective corrosion inhibitors for iron in industrial applications.
![Quantum chemical and molecular dynamics simulation studies on
inhibition performances of some thiazole and thiadiazole derivatives
against corrosion of iron
Savaş Kaya a,
⁎, Cemal Kaya a
, Lei Guo b
, Fatma Kandemirli c
, Burak Tüzün a
, İlkay Uğurlu a
,
Loutfy H. Madkour d
, Murat Saraçoğlu e
a
Cumhuriyet University, Faculty of Science, Department of Chemistry, 58140 Sivas, Turkey
b
School of Material and Chemical Engineering, Tongren University, Tongren 554300, PR China
c
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering and Architecture, Kastamonu University, 37150 Kastamonu, Turkey
d
Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science and Arts, Baljarashi, Al-Baha University, P.O. Box 1988, Al-Baha, Saudi Arabia
e
Faculty of Education, Erciyes University, 38039 Kayseri, Turkey
a b s t r a c ta r t i c l e i n f o
Article history:
Received 11 December 2015
Accepted 12 March 2016
Available online xxxx
In the present study, to predict corrosion inhibition performances of 2-amino-4-(4-chlorophenyl)-thiazole
(Inh1), 2-amino-4-(4-bromophenyl)-thiazole (Inh2), 4-(2-aminothiazole-4-yl)-phenol (Inh3), 5,5′-(ethane-1,
2-diyldisulfanediyl) bis-(1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-amine) (Inh4), 5,5′-(propane-1,3-diyldisulfanediyl) bis-(1,3,4-
thiadiazole-2-amine) (Inh5) against corrosion of Fe metal, density functional theory (DFT) calculations and mo-
lecular dynamics simulations approach were performed on these mentioned molecules. Firstly, quantum chem-
ical parameters such as the highest occupied molecular orbital energy (EHOMO), lowest unoccupied molecular
orbital energy (ELUMO), the energy gap between ELUMO and EHOMO (ΔE), chemical hardness, softness, electroneg-
ativity, proton affinity, global electrophilicity, global nucleophilicity and total energy (sum of electronic and zero-
point energies) were calculated and discussed with the help of HF/SDD, HF/6-311G, HF/6-31++G, B3LYP/SDD,
B3LYP/6-311G and B3LYP/6-31++G methods. Then, we calculated binding energies on Fe(110) surface of afore-
mentioned thiazole and thiadiazole derivatives to investigate the strength of the interactions between metal sur-
face and these molecules. The theoretical data obtained are in good agreement with the experimental inhibition
efficiency results earlier reported.
© 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Keywords:
Density functional theory
Molecular dynamics simulation
Corrosion
Thiazole
Thiadiazole
Iron
1. Introduction
The prevention of corrosion using various methods is an important
issue for industrial applications of materials. To prevent the corrosion
of the materials, organic compounds having π-bonds and heteroatoms
such O, N and S have been widely used [1–4]. The inhibitive perfor-
mances of a molecule are substantially connected on its adsorption on
metal surface. As is known, iron is one of the metals used widely used
in industry and this metal may be exposed to corrosion due environ-
mental factors. For this reason, the synthesis and design of new corro-
sion inhibitors to prevent the corrosion of iron are quite important.
In recent years, theoretical methods and computational chemistry
programs such as Gaussian and Monte Carlo have become important
tools for the prediction of corrosion inhibition performances of mole-
cules because experimental methods used to determine the corrosion
inhibition efficiencies of and to understand the inhibition mechanisms
of chemical compounds such as weight loss [5], potentiodynamic
polarization (PDP) [6], electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS)
[7], Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) [8] and scanning
electron microscopy (SEM) [9] are in general expensive and time-
consuming too. Density functional theory considers their electron den-
sity for the analysis of chemical reactivity of compounds [10–16]. Quan-
tum chemical parameters such as hardness [17,18], electronegativity
[19], softness [20], chemical potential [21] are defined based on ioniza-
tion energies and electron affinities of chemical species through this
theory that provides great contributions in the evaluation of quantum
chemistry. With the help of molecular dynamics simulation approach,
binding energy and interaction energies between metal surfaces and in-
hibitor molecules can be easily determined.
Many papers have been published about that thiazole and
thiadiazole derivatives are effective against the corrosion of metals
such as mill steel, copper and aluminum [22–24]. In recent years,
I.H. R. Tomi [25] and coworkers synthesized some thiazole and
thiadiazole derivatives given in Fig. 1 and investigated experimen-
tally their inhibitory effects towards the corrosion of copper in
acidic media. They obtained that the relative strength of these
compounds as corrosion inhibitors decreases in the following
Journal of Molecular Liquids 219 (2016) 497–504
⁎ Corresponding author.
E-mail address: savaskaya@cumhuriyet.edu.tr (S. Kaya).
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.03.042
0167-7322/© 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Contents lists available at ScienceDirect
Journal of Molecular Liquids
journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/molliq](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jm-liquids-160419140503/75/Jm-liquids-1-2048.jpg)
![order: Inh5 N Inh4 N Inh3 N Inh2 N Inh1. The goal of this work is to
investigate the inhibitive performances of molecules synthesized
by aforementioned scientists against the corrosion of iron using
DFT and molecular dynamics simulations approaches and to theo-
retically predict the most effective inhibitor among them.
2. Computational details
2.1. Quantum chemical calculations
In the section based on DFT calculations of this study, all calculations
were carried out using HF and DFT/B3LYP methods with SDD, 6-
31++G (d, p) and 6-31 G basis sets of Gaussian program [26]. For op-
timization of molecules was performed with the help of 6-31++G (d,
p) basis set because this basis set is known as one of the basis sets
that gives more accurate results in terms of the determination of geom-
etries and electronic properties for a wide range of organic compounds.
Quantum chemical parameters such as the energy of the highest occu-
pied molecular orbital (EHOMO), the energy of the lowest unoccupied
molecular orbital (ELUMO), HOMO–LUMO energy gap (ΔE), chemical
hardness, softness, electronegativity, proton affinity, electrophilicity,
nucleophilicity and sum of electronic and zero-point energies (SEZPE)
were calculated and discussed.
