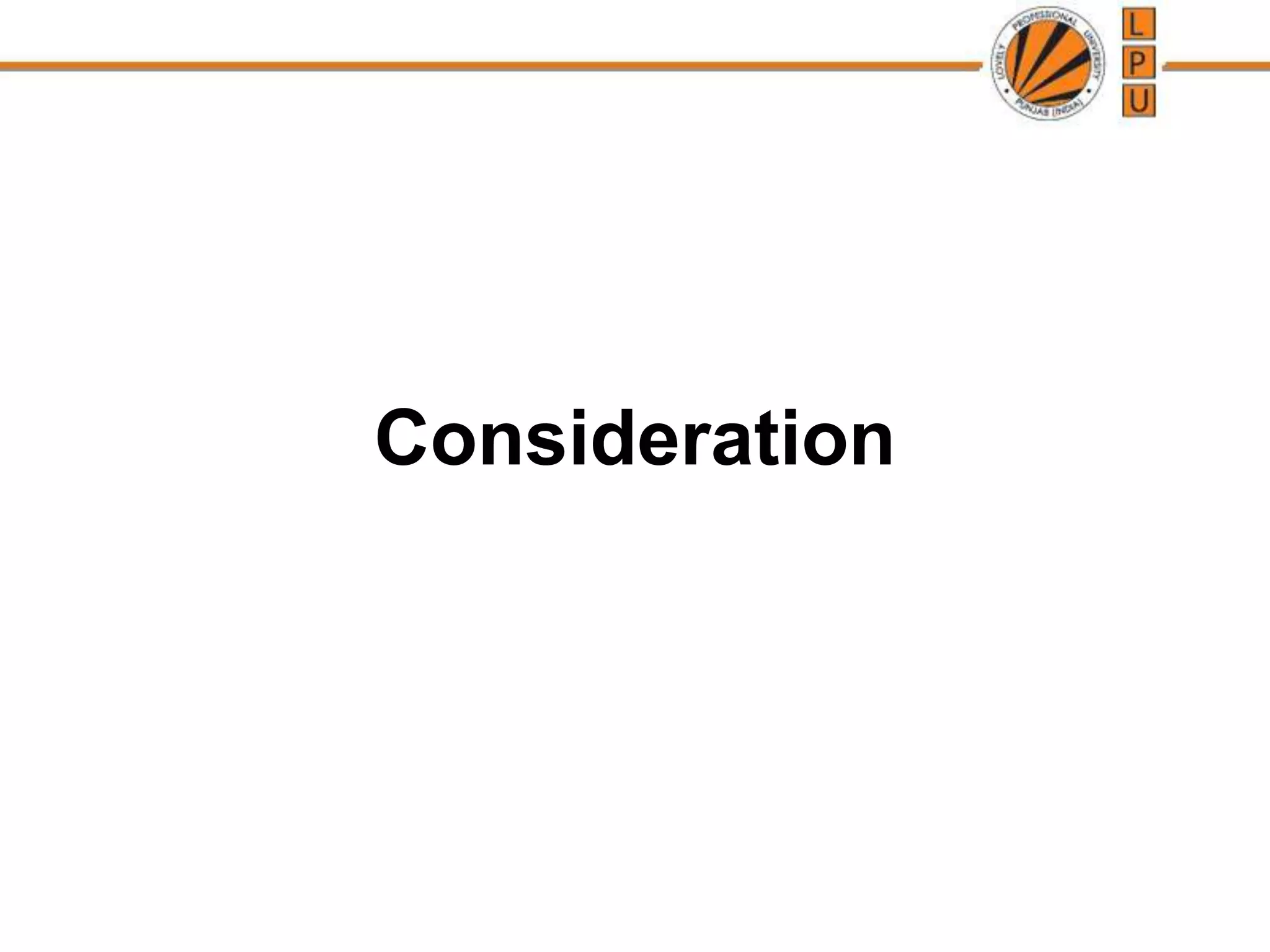
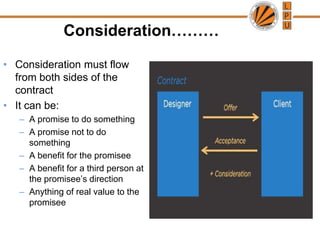
This document discusses the concept of consideration in contracts. It defines consideration as something of legal value that is bargained for and given in exchange for an act or promise. Consideration must flow from both parties to a contract and can take several forms, like a promise to do or not do something. The document outlines several rules for consideration, like that it must move at the desire of the promisor. It also discusses exceptions to the rule that without consideration there is no contract, like natural love and affection in some cases. Privity of contract, or strangers to a contract, are also addressed, along with exceptions where a third party can sue.




