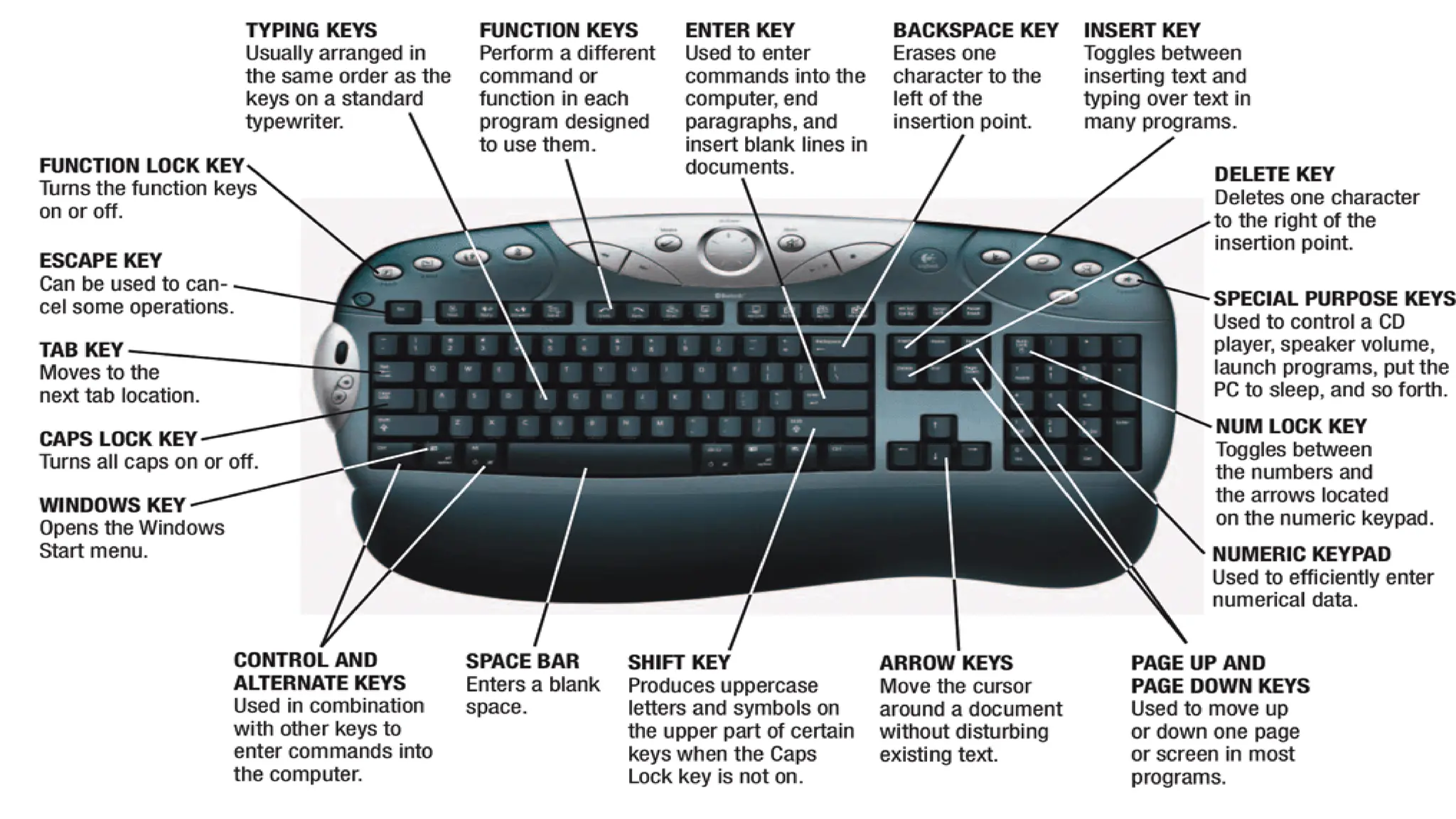