Density functional theory of chemical reactivity is called as concep-
tual density functional theory (CDFT) [27]. Conceptual density function-
al theory that is a subfield of DFT helps understand and predict the
chemical behaviors of molecules. Via the mentioned theory, chemical
reactivity descriptors such as chemical potential, electronegativity and
chemical hardness are defined as below as the derivative of electronic
energy (E) with respect to number of electron (N) at a constant external
potential υ(r) [28,29].
χ ¼ −μ ¼ −
∂E
∂N
υ rð Þ
ð1Þ
η ¼
1
2
∂μ
∂N
υ rð Þ
¼
1
2
∂
2
E
∂N2
!
υ rð Þ
: ð2Þ
Pearson and Parr obtained the mathematical formulations based on
ionization energy and electron affinity values of chemical compounds
for aforementioned reactivity descriptors by applying the finite differ-
ences approximation [30] to Eqs. (1) and (2). These formulas obtained
are given as:
η ¼
I−A
2
ð3Þ
χ ¼ −μ ¼
I þ A
2
: ð4Þ
Koopmans's Theorem [31] that presents an alternative method to
predict the ionization energy and electron affinities of molecules is
quite important in terms of the calculation based on frontier orbital
energies of chemical reactivity descriptors. This theory states that
the negative value of highest occupied and lowest unoccupied
Fig. 1. Chemical structures of studied thiazole and thiadiazole derivatives.
498 S. Kaya et al. / Journal of Molecular Liquids 219 (2016) 497–504](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jm-liquids-160419140503/85/Jm-liquids-2-320.jpg)
![molecular orbital energy correspond to ionization energy and elec-
tron affinity respectively (−EHOMO = I and −ELUMO = A). If so, with-
in the framework of the theory, chemical hardness, chemical
potential and electronegativity can be calculated with the help of
the following equations [32].
μ ¼ −χ ¼
ELUMO þ EHOMO
2
ð5Þ
η ¼
ELUMO−EHOMO
2
: ð6Þ
R.G. Pearson who put forward the chemical hardness concept
proposed the softness as the multiplicative inverse of hardness
[33].
σ ¼
1
η
¼
2
ELUMO‐EHOMO
: ð7Þ
The electrophilicity [34] is a useful reactivity descriptor that can be
used to compare the electron-donating abilities of molecules. In recent
times, electrophilicity index proposed by Parr [35] has been widely
used in many studies regarding site selectivity, toxicity and corrosion
inhibition performance of molecules. This index mentioned is defined
mathematically by Eq. (8). In addition, it is important to note that Parr
is also presented as the multiplicative inverse of the electrophilicity
the nucleophilicity.
ω ¼
μ2
2η
¼
χ2
2η
ð8Þ
ε ¼ 1=ω: ð9Þ
For the prediction of the proton affinities of molecules, in general,
the following equations are considered.
PA ¼ E proð Þ− E non‐proð Þ þ EHþ
À Á
ð10Þ
where, Enon-pro and Epro are the energies of the non-protonated and pro-
tonated inhibitors, respectively. EH
+
is the energy of H+
ion and was cal-
culated as:
EHþ ¼ E H3Oþ
ð Þ−E H2Oð Þ: ð11Þ
2.2. Molecular dynamics simulation
MD simulation is very popular for the investigation regarding the in-
teraction between the inhibitor molecule and the concerned metal sur-
face [36–38]. The interaction between inhibitors and the iron (Fe)
Table 1
Calculated quantum chemical parameters for non-protonated molecules in gas phase.
EHOMO
(eV)
ELUMO
(eV)
I A ΔE η σ χ PA ω ε Energy
(eV)
HF/SDD level
Inh 1 −8.20348 2.12332 8.20348 −2.12332 10.32680 5.16340 0.19367 3.04008 −1.08055 0.89496 1.11737 −35659.24878
Inh 2 −8.16430 2.05312 8.16430 −2.05312 10.21741 5.10871 0.19574 3.05559 −1.09258 0.91380 1.09434 −23514.10801
Inh 3 −7.86905 2.67925 7.86905 −2.67925 10.54830 5.27415 0.18960 2.59490 −1.25019 0.63835 1.56654 −25208.97786
Inh 4 −9.03099 3.21151 9.03099 −3.21151 12.24250 6.12125 0.16337 2.90974 −0.81553 0.69157 1.44598 −58450.70497
Inh 5 −8.99534 3.29342 8.99534 −3.29342 12.28876 6.14438 0.16275 2.85096 −0.84982 0.66141 1.51191 −59511.86907
HF/6-31G level
Inh 1 −8.23967 2.27652 8.23967 −2.27652 10.51619 5.25810 0.19018 2.98158 −1.13236 0.84534 1.18295 −35662.07454
Inh 2 −8.16593 2.29367 8.16593 −2.29367 10.45959 5.22980 0.19121 2.93613 −1.16229 0.82421 1.21329 −93155.95048
Inh 3 −7.88919 2.86593 7.88919 −2.86593 10.75511 5.37756 0.18596 2.51163 −1.31454 0.58654 1.70492 −25210.92374
Inh 4 −9.00595 2.82538 9.00595 −2.82538 11.83133 5.91567 0.16904 3.09029 −0.87257 0.80717 1.23890 −58454.86135
Inh 5 −8.98037 2.89531 8.98037 −2.89531 11.87569 5.93784 0.16841 3.04253 −0.90087 0.77949 1.28289 −59516.09726
HF/6-31++G level
Inh 1 −8.25818 0.95295 8.25818 −0.95295 9.21113 4.60556 0.21713 3.65261 −1.05374 1.44842 0.69041 −35658.93759
Inh 2 −8.01926 0.93771 8.01926 −0.93771 8.95697 4.47849 0.22329 3.54077 −0.99785 1.39970 0.71444 −93084.48738
Inh 3 −7.94579 0.99431 7.94579 −0.99431 8.94010 4.47005 0.22371 3.47574 −1.21756 1.35130 0.74003 −25207.87473
Inh 4 −9.05575 0.92138 9.05575 −0.92138 9.97713 4.98857 0.20046 4.06718 −0.79464 1.65799 0.60314 −58449.85096
Inh 5 −9.02609 0.94207 9.02609 −0.94207 9.96815 4.98408 0.20064 4.04201 −0.82811 1.63901 0.61013 −59510.91086
B3LYP/SDD level
