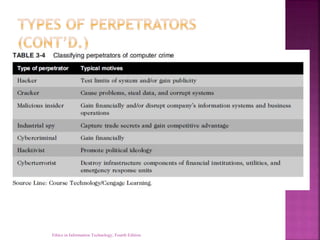
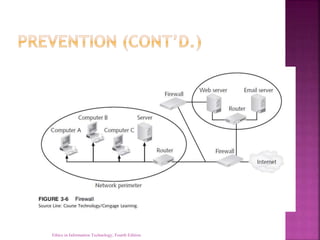
This document discusses computer and internet crime. It identifies increasing complexity as increasing vulnerability and reliance on commercial software with known vulnerabilities. Various types of attacks are discussed like viruses, worms, Trojan horses, and phishing. Perpetrators include hackers, crackers, insiders, and cybercriminals. Managing security requires a multilayer approach including assessment, policies, user education, and tools to prevent breaches. Computer forensics is important for addressing computer crime in court.