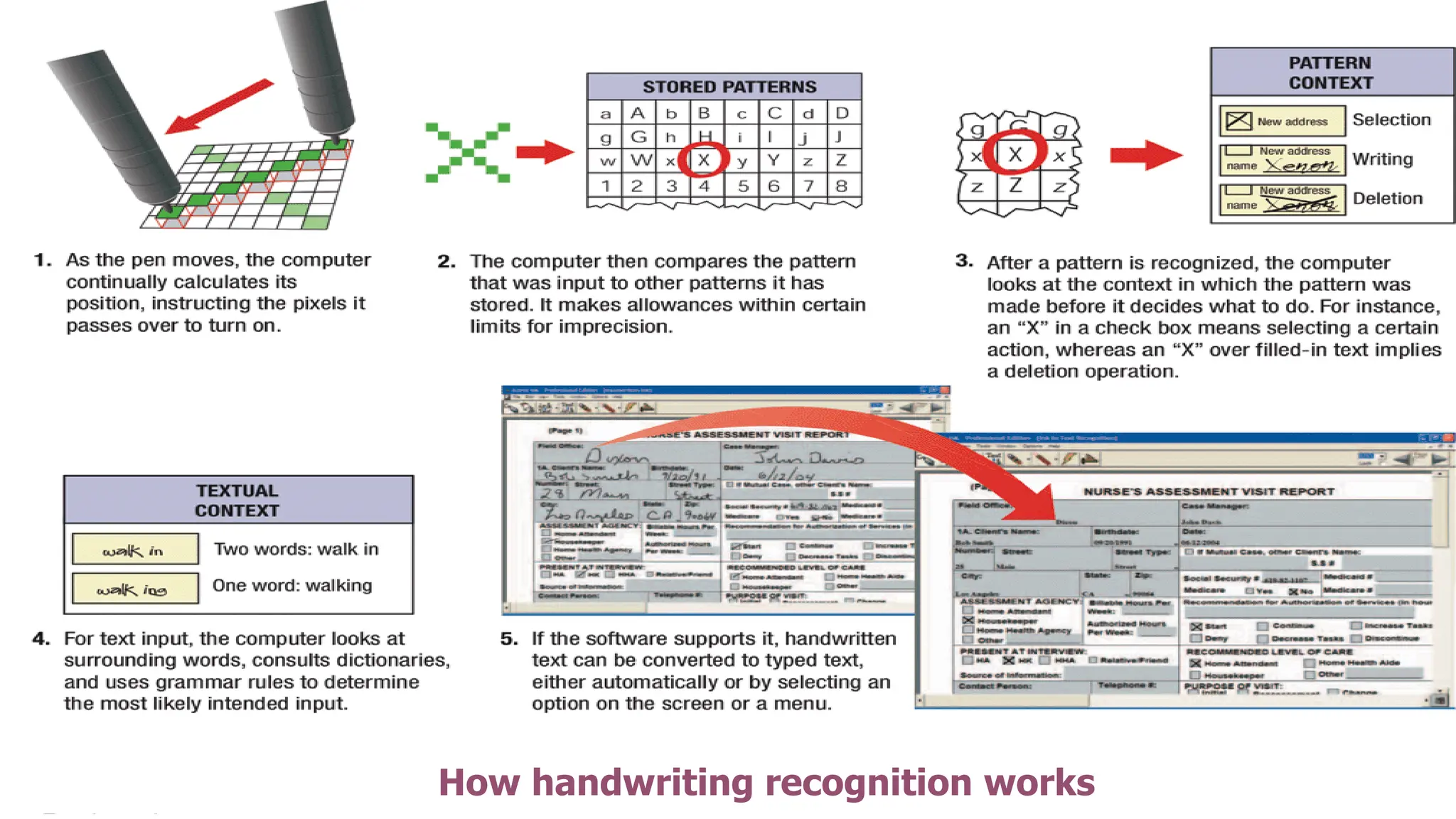