Inh 1 −5.71035 −1.48004 5.71035 1.48004 4.23032 2.11516 0.47278 3.59520 −1.25791 3.05543 0.32729 −35778.53094
Inh 2 −5.71362 −1.52031 5.71362 1.52031 4.19331 2.09665 0.47695 3.61697 −1.20064 3.11984 0.32053 −23620.39132
Inh 3 −5.36531 −1.06561 5.36531 1.06561 4.29970 2.14985 0.46515 3.21546 −1.46709 2.40462 0.41587 −25319.10174
Inh 4 −6.09676 −0.81907 6.09676 0.81907 5.27769 2.63884 0.37895 3.45791 −1.07709 2.26561 0.44138 −58622.23552
Inh 5 −6.06193 −0.74206 6.06193 0.74206 5.31987 2.65993 0.37595 3.40199 −1.08907 2.17554 0.45966 −59691.19846
B3LYP/6-31G level
Inh 1 −5.82764 −1.44412 5.82764 1.44412 4.38352 2.19176 0.45625 3.63588 −1.23209 3.01575 0.33159 −35781.63412
Inh 2 −5.77212 −1.40602 5.77212 1.40602 4.36610 2.18305 0.45807 3.58907 −1.27024 2.95033 0.33894 −93303.89796
Inh 3 −5.45919 −0.96656 5.45919 0.96656 4.49264 2.24632 0.44517 3.21287 −1.44954 2.29766 0.43523 −25321.36833
Inh 4 −6.19037 −0.86778 6.19037 0.86778 5.32259 2.66129 0.37576 3.52907 −1.12077 2.33990 0.42737 −58626.56031
Inh 5 −6.16778 −0.79540 6.16778 0.79540 5.37239 2.68619 0.37227 3.48159 −1.04825 2.25625 0.44321 −59695.60473
B3LYP/6-31++G level
Inh 1 −5.85539 −1.55678 5.85539 1.55678 4.29862 2.14931 0.46527 3.70608 −1.15290 3.19523 0.31297 −35777.92483
Inh 2 −5.78709 −1.60902 5.78709 1.60902 4.17807 2.08903 0.47869 3.69806 −1.18630 3.27319 0.30551 −93233.27790
Inh 3 −5.53402 −1.14751 5.53402 1.14751 4.38651 2.19325 0.45594 3.34077 −1.34243 2.54433 0.39303 −25317.91825
Inh 4 −6.24942 −1.06697 6.24942 1.06697 5.18245 2.59122 0.38592 3.65819 −0.93630 2.58225 0.38726 −58620.74903
Inh 5 −6.22411 −0.98452 6.22411 0.98452 5.23959 2.61980 0.38171 3.60431 −0.96368 2.47940 0.40332 −59689.63088
499S. Kaya et al. / Journal of Molecular Liquids 219 (2016) 497–504](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jm-liquids-160419140503/85/Jm-liquids-3-320.jpg)
![surface was simulated by the Forcite module from Accelrys Inc. [39,40].
Herein, the Fe(110) surface was chosen to simulate the adsorption pro-
cess. The simulation of the interaction was carried out in a simulation
box (2.48 × 2.48 × 3.81 nm) with periodic boundary conditions. Five
layers of iron atoms were used to ensure that the depth of the surface
was greater than the non-bond cutoff used in the calculation.
COMPASS forcefield [41] was chosen to optimize the structures of all
components of the system. The MD simulation is performed at 298.0 K
under canonical ensemble (NVT) using a time step of 1.0 fs and a simu-
lation time of 600 ps. Details of simulation process can be referred to
some previous literature [42,43].
The interaction energy between the inhibitor molecules and the
Fe(110) surface is calculated by Eq. (12)
Einteraction ¼ Etotal− Esurface þ Einhibitorð Þ: ð12Þ
Herein, the total energy of the surface and inhibitor molecule is
designated as Etotal, Esurface is the surface energy without the inhibi-
tor and Einhibitor is the energy of the adsorbed inhibitor on the sur-
face. The binding energy of the inhibitor molecule is expressed as
Ebinding = −Einteraction.
3. Results and discussion
In this theoretical study, to predict the corrosion inhibition perfor-
mance of thiazole and thiadiazole derivatives that their chemical struc-
tures are given in Fig. 1 against the corrosion of iron, quantum chemical
parameters widely considered in corrosion studies were calculated
using some methods and basis sets of Gaussian program and discussed.
For the analysis of the strength of the interactions between metal sur-
face and inhibitor molecules, molecular dynamics simulation approach
was used. All data obtained in the study and required discussions are
given below in detail.
Chemical reactivity descriptors such as EHOMO, ELUMO, ΔE (HOMO–
LUMO energy gap), chemical hardness, softness, electronegativity, pro-
ton affinity, electrophilicity and nucleophilicity give important clues
about electron-donating and accepting abilities of molecules. In the
present study, calculated chemical reactivity descriptors in both gas
phase and aqueous phase for the protonated and non-protonated
forms of studied thiazole and thiadizole derivatives are given in
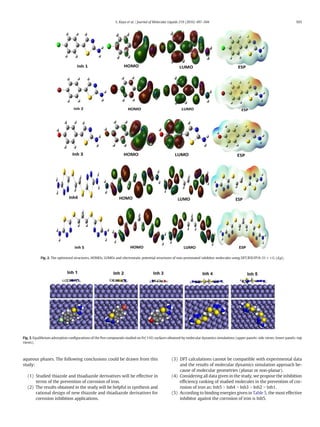
Tables 1–4. The optimized structures, HOMOs, LUMOs and electrostatic
potential structures of studied compounds are given in Fig. 2.
In the defining of chemical reactivity or stability of molecules, the
energies of highest occupied molecular orbital and lowest unoccupied
molecular orbital are important tools. Fukui recognized the importance
of the frontier orbitals in chemical reactions and the analysis of the reac-
tivity. Later on, Parr and Yang demonstrated that density functional the-
ory [33] and molecular orbital theory can be considered in conjunction
for reactivity analysis. EHOMO and ELUMO are associated with electron-do-
nating ability and electron accepting ability of a molecule, respectively.
In general, molecules having high EHOMO and high ELUMO are good corro-
sion inhibitors. It is important to note that a higher value of EHOMO
means that the molecule tends to donate electrons to metal surface.
