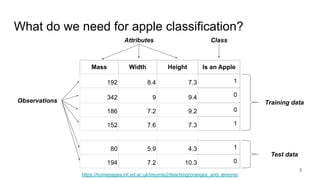
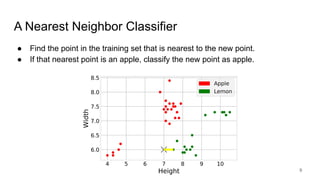
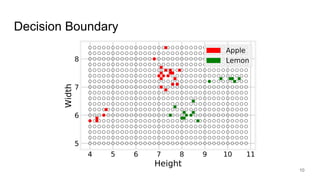
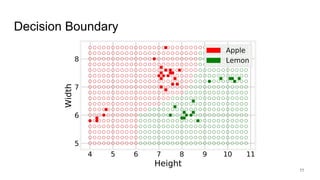
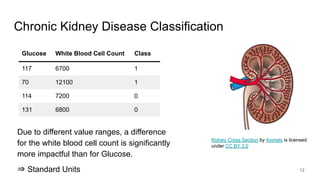
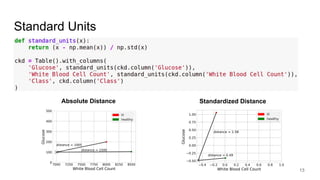
The document discusses classification, particularly through the k-nearest neighbors approach, where examples are used to classify new observations. It covers the concepts of training and testing data, decision boundaries, and accuracy measurement for models. The document emphasizes the importance of not using training data for testing and provides steps for implementing a classifier.