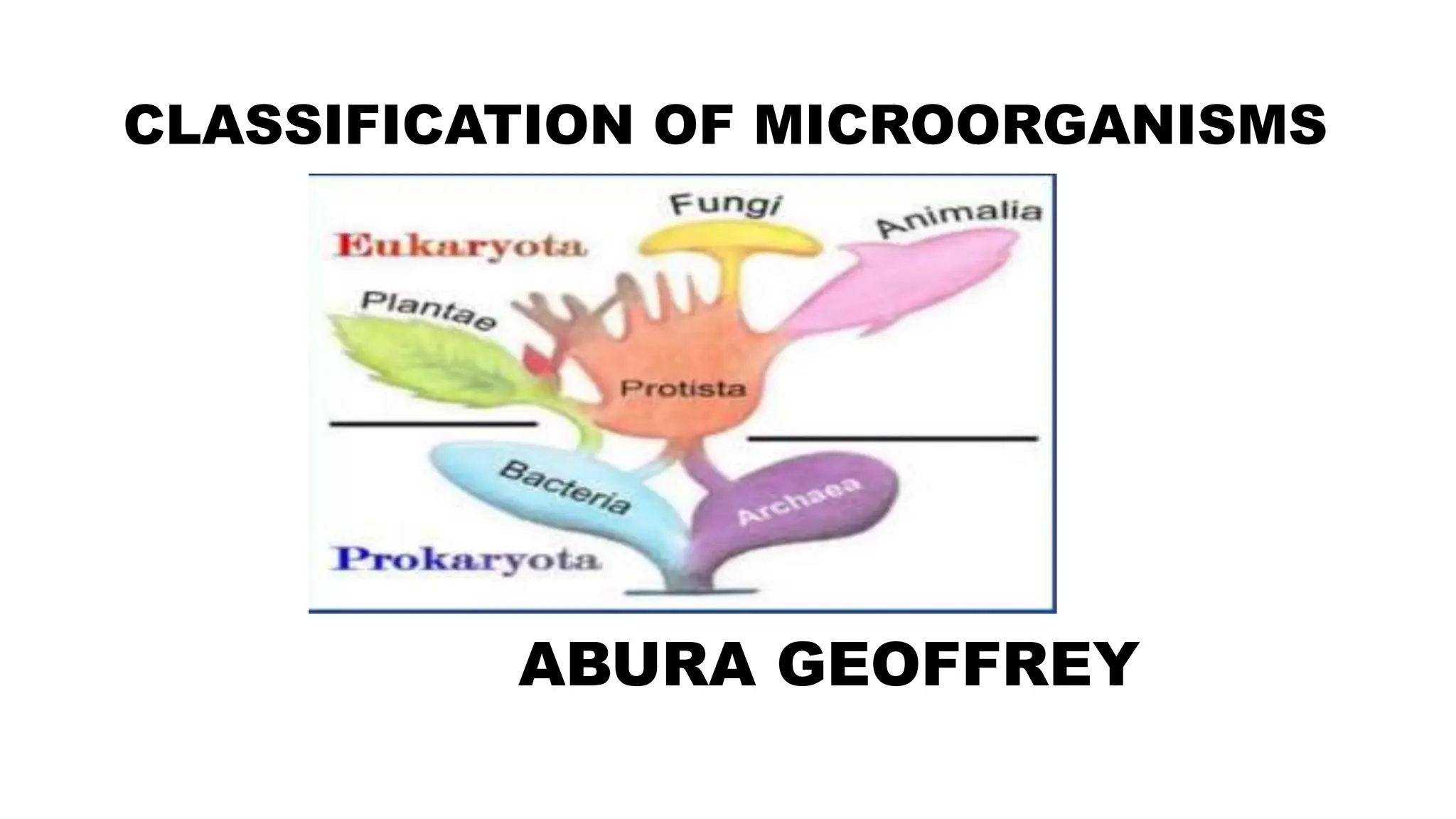
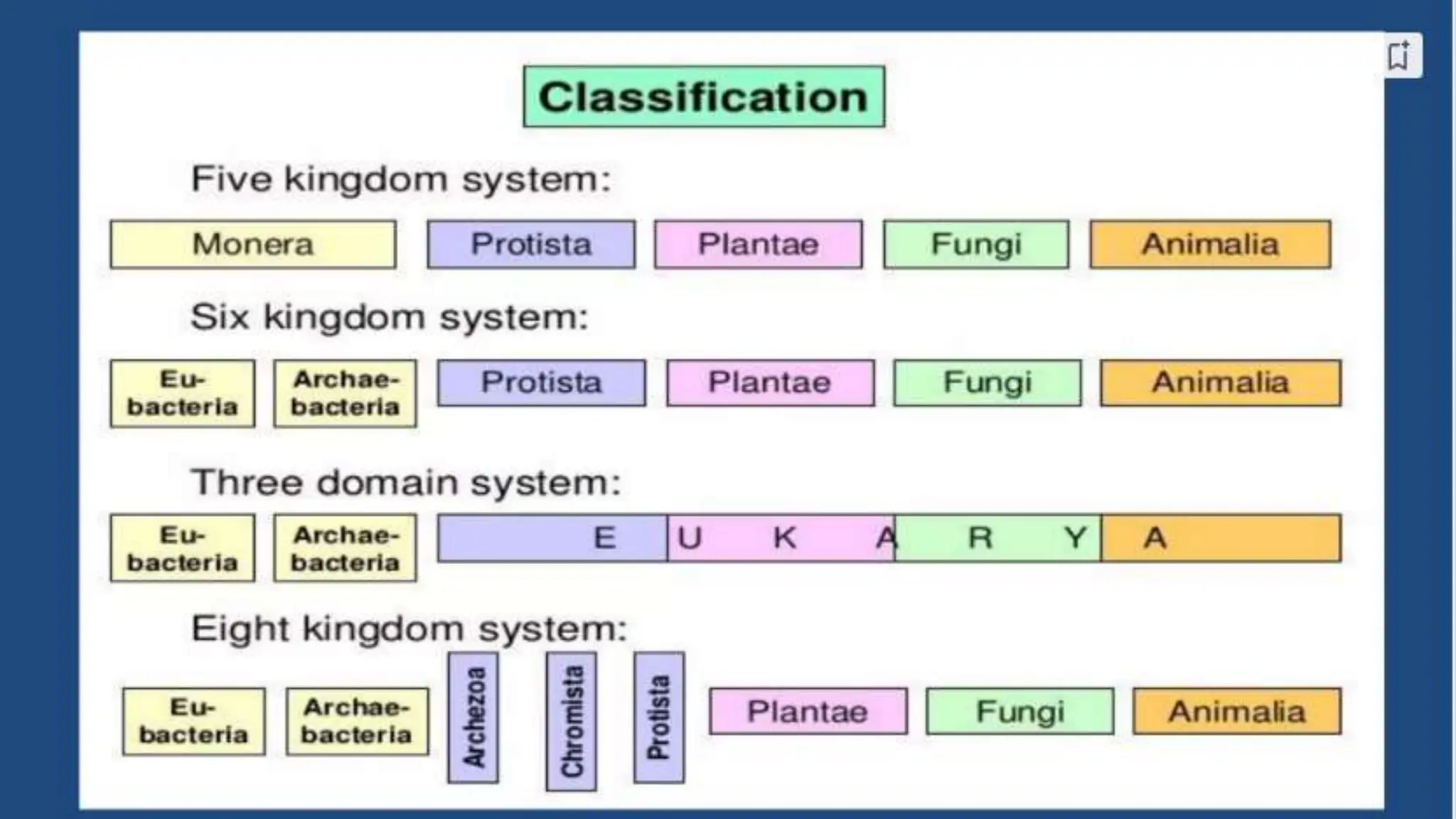
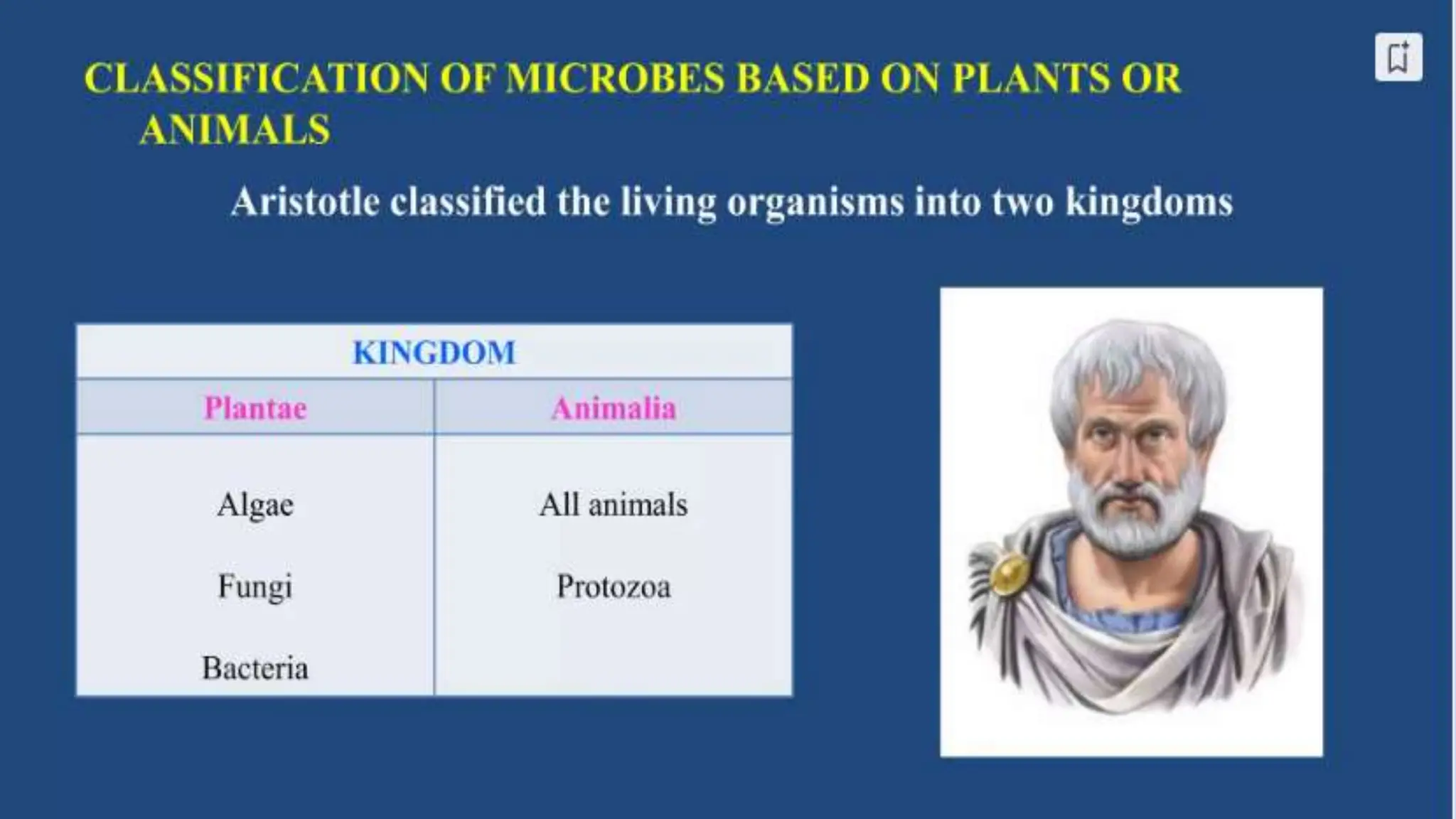