Within the framework this information given, considering HOMO and
Table 2
Calculated quantum chemical parameters for non-protonated molecules in aqueous phase.
EHOMO
(eV)
ELUMO
(eV)
I A ΔE η σ χ PA ω ε Energy
(eV)
HF/SDD level
Inh 1 −8.17409 2.04550 8.17409 −2.04550 10.21959 5.10979 0.19570 3.06430 −3.46576 0.91882 1.08836 −35659.65080
Inh 2 −8.14362 1.96794 8.14362 −1.96794 10.11156 5.05578 0.19779 3.08784 −3.45890 0.94295 1.06050 −23514.49760
Inh 3 −7.94633 2.49041 7.94633 −2.49041 10.43674 5.21837 0.19163 2.72796 −3.51797 0.71304 1.40245 −25209.51399
Inh 4 −9.14065 3.10294 9.14065 −3.10294 12.24359 6.12179 0.16335 3.01885 −3.26172 0.74435 1.34346 −58451.53522
Inh 5 −9.11779 3.16172 9.11779 −3.16172 12.27951 6.13975 0.16287 2.97804 −3.26232 0.72224 1.38459 −59512.77181
HF/6-31G level
Inh 1 −8.20702 2.22809 8.20702 −2.22809 10.43510 5.21755 0.19166 2.98947 −3.05494 0.85643 1.16764 −35782.44677
Inh 2 −8.15913 2.22509 8.15913 −2.22509 10.38422 5.19211 0.19260 2.96702 −2.44720 0.84775 1.17960 −93305.31003
Inh 3 −7.96048 2.69259 7.96048 −2.69259 10.65307 5.32653 0.18774 2.63395 −3.00033 0.65124 1.53554 −25322.42604
Inh 4 −9.13112 2.55816 9.13112 −2.55816 11.68929 5.84464 0.17110 3.28648 −3.22784 0.92400 1.08225 −58455.73403
Inh 5 −9.09058 3.01559 9.09058 −3.01559 12.10617 6.05308 0.16521 3.03749 −3.29029 0.76212 1.31213 −59516.97187
HF/6-31++G level
Inh 1 −8.22716 1.18697 8.22716 −1.18697 9.41413 4.70706 0.21245 3.52009 −3.45911 1.31622 0.75975 −35659.32250
Inh 2 −8.03831 1.19051 8.03831 −1.19051 9.22881 4.61441 0.21671 3.42390 −3.48124 1.27027 0.78723 −93084.87460
Inh 3 −8.00620 1.16493 8.00620 −1.16493 9.17113 4.58556 0.21808 3.42063 −3.50217 1.27582 0.78381 −25208.39915
Inh 4 −9.16623 1.31459 9.16623 −1.31459 10.48082 5.24041 0.19082 3.92582 −3.24031 1.47050 0.68004 −58450.68690
Inh 5 −9.14745 1.32330 9.14745 −1.32330 10.47075 5.23538 0.19101 3.91208 −3.27786 1.46163 0.68417 −59511.80634
B3LYP/SDD level
Inh 1 −5.74138 −1.56684 5.74138 1.56684 4.17453 2.08727 0.47910 3.65411 −3.50594 3.19857 0.31264 −35778.89854
Inh 2 −5.74382 −1.59406 5.74382 1.59406 4.14977 2.07488 0.48195 3.66894 −3.51120 3.24382 0.30828 −23620.75288
Inh 3 −5.49565 −1.27867 5.49565 1.27867 4.21698 2.10849 0.47427 3.38716 −3.58119 2.72064 0.36756 −25319.60246
Inh 4 −6.22629 −0.96846 6.22629 0.96846 5.25783 2.62891 0.38039 3.59737 −3.31560 2.46130 0.40629 −58622.99236
Inh 5 −6.20207 −0.91132 6.20207 0.91132 5.29075 2.64538 0.37802 3.55669 −3.32586 2.39098 0.41824 −59692.01454
B3LYP/6-31G level
Inh 1 −5.81430 −1.52031 5.81430 1.52031 4.29399 2.14700 0.46577 3.66731 −3.52448 3.13208 0.31928 −35781.97723
Inh 2 −5.78491 −1.50317 5.78491 1.50317 4.28175 2.14087 0.46710 3.64404 −3.52663 3.10131 0.32244 −93304.23060
Inh 3 −5.57892 −1.15513 5.57892 1.15513 4.42379 2.21189 0.45210 3.36703 −3.59550 2.56271 0.39021 −25321.83087
Inh 4 −6.29676 −0.99105 6.29676 0.99105 5.30572 2.65286 0.37695 3.64391 −3.32205 2.50259 0.39959 −58627.20877
Inh 5 −6.27989 −0.93880 6.27989 0.93880 5.34109 2.67055 0.37446 3.60935 −3.33064 2.43909 0.40999 −59696.35297
B3LYP/6-31++G level
Inh 1 −5.83090 −1.59814 5.83090 1.59814 4.23276 2.11638 0.47250 3.71452 −3.44973 3.25973 0.30677 −35778.27169
Inh 2 −5.79090 −1.63106 5.79090 1.63106 4.15984 2.07992 0.48079 3.71098 −3.45650 3.31056 0.30206 −93233.62025
Inh 3 −5.62056 −1.29799 5.62056 1.29799 4.32256 2.16128 0.46269 3.45927 −3.50187 2.76840 0.36122 −25318.39943
Inh 4 −6.34847 −1.10098 6.34847 1.10098 5.24748 2.62374 0.38113 3.72472 −3.23933 2.64385 0.37824 −58621.50693
Inh 5 −6.33132 −1.05418 6.33132 1.05418 5.27715 2.63857 0.37899 3.69275 −3.29062 2.58405 0.38699 −59690.43142
500 S. Kaya et al. / Journal of Molecular Liquids 219 (2016) 497–504](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jm-liquids-160419140503/85/Jm-liquids-4-320.jpg)
![LUMO energy values given in related tables for non-protonated forms of
studied molecules, it can be said that the inhibition efficiencies accord-
ing to LUMO energies [4] obey the order: Inh5 N Inh4 N Inh3 N
Inh2 N Inh1 but we could not get compatible result with experimental
data in terms of HOMO energies.
