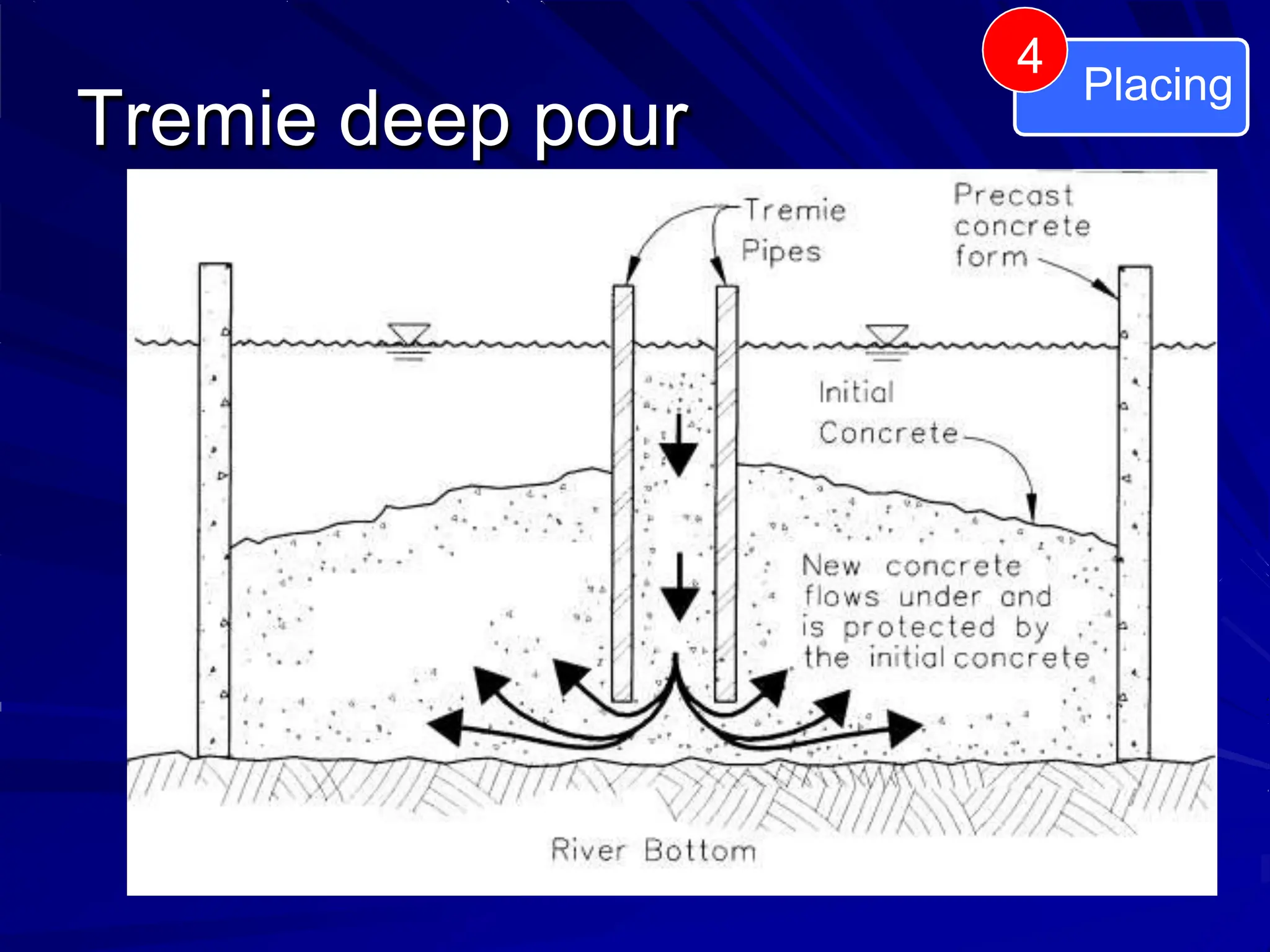
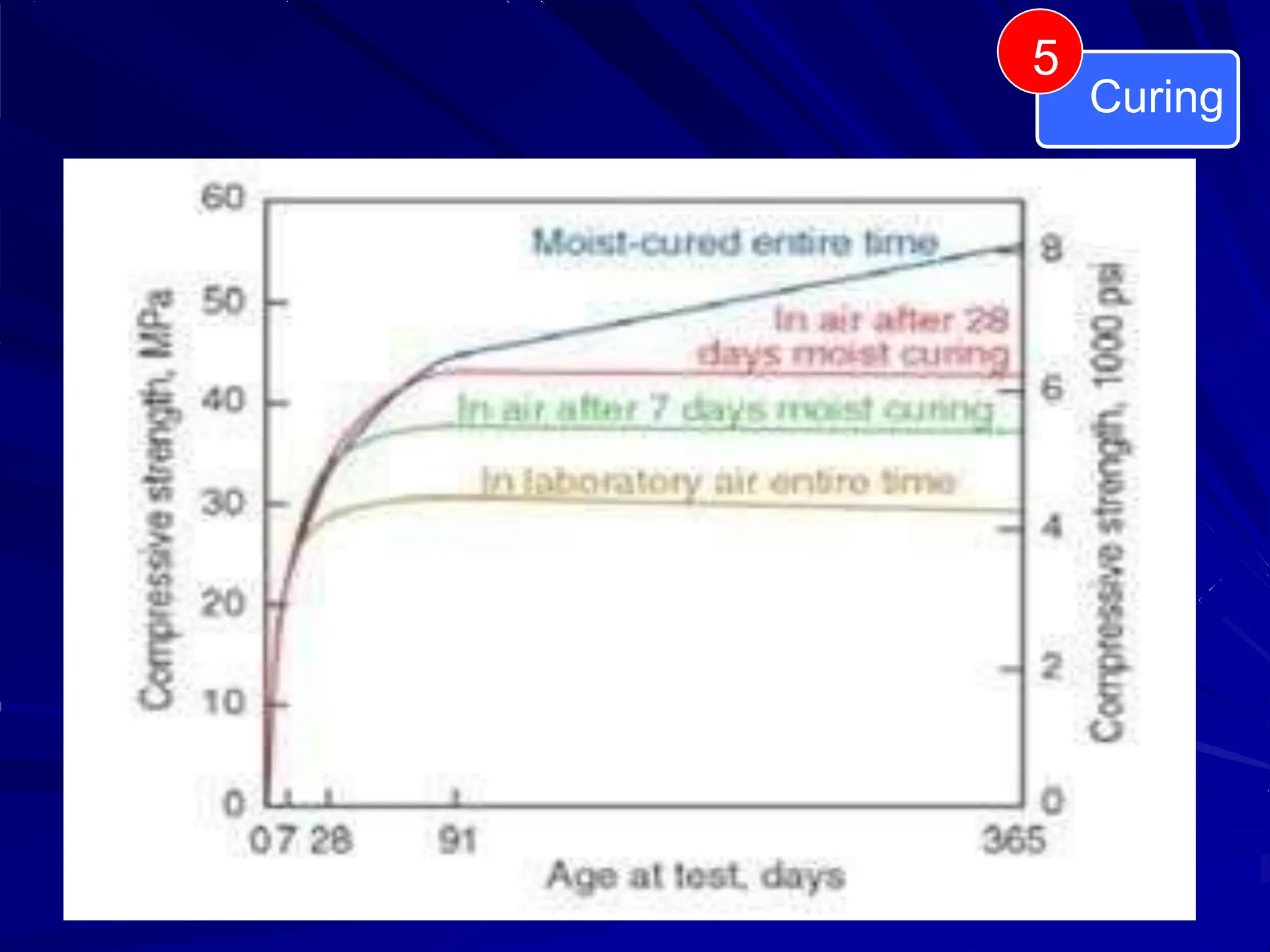
The document covers key aspects of concrete technology for civil engineering, including the processes of placing, compacting, finishing, and curing fresh concrete. It details methods for placement in various conditions, compaction techniques to enhance the strength and durability of concrete, and the importance of curing to prevent moisture loss during hydration. Additionally, it discusses specific methods and precautions for effectively managing these processes in construction projects.