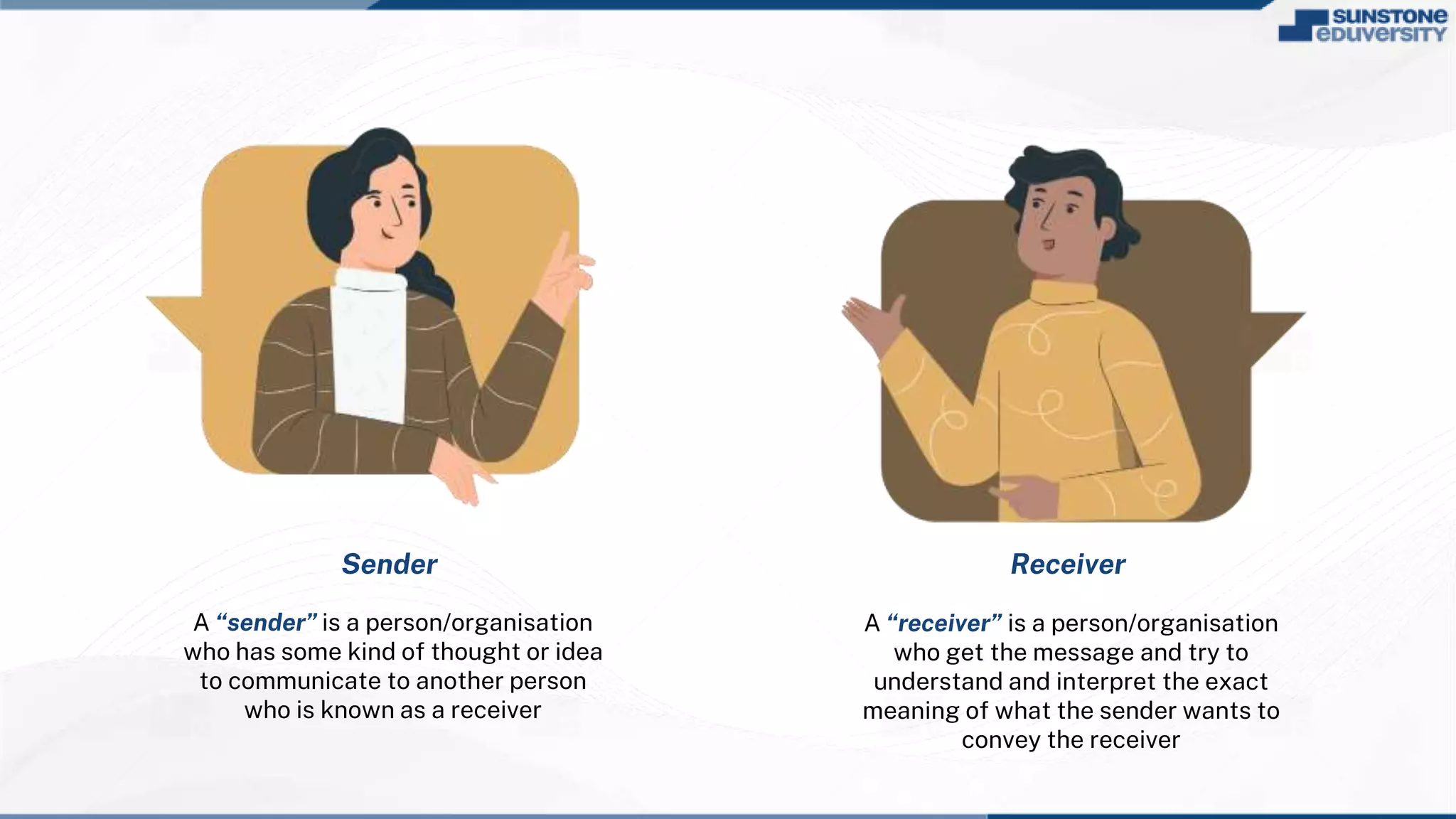
The document provides an introduction to business communication. It outlines the objectives and lessons, which include understanding written, web and verbal communication, and analyzing the essentials, process, and barriers of communication. The essentials of communication are defined as listening, understanding, and responding. The key elements of the communication process are identified as the sender, receiver, message, feedback, medium, encoding, decoding, and noise. Finally, 10 common barriers to effective communication are listed.