Chemical hardness, softness and HOMO–LUMO energy gap are
closely interrelated chemical properties. According to Maximum Hard-
ness Principle [44], chemical hardness is a measure of the stability of
chemical species. More stable molecules have large HOMO–LUMO ener-
gy gap and less stable molecules have small HOMO–LUMO gap. Softness
is a measure of the polarizability and soft molecules give more easily
electrons to an electron acceptor molecule or surface [45]. It is apparent
that we can write the same corrosion inhibition ranking considering
these aforementioned chemical properties. On the basis of the calculat-
ed chemical hardness, softness and energy gap given in the related ta-
bles, the corrosion inhibition efficiency ranking of studied chemical
compounds can be written as: Inh2 N Inh1 N Inh3 N Inh4 N Inh5. Accord-
ing to Ebenso at al. [46], molecular geometry is an important factor that
determines the degree of adsorption of inhibitor molecules on metal
surface. Because of the planar geometry of the inhibitor molecule, in
such a case that metal surface and molecule plane are parallel to each
other, molecular adsorption is stronger. The inhibition efficiency rank-
ing obtained for studied molecules considering chemical hardness, soft-
ness and HOMO–LUMO energy gap values calculated is inconsistent
with experimental data. As can be clearly seen from Fig. 3, this result
can be explained through molecular geometries of inhibitors.
Electronegativity that represents the power to attract the electrons
of chemical species is a useful quantity in the prediction of inhibitive
performance of molecules. In addition, this parameter has an important
function in the determination of fraction of electrons transferred from
inhibitor molecule to metal surface. Tables 1 and 2 show the electroneg-
ativity values calculated using different basis sets and methods for stud-
ied molecules. A good corrosion inhibitor has low χ value. For this
reason, looking at electronegativity values in related tables, it can be
said that the inhibition efficiencies of studied molecules obey the
order: Inh3 N Inh5 N Inh4 N Inh2 b Inh1.
Electrophilicity and nucleophilicity are useful quantum chemical pa-
rameters for the prediction chemical behavior of molecules and these
quantities can be used to compare the efficiencies of the inhibitor mol-
ecules. It should be noted that a molecule that has large electrophilicity
value is powerless in terms of the prevention of corrosion. On the other
hand, a molecule that has large nucleophilicity value is a good corrosion
inhibitor. Predicted corrosion inhibition efficiency ranking obtained
considering electrophilicity and nucleophilicity values of studied mole-
cules can be given as: Inh5 N Inh3 N Inh4 N Inh2 N Inh1.
G.N. Lewis defined the base as electron pair donor [47]. Proton affinity
that is defined as the enthalpy of the reaction with H+
ion of a chemical
species in gas phase is a measure of the basicity. This parameter is quite
important to compare the electron-donating abilities of molecules. The
presence of the heteroatoms such as nitrogen and sulfur in the molecules
of thiazole and thiadiazole derivatives leads to high tendency for proton-
ation in acidic medium. Thus, analysis of the protonated forms of studied
Table 3
Calculated quantum chemical parameters for protonated molecules in gas phase.
EHOMO
(eV)
ELUMO
(eV)
I A ΔE η σ χ ω ε Energy
(eV)
HF/SDD level
Inh 1 −12.04440 −2.25040 12.04440 2.25040 9.79400 4.89700 0.20421 7.14740 5.21598 0.19172 −35667.68933
Inh 2 −11.81201 −2.23679 11.81201 2.23679 9.57522 4.78761 0.20887 7.02440 5.15312 0.19406 −23522.56059
Inh 3 −11.47241 −1.97856 11.47241 1.97856 9.49386 4.74693 0.21066 6.72548 4.76436 0.20989 −25217.58805
Inh 4 −10.81443 −2.19761 10.81443 2.19761 8.61683 4.30841 0.23210 6.50602 4.91229 0.20357 −58458.88050
Inh 5 −10.54313 −2.15135 10.54313 2.15135 8.39179 4.19589 0.23833 6.34724 4.80082 0.20830 −59520.07889
HF/6-31G level
Inh 1 −12.09692 −2.16659 12.09692 2.16659 9.93033 4.96516 0.20140 7.13175 5.12187 0.19524 −35670.56690
Inh 2 −11.81881 −2.13094 11.81881 2.13094 9.68787 4.84394 0.20644 6.97488 5.02163 0.19914 −93164.47277
Inh 3 −11.47241 −1.90427 11.47241 1.90427 9.56814 4.78407 0.20903 6.68834 4.67529 0.21389 −25219.59828
Inh 4 −10.78994 −2.18917 10.78994 2.18917 8.60077 4.30038 0.23255 6.48955 4.89658 0.20422 −58463.09392
Inh 5 −10.52572 −2.16659 10.52572 2.16659 8.35913 4.17957 0.23926 6.34615 4.81792 0.20756 −59524.35813
HF/6-31++G level
Inh 1 −12.08358 −3.11464 12.08358 3.11464 8.96894 4.48447 0.22299 7.59911 6.43849 0.15532 −35667.35133
Inh 2 −11.70834 −3.09505 11.70834 3.09505 8.61329 4.30664 0.23220 7.40169 6.36053 0.15722 −93092.84523
Inh 3 −11.49962 −3.00198 11.49962 3.00198 8.49764 4.24882 0.23536 7.25080 6.18691 0.16163 −25216.45229
Inh 4 −10.83076 −3.26158 10.83076 3.26158 7.56918 3.78459 0.26423 7.04617 6.55930 0.15246 −58458.00560
Inh 5 −10.57143 −3.24253 10.57143 3.24253 7.32890 3.66445 0.27289 6.90698 6.50936 0.15362 −59519.09897
B3LYP/SDD level
