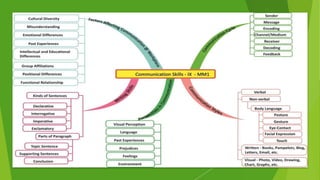
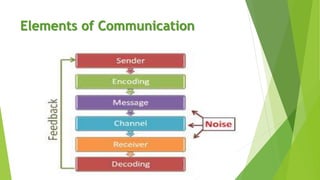
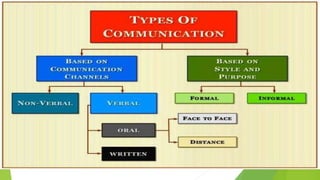
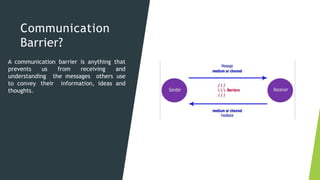
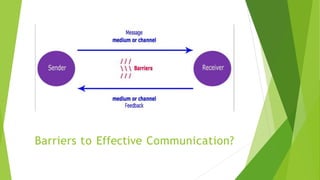
This document discusses communication skills and barriers to effective communication. It defines communication and its key elements, including the sender, message, encoding, channels, receiver, feedback. It also describes the 7Cs of effective communication: clear, concise, concrete, correct, coherent, complete and courteous. Various barriers to communication are outlined such as physical, language, gender, attitudinal, perceptual and emotional barriers. The document concludes with an activity to practice communication skills through a blindfold game to build trust, listening and instructional abilities.