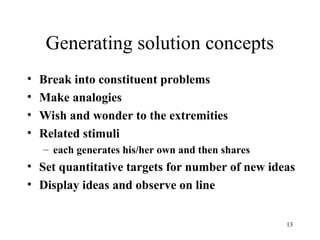
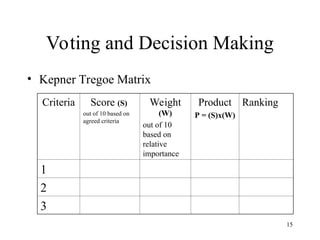
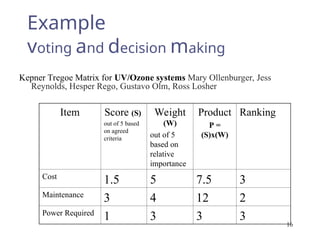
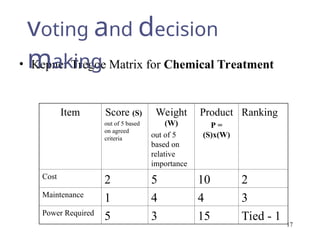
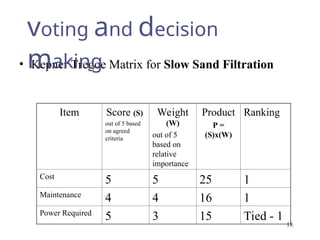
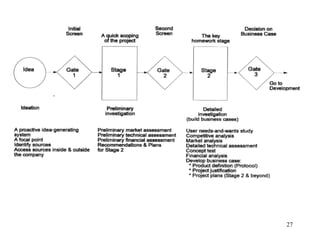
The document outlines a lecture focused on the engineering of creativity and its application in problem-solving across various stages of product development. It emphasizes the importance of clearly defining problems, structured brainstorming, and decision-making processes like the Kepner Tregoe matrix in generating innovative ideas. Additionally, it highlights examples of generating concepts and categorizing them to refine potential solutions, encouraging collaboration and diverse input during the creative process.