Inh 1 −9.68107 −5.97920 9.68107 5.97920 3.70187 1.85093 0.54027 7.83014 16.56220 0.06038 −35787.14885
Inh 2 −9.50855 −5.98682 9.50855 5.98682 3.52173 1.76086 0.56790 7.74769 17.04467 0.05867 −23628.95196
Inh 3 −9.19344 −5.68505 9.19344 5.68505 3.50839 1.75420 0.57006 7.43924 15.77428 0.06339 −25327.92883
Inh 4 −7.93354 −6.12370 7.93354 6.12370 1.80984 0.90492 1.10507 7.02862 27.29601 0.03664 −58630.67261
Inh 5 −7.65653 −6.08778 7.65653 6.08778 1.56875 0.78437 1.27490 6.87215 30.10456 0.03322 −59699.64753
B3LYP/6-31G level
Inh 1 −9.83400 −5.98111 9.83400 5.98111 3.85289 1.92645 0.51909 7.90755 16.22922 0.06162 −35790.22621
Inh 2 −9.55481 −5.92614 9.55481 5.92614 3.62867 1.81433 0.55117 7.74048 16.51156 0.06056 −93312.52820
Inh 3 −9.26691 −5.67525 9.26691 5.67525 3.59166 1.79583 0.55685 7.47108 15.54074 0.06435 −25330.17787
Inh 4 −8.34961 −5.92587 8.34961 5.92587 2.42374 1.21187 0.82517 7.13774 21.02015 0.04757 −58635.04108
Inh 5 −7.75803 −6.10628 7.75803 6.10628 1.65174 0.82587 1.21084 6.93216 29.09335 0.03437 −59704.01298
B3LYP/6-31++G level
Inh 1 −9.78910 −5.99744 9.78910 5.99744 3.79166 1.89583 0.52747 7.89327 16.43175 0.06086 −35786.43773
Inh 2 −9.56488 −5.96424 9.56488 5.96424 3.60064 1.80032 0.55546 7.76456 16.74380 0.05972 −93241.82420
Inh 3 −9.29439 −5.72586 9.29439 5.72586 3.56853 1.78426 0.56045 7.51013 15.80540 0.06327 −25326.62068
Inh 4 −8.06742 −6.15526 8.06742 6.15526 1.91216 0.95608 1.04594 7.11134 26.44717 0.03781 −58629.04533
Inh 5 −7.80401 −6.12724 7.80401 6.12724 1.67678 0.83839 1.19276 6.96563 28.93640 0.03456 −59697.95456
501S. Kaya et al. / Journal of Molecular Liquids 219 (2016) 497–504](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jm-liquids-160419140503/85/Jm-liquids-5-320.jpg)
![molecules is important in terms of the calculation of the proton affinities
of neutral inhibitors. According to proton affinity values given in the
Tables 1 and 2 for studied compounds, the inhibition efficiencies of men-
tioned compounds follow the order: Inh3 N Inh2 N Inh1 N Inh5 N Inh4.
Here, we could not get compatible results with experimental data and
molecular simulation approach.
3.1. Molecular dynamics simulations
In recent times, molecular dynamics simulation approach is widely
used for the calculation of binding and interaction energies of inhibitor
molecules on metal surface. Large negative values of interaction ener-
gies mean that the interaction between inhibitor molecule and Fe sur-
face is strong. It is apparent that Inh5 has more negative interaction
energy compared to other inhibitors. Moreover, it is important to note
that adsorption abilities on Fe surface of inhibitor molecules can be pre-
dicted via binding energies given in Table 5. According to interaction en-
ergy and binding energy values calculated with the help of molecular
dynamics simulation approach, corrosion inhibition performances of
studied inhibitors against the corrosion of iron can be given as:
Inh5 N Inh4 N Inh2 N Inh1 N Inh3. Actually, this ranking is compatible
with inductive effects of functional groups bonded to aromatic ring
and Hard and Soft Acid–Base (HSAB) Principle [48,49]. Within the
framework of HSAB Principle, S containing molecular structures act as
soft base generally. Soft molecules are polarizable and give easily elec-
trons to an electron acceptor molecule and surface. It is clearly seen
from Fig. 1, Inh5 and Inh4 have two sulfur atoms in their molecular
structure. If so, these molecules can be strongly adsorbed to metal sur-
face. Many papers have been published about that chain length in mol-
ecule plays important role corrosion inhibition properties of molecules.
S. Yoo et al. [50] noted that adsorption equilibrium constant increases as
chain length increases. From the light of this information, it can be said
that Inh5 should be more effective inhibitor compared to Inh4 because
the chain between two aromatic rings is longer.
As is known, inductive effect is the effect on electron density due to
electron-withdrawing or electron-donating groups in a molecule. The
molecules including electron-donating groups give more easily elec-
trons to an electron acceptor molecule or surface. If so, the differences
between the binding energies calculated given in Table 5 for Inh 1,
Inh2 and Inh 3 can be explained with the help of inductive effects of
OH,Cl andBr groups. The electron-withdrawing powers of men-
tioned groups obey the order –OH ≥ Cl N Br. For this reason, for inhibi-
tion efficiencies of Inh1, Inh2 and Inh3, we can write the following
order: Inh2 N Inh1 N Inh3.
4. Conclusion
Hartree Fock (HF), density functional theory at B3LYP with different
basis sets and molecular dynamic simulation approach were employed
to evaluate the corrosion inhibition efficiencies of some thiazole and
thiadiazole derivatives at the molecular level. The neutral and protonat-
ed forms were considered in quantum chemical calculations in gas and
Table 4
Calculated quantum chemical parameters for protonated molecules in aqueous phase.