![Contract without consideration are purely gratuitous in natureAbsence of legal binding [Case: Abdul Aziz v. Mazum Ali ]A person verbally promised the secretary of the Mosque Committee to subscribe Rs. 500 for rebuilding of a mosque. Later, he declined to pay the said amount.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-111001013201-phpapp02/85/Lecture-4-7-320.jpg)



![12 Rules for considerationIt must move at the desire of the promisor[Case: Durga Prasad Vs Baldeo case], Facts of the case:D constructed a market at the instance of the Collector of a District. The occupants of the shops in the said market promised to pay D a commission on articles sold through their shops. Later on they failed to pay commission and D filed a suit for the recovery of same](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-111001013201-phpapp02/85/Lecture-4-12-320.jpg)

![2. It may move from the promisee or any other person[ Case :Chinnayyav.Ramayya ] A, a lady, by a deed of gift transferred certain property to her daughter, with a direction that the daughter should pay an annuity to A’s brother.On the same day the daughter executed a writing in favour of her uncle, agreeing to pay the annuity. Afterwards, she declined to fulfil her promise saying that no consideration had moved from her uncle.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-111001013201-phpapp02/85/Lecture-4-14-320.jpg)


![4. It may be past, present or future [Sindhav. Abraham]‘A’, a minor was given the benefit of certain services by the plaintiff, who rendered those services, not voluntarily but at the desire of ‘A’ These services were continued even after majority at the request of ‘A’ Subsequently A promised to pay an annuity to the plaintiffDecision : It was held that the past consideration was a good consideration17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-111001013201-phpapp02/85/Lecture-4-17-320.jpg)




![Exceptions to the Rule “No Consideration No Contract”Natural love and affection: [Case: Venkatswamy v. Rangaswamy ]An elder brother, on account of natural love and affection, promised to pay the debts of his younger brother. The agreement was put to writing and was registered.Held : The agreement was valid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-111001013201-phpapp02/85/Lecture-4-23-320.jpg)
![[Case: RaihikhyDohee v. Bhootnath]A Hindu husband by a registered document, after referring to quarrels and disagreements between himself and his wife, promised to pay his wife a sum of money for her maintenance and separate residence. it was held that the promise was unenforceable](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-111001013201-phpapp02/85/Lecture-4-24-320.jpg)


![Stranger to Contract or Privity of contract [Case: Jamna Das v. Ram Avtar]A mortgaged some property to X.A sold his property to B, B having agreed with A to pay off the mortgage debt to XX brought an action to recover the mortgage money against B.Held: No contract between X and B so X could not enforce the contract to recover the amount from B](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-111001013201-phpapp02/85/Lecture-4-27-320.jpg)
![Exceptions : Stranger to contract can sue in the following casesTrust[Case: RanaUmaNathBaksh Singh v. Jang Bahadur]A father appointed his son as his successor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-111001013201-phpapp02/85/Lecture-4-28-320.jpg)


![2. In case where a charge has been created:[Case: Khwaja Muhammad v. HussainiBegum]An immovable property was charged in favor of Hussaini Begum for payment of her kharchane-e-paandaan by her father. Held: Hussaini Begum though stranger to contract between mortgagor and mortgagee, can sue.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-111001013201-phpapp02/85/Lecture-4-31-320.jpg)
![3. Provision made in partition or family settlement:[ Case: Shuppuammal v. Subramaniyam]2 brothers on the partition of joint property, agreed to invest in equal shares a certain sum of money for the maintenance of their mother. Held: She can compel her sons to make investment.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture4-111001013201-phpapp02/85/Lecture-4-32-320.jpg)