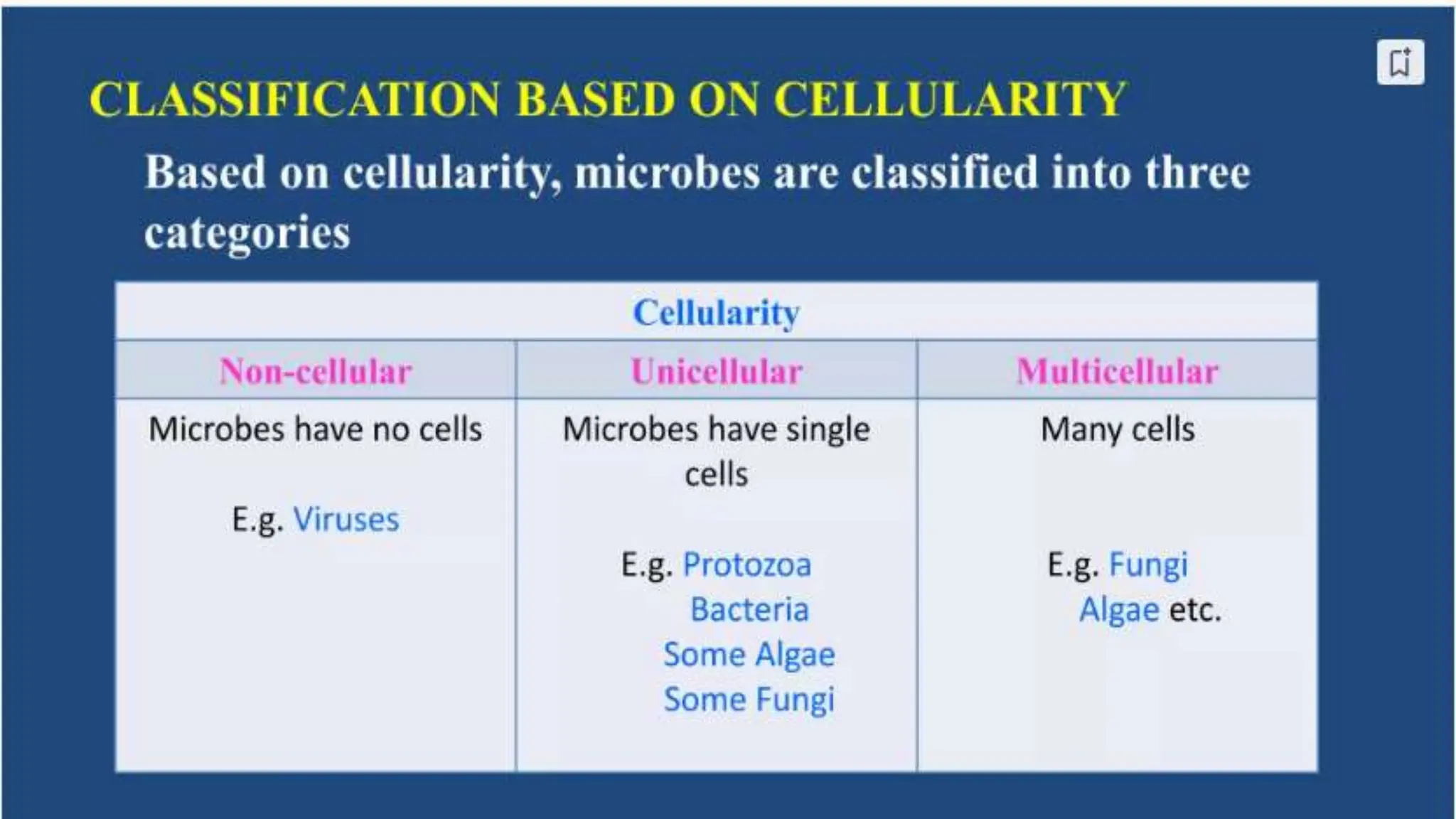
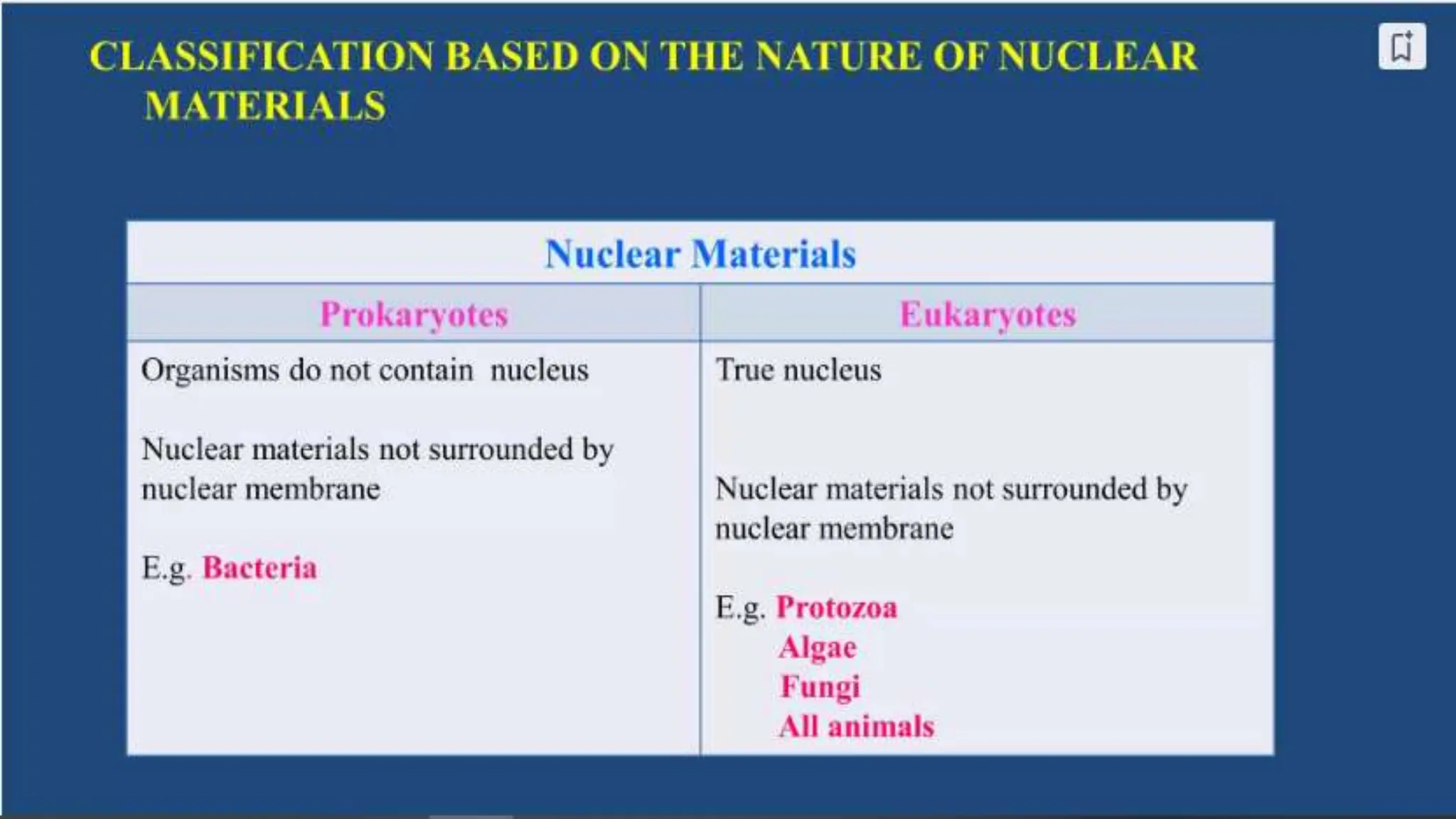
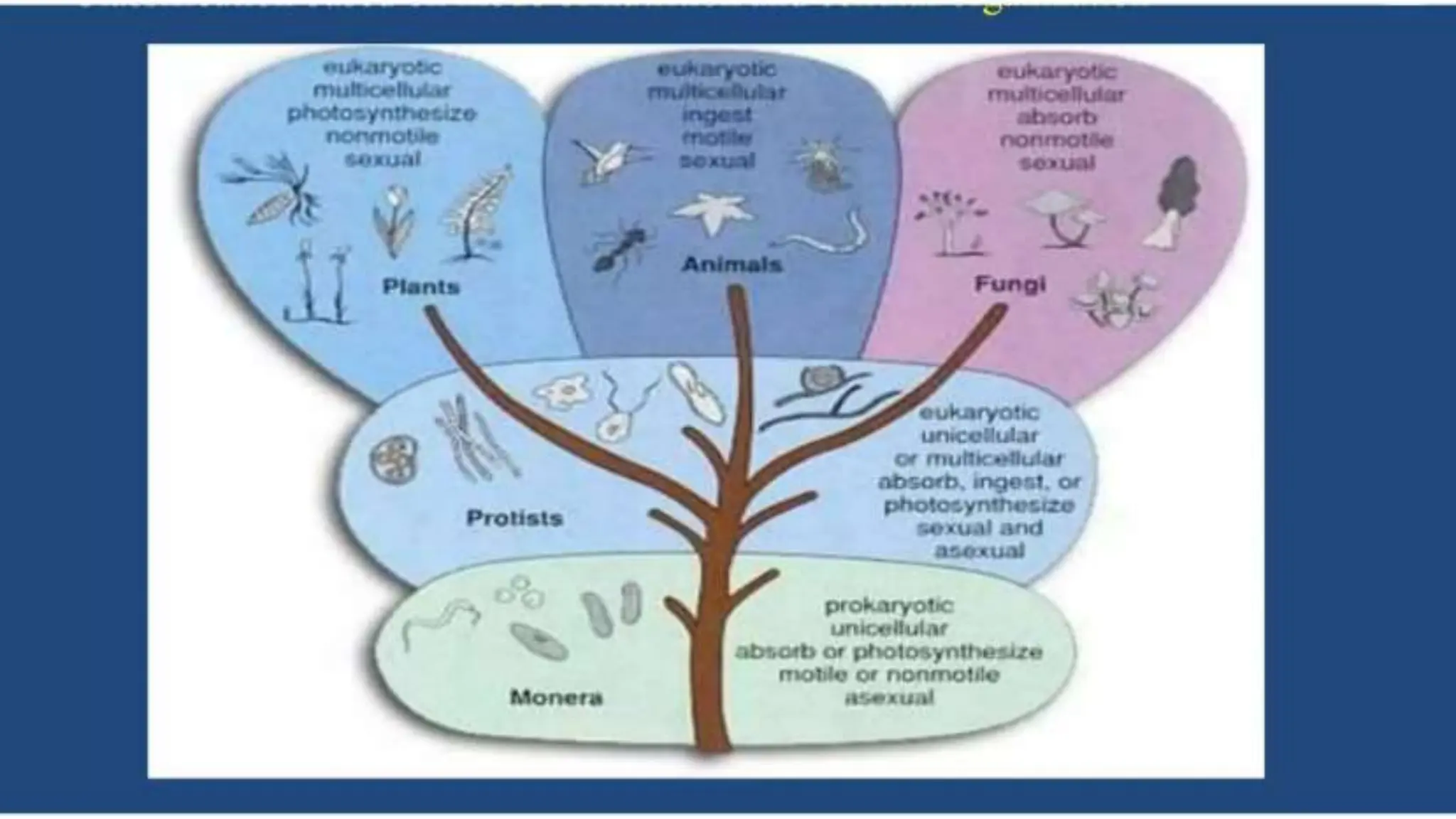
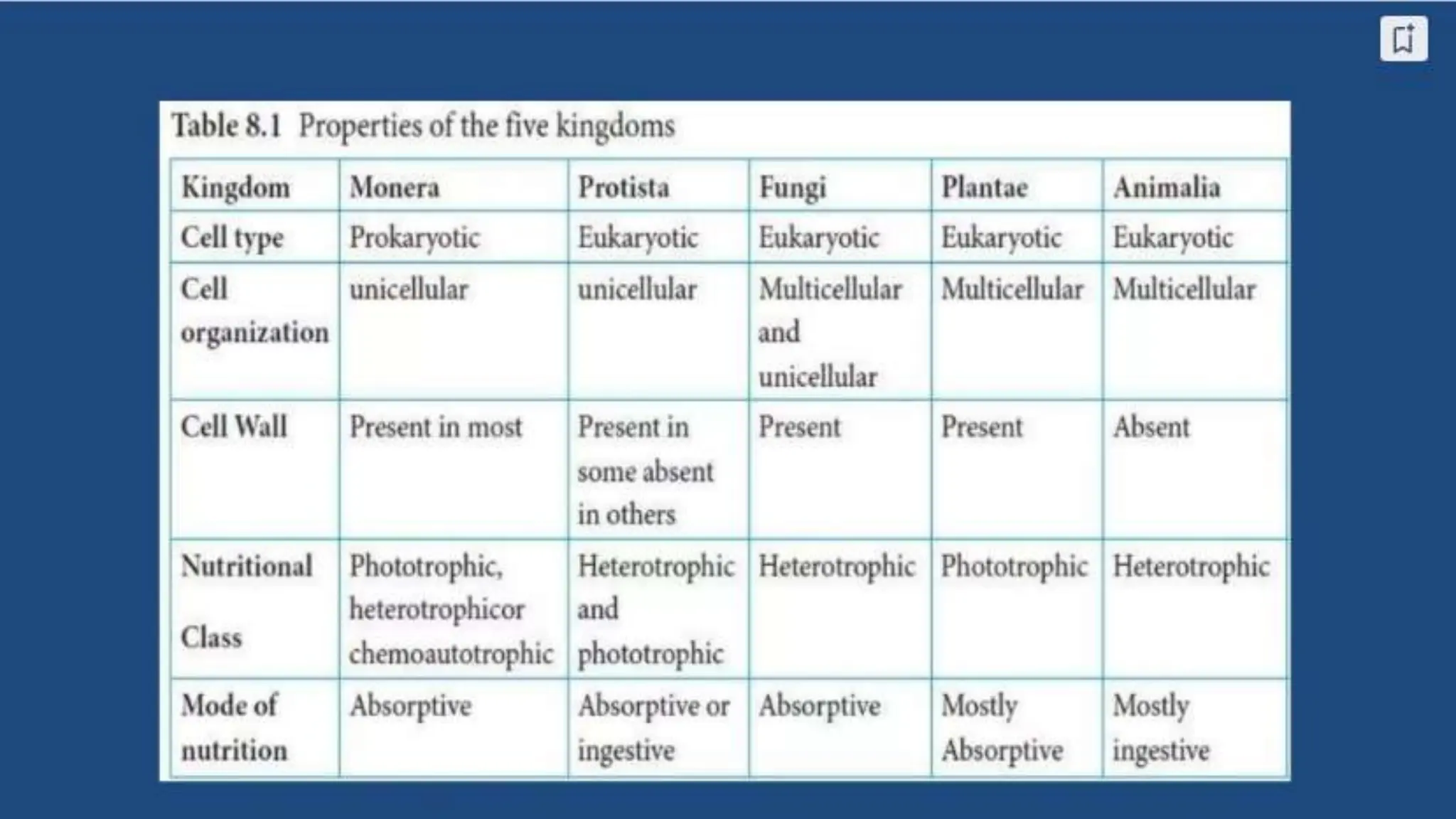
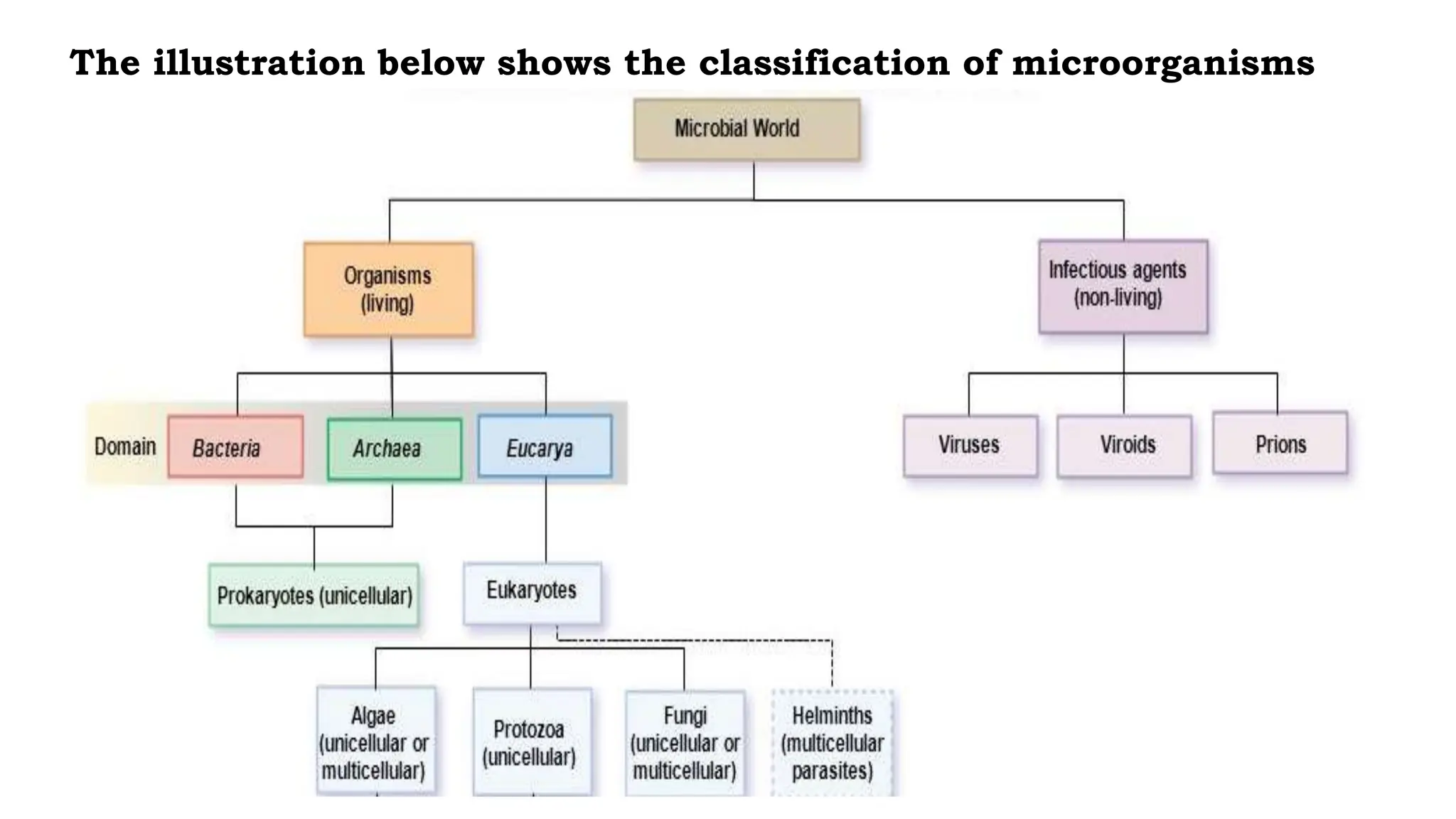