EHOMO
(eV)
ELUMO
(eV)
I A ΔE η σ χ ω ε Energy
(eV)
HF/SDD level
Inh 1 −9.27861 1.26289 9.27861 −1.26289 10.54150 5.27075 0.18973 4.00786 1.52378 0.65626 −35670.47656
Inh 2 −9.19752 1.24684 9.19752 −1.24684 10.44436 5.22218 0.19149 3.97534 1.51310 0.66090 −23525.31650
Inh 3 −8.77656 1.49065 8.77656 −1.49065 10.26721 5.13360 0.19479 3.64295 1.29257 0.77365 −25220.39196
Inh 4 −9.22854 1.62426 9.22854 −1.62426 10.85280 5.42640 0.18428 3.80214 1.33203 0.75073 −58462.15694
Inh 5 −9.15507 1.66698 9.15507 −1.66698 10.82205 5.41103 0.18481 3.74404 1.29531 0.77202 −59523.39413
HF/6-31G level
Inh 1 −7.07338 −2.46374 7.07338 2.46374 4.60965 2.30482 0.43387 4.76856 4.93296 0.20272 −35792.86171
Inh 2 −6.95148 −2.44796 6.95148 2.44796 4.50352 2.25176 0.44410 4.69972 4.90446 0.20390 −93315.11723
Inh 3 −6.49922 −2.27407 6.49922 2.27407 4.22515 2.11257 0.47336 4.38665 4.55432 0.21957 −25332.78637
Inh 4 −9.19371 1.63623 9.19371 −1.63623 10.82994 5.41497 0.18467 3.77874 1.31846 0.75846 −58466.32187
Inh 5 −9.12623 1.67324 9.12623 −1.67324 10.79947 5.39973 0.18519 3.72649 1.28587 0.77768 −59527.62216
HF/6-31++G level
Inh 1 −9.33739 0.97853 9.33739 −0.97853 10.31592 5.15796 0.19388 4.17943 1.69327 0.59057 −35670.14161
Inh 2 −9.23181 0.97935 9.23181 −0.97935 10.21115 5.10558 0.19586 4.12623 1.66737 0.59975 −93095.71584
Inh 3 −8.83180 0.98696 8.83180 −0.98696 9.81876 4.90938 0.20369 3.92242 1.56693 0.63819 −25219.26132
Inh 4 −9.25249 1.00520 9.25249 −1.00520 10.25768 5.12884 0.19498 4.12365 1.65773 0.60324 −58461.28721
Inh 5 −9.18555 1.00846 9.18555 −1.00846 10.19401 5.09700 0.19619 4.08854 1.63980 0.60983 −59522.44420
B3LYP/SDD level
Inh 1 −6.90766 −2.53068 6.90766 2.53068 4.37699 2.18849 0.45694 4.71917 5.08811 0.19654 −35789.76448
Inh 2 −6.87120 −2.54701 6.87120 2.54701 4.32420 2.16210 0.46251 4.70910 5.12827 0.19500 −23631.62408
Inh 3 −6.42439 −2.33965 6.42439 2.33965 4.08473 2.04237 0.48963 4.38202 4.70094 0.21272 −25330.54365
Inh 4 −6.30710 −2.46537 6.30710 2.46537 3.84173 1.92087 0.52060 4.38624 5.00792 0.19968 −58633.66796
Inh 5 −6.23962 −2.42347 6.23962 2.42347 3.81615 1.90808 0.52409 4.33154 4.91654 0.20340 −59702.70040
B3LYP/6-31G level
Inh 1 −7.07338 −2.46374 7.07338 2.46374 4.60965 2.30482 0.43387 4.76856 4.93296 0.20272 −35792.86171
Inh 2 −6.95148 −2.44796 6.95148 2.44796 4.50352 2.25176 0.44410 4.69972 4.90446 0.20390 −93315.11723
Inh 3 −6.49922 −2.27407 6.49922 2.27407 4.22515 2.11257 0.47336 4.38665 4.55432 0.21957 −25332.78637
Inh 4 −6.37595 −2.46428 6.37595 2.46428 3.91167 1.95583 0.51129 4.42012 4.99465 0.20021 −58637.89082
Inh 5 −6.31554 −2.42918 6.31554 2.42918 3.88636 1.94318 0.51462 4.37236 4.91913 0.20329 −59707.04361
B3LYP/6-31++G level
Inh 1 −7.00780 −2.49231 7.00780 2.49231 4.51549 2.25775 0.44292 4.75006 4.99681 0.20013 −35789.08142
Inh 2 −6.91855 −2.48932 6.91855 2.48932 4.42923 2.21462 0.45155 4.70393 4.99567 0.20017 −93244.43675
Inh 3 −6.51691 −2.33122 6.51691 2.33122 4.18569 2.09284 0.47782 4.42406 4.67601 0.21386 −25329.26130
Inh 4 −6.42711 −2.50047 6.42711 2.50047 3.92663 1.96332 0.50934 4.46379 5.07443 0.19707 −58632.10626
Inh 5 −6.36779 −2.46564 6.36779 2.46564 3.90214 1.95107 0.51254 4.41671 4.99914 0.20003 −59701.08204
502 S. Kaya et al. / Journal of Molecular Liquids 219 (2016) 497–504](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jm-liquids-160419140503/85/Jm-liquids-6-320.jpg)
![References
[1] S.N. Raicheva, B.V. Aleksiev, E.I. Sokolova, Corros. Sci. 34 (1993) 343–350.
[2] H.D. Leçe, K.C. Emregül, O. Atakol, Corros. Sci. 50 (2008) 1460–1468.
[3] I.B. Obot, D.D. Macdonald, Z.M. Gasem, Corros. Sci. 99 (2015) 1–30.
[4] S. Kaya, B. Tuzun, C. Kaya, I.B. Obot, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 58 (2016) 528–535.
[5] M.A. Amin, et al., Electrochim. Acta 52 (2007) 3588–3600.
[6] R.I. Holland, Dent. Mater. 8 (4) (1992) 241–245.
[7] R.G. Duarte, A.S. Castela, R. Neves, L. Freire, M.F. Montemor, Electrochim. Acta 124
(2014) 218–224.
[8] S. Musić, M. Gotić, S. Popović, J. Mater. Sci. 28 (1993) 5744–5752.
[9] J.A. Walocha, J.A. Litwin, A.J. Miodoński, Hum. Reprod. 18 (2003) 1088–1093.
[10] S.Kr. Saha, P. Ghosh, A. Hens, N.C. Murmu, P. Banerjee, Phys. E. 66 (2015) 332–341.
[11] T. Chakraborty, A. Hens, S. Kulashrestha, N.C. Murmu, P. Banerjee, Phys. E. 69 (2015)
371–377.
[12] S.Kr. Saha, A. Hens, A. Roychowdhury, A.Kr. Lohar, N.C. Murmu, P. Banerjee, Can.
Chem. Trans. 2 (2014) 489–503.
[13] K.F. Khaled, Electrochim. Acta 53 (2008) 3484–3492.
[14] I.B. Obot, E.E. Ebenso, M.M. Kabanda, J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 1 (2013) 431–439.
[15] M.M. Kabanda, I.B. Obot, E.E. Ebenso, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 8 (2013) 10839–10850.
[16] I.B. Obot, N.O. Obi-Egbedi, Corros. Sci. 52 (2010) 657–660.
[17] S. Kaya, C. Kaya, Mol. Phys. 113 (2015) 1311–1319.
[18] S. Kaya, C. Kaya, Comput. Theor. Chem. 1060 (2015) 66–70.
[19] S. Kaya, C. Kaya, Comput. Theor. Chem. 1052 (2015) 42–46.
[20] W. Yang, C. Lee, S.K. Ghosh, J. Phys. Chem. 89 (1985) 5412–5414.
[21] Z.S. Safi, S. Omar, Chem. Phys. Lett. 610 (2014) 321–330.
[22] A. Döner, R. Solmaz, M. Ozcan, G. Kardaş, Corros. Sci. 53 (2011) 2902–2913.
[23] M.A. Quraishi, M. Wajid Khan, M. Ajmal, S. Muralidharan, S. Venkatakrishna Iyer,
Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 43 (1996) 5–8.
[24] H. Tian, W. Li, K. Cao, B. Hou, Corros. Sci. 73 (2013) 281–291.
[25] I.H.R. Tomi, A.H.R. Al-Daraji, S.A. Aziz, Synth. React. Inorg. Met.-Org. Nano-Met.
Chem. 45 (2015) 605–613.
[26] M.J. Frisch, G.W. Trucks, H.B. Schlegel, G.E. Scuseria, M.A. Robb, J.R. Cheeseman Jr.,
J.A. Montgomery, T. Vreven, K.N. Kudin, J.C. Burant, J.M. Millam, S.S. Iyengar, J.
Tomasi, V. Barone, B. Mennucci, M. Cossi, G. Scalmani, N. Rega, G.A. Petersson, H.
Nakatsuji, M. Hada, M. Ehara, K. Toyota, R. Fukuda, J. Hasegawa, M. Ishida, T.
Nakajima, Y. Honda, O. Kitao, H. Nakai, M. Klene, X. Li, J.E. Knox, H.P. Hratchian,
J.B. Cross, V. Bakken, C. Adamo, J. Jaramillo, R. Gomperts, R.E. Stratmann, O.
Yazyev, A.J. Austin, R. Cammi, C. Pomelli, J.W. Ochterski, P.Y. Ayala, K. Morokuma,
G.A. Voth, P. Salvador, J.J. Dannenberg, V.G. Zakrzewski, S. Dapprich, A.D. Daniels,
M.C. Strain, O. Farkas, D.K. Malick, A.D. Rabuck, K. Raghavachari, J.B. Foresman, J.V.
Ortiz, Q. Cui, A.G. Baboul, S. Clifford, J. Cioslowski, B.B. Stefanov, G. Liu, A. Liashenko,
P. Piskorz, I. Komaromi, R.L. Martin, D.J. Fox, T. Keith, M.A. Al-Laham, C.Y. Peng, A.
Nanayakkara, M. Challacombe, P.M.W. Gill, B. Johnson, W. Chen, M.W. Wong, C.
Gonzalez, J.A. Pople, Gaussian 03 W, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford, CT, 2004.
[27] S. Kaya, C. Kaya, I.B. Obot, N. Islam, Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 154
(2016) 103–107.
[28] H. Chermette, J. Comput. Chem. 20 (1999) 129–154.
[29] R.G. Parr, P.K. Chattaraj, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 113 (1991) 1854–1855.
[30] R.P. Iczkowski, J.L. Margrave, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 83 (1961) 3547–3551.
[31] T. Koopmans, Physica 1 (1933) 104–113.
[32] N. Islam, D.C. Ghosh, Int. J. Quantum Chem. 109 (2011) 917–931.
[33] W. Yang, R.G. Parr, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 82 (1985) 6723–6726.
[34] P.K. Chattaraj, U. Sarkar, D.R. Roy, Chem. Rev. 106 (2006) 2065–2091.
[35] R.G. Parr, L. Sventpaly, S. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121 (1999) 1922–1924.
[36] L. Li, X. Zhang, S. Gong, H. Zhao, Y. Bai, Q. Li, L. Ji, Corros. Sci. 99 (2015) 76–88.
[37] I.B. Obot, Z.M. Gasem, Corros. Sci. 83 (2014) 359–366.
[38] K.F. Khaled, A. El-Maghraby, Arab. J. Chem. 7 (2014) 319–326.
[39] D. Frenkel, B. Smit, Understanding Molecular Simulations: from Algorithms to Appli-
cations, 2nd ed. Academic Press, San Diego, 2002.
[40] S. Kirkpatrick, C.D. Gelatt, M.P. Vecchi, Science 220 (1983) 671–680.
[41] H. Sun, J. Phys. Chem. B 102 (1998) 7338–7364.
[42] L. Guo, S. Zhu, S. Zhang, J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 24 (2015) 174–180.
[43] Y. Zhou, S. Xu, L. Guo, S. Zhang, H. Lu, Y. Gong, F. Gao, RSC Adv. 5 (2015)
14804–14813.
[44] R.G. Pearson, Acc. Chem. Res. 26 (1993) 250–255.
[45] Lieng-Huang Lee, Langmuir 12 (1996) 1681–1687.
[46] E.E. Ebenso, M.M. Kabanda, L.C. Murulana, A.K. Singh, S.K. Shukla, J. Ind. Eng. Chem.
Res. 51 (2012) 12940–12958.
[47] G.N. Lewis, J. Frankl. Inst. 226 (1938) 293–313.
[48] R.G. Pearson, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 85 (1963) 3533–3539.
[49] R.G. Pearson, J. Chem. Educ. 45 (1968) 581–587.
[50] S.H. Yoo, Y.W. Kim, J. Shin, N.K. Kim, J.S. Kim, Bull. Kor. Chem. Soc. 36 (2015)
346–355.
Table 5
Interaction and binding energies of five inhibitors adsorbed on Fe(110) surface.
Systems Ebinding (kJ mol−1
) Einteraction (kJ mol−1
)
Fe(110) + (1) 430.1 −430.1
Fe(110) + (2) 432.3 −432.3
Fe(110) + (3) 409.9 −409.9
Fe(110) + (4) 532.4 −532.4
Fe(110) + (5) 606.1 −606.1
504 S. Kaya et al. / Journal of Molecular Liquids 219 (2016) 497–504](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jm-liquids-160419140503/85/Jm-liquids-8-320.jpg)