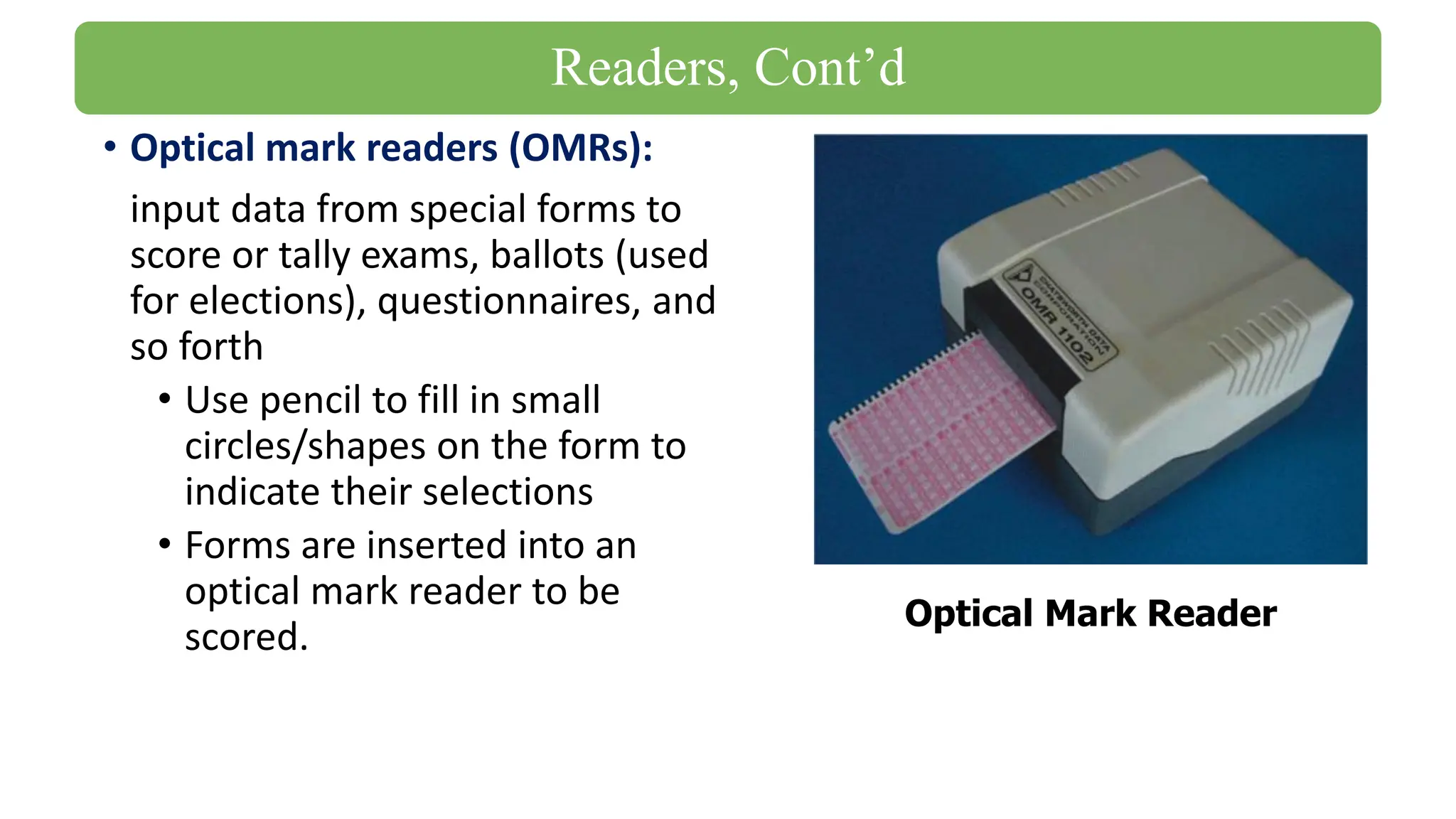