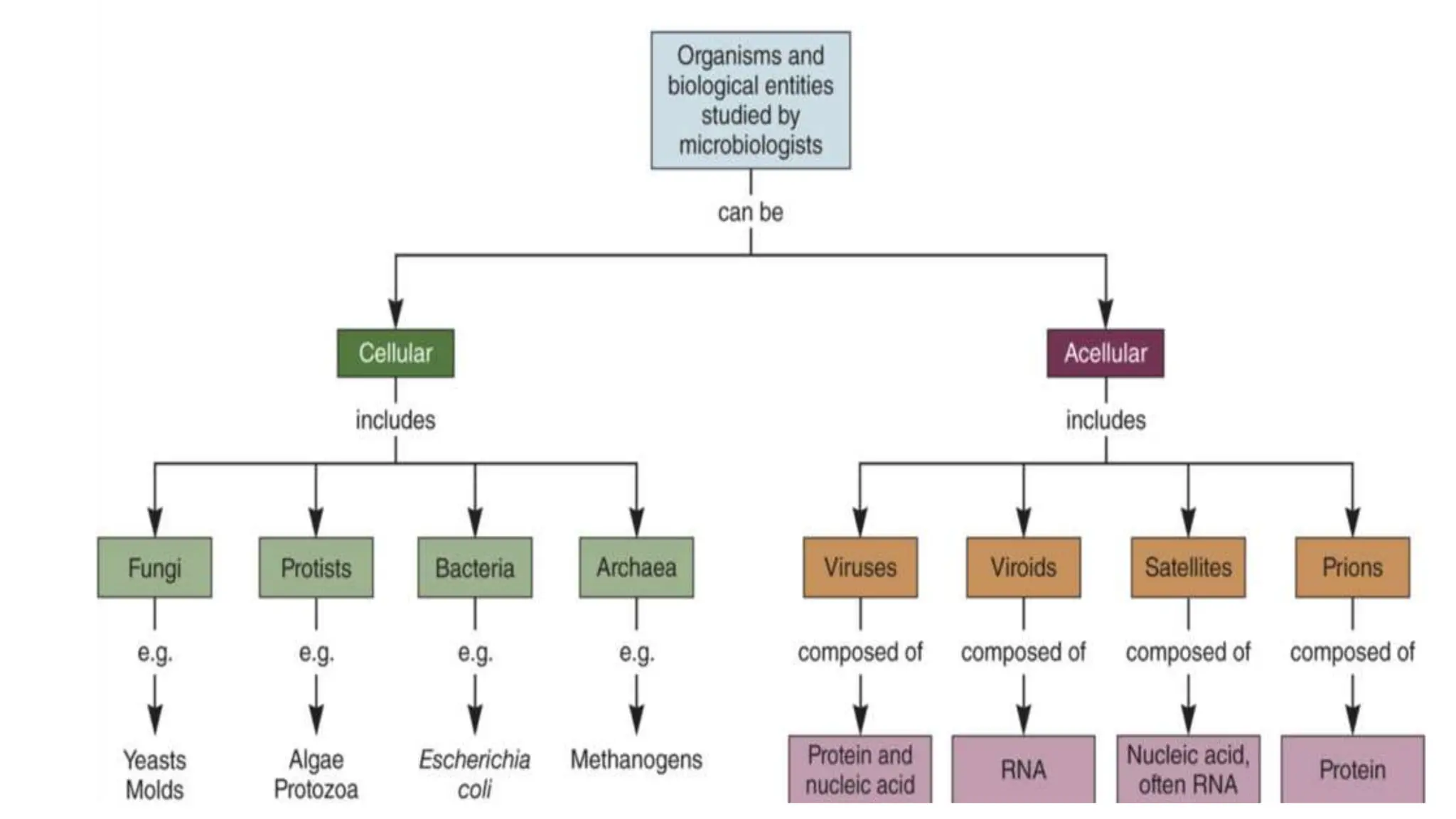
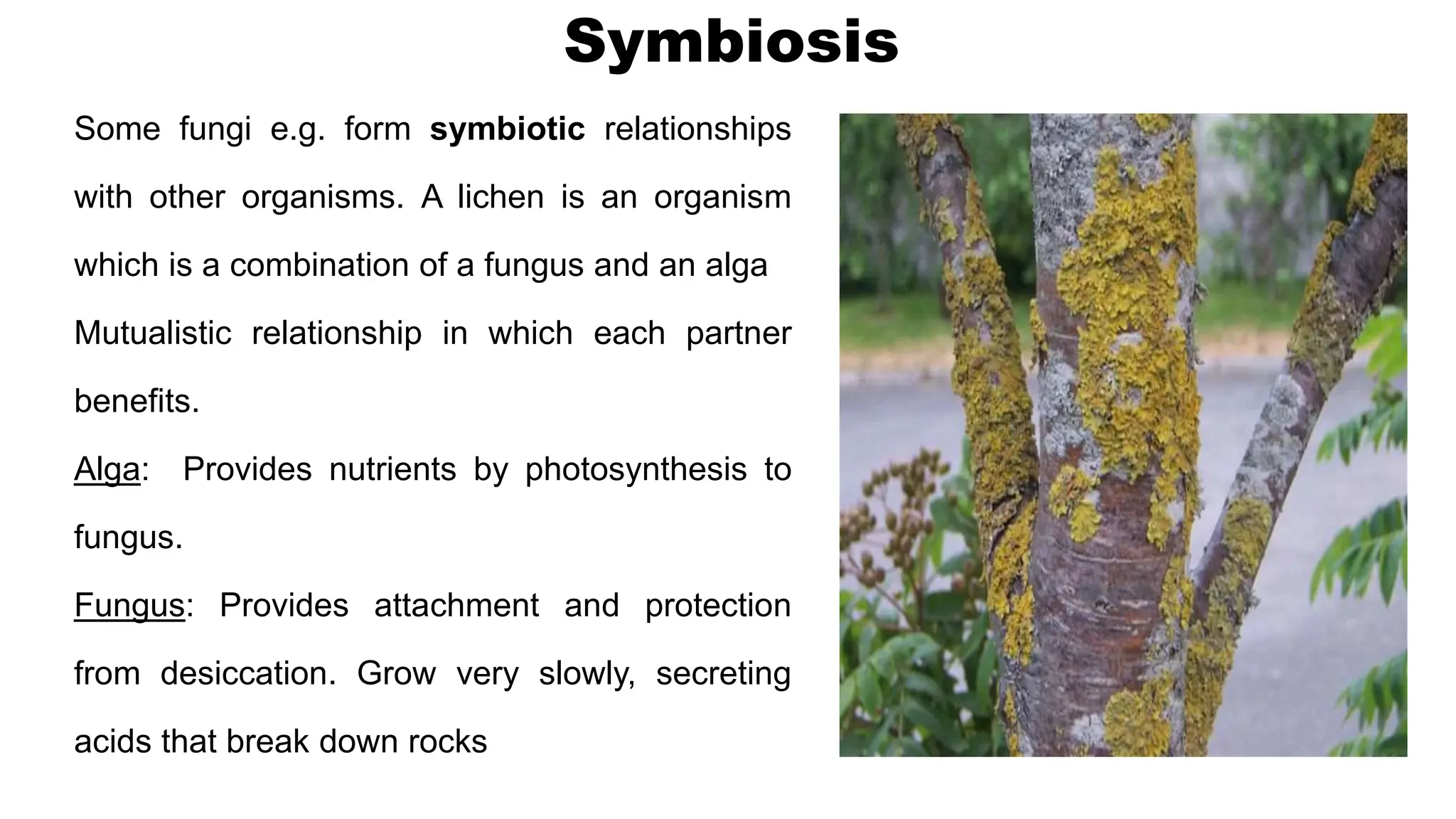
The document discusses the classification of microorganisms, introducing taxonomy as the science of categorizing living organisms. It outlines historical developments in classification, from Linnaeus's two-kingdom system to Woese's three-domain model, and describes various types of microorganisms, including viruses, viroids, prions, algae, protozoa, and fungi. The document also highlights the symbiotic relationships found in nature, such as lichens, where fungi and algae mutually benefit each other.