1) Maintenance is defined as actions intended to retain or restore an item to a state in which it can perform its required function.
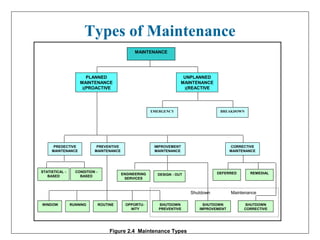
2) There are different types of maintenance including preventive maintenance, which aims to reduce failures before they occur; corrective maintenance, which repairs items after failure; and run-to-failure maintenance, which only repairs items after breakdown.
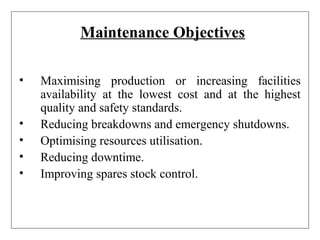
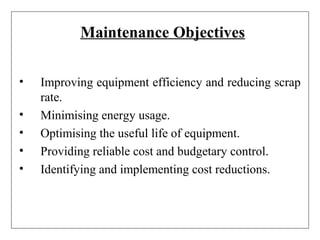
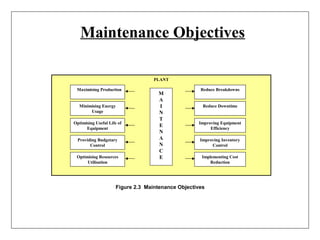
3) Attitudes toward maintenance have changed over time from seeing it as only fixing items after failure, to recognizing the benefits of preventive maintenance in reducing costs and improving availability, quality, safety and reliability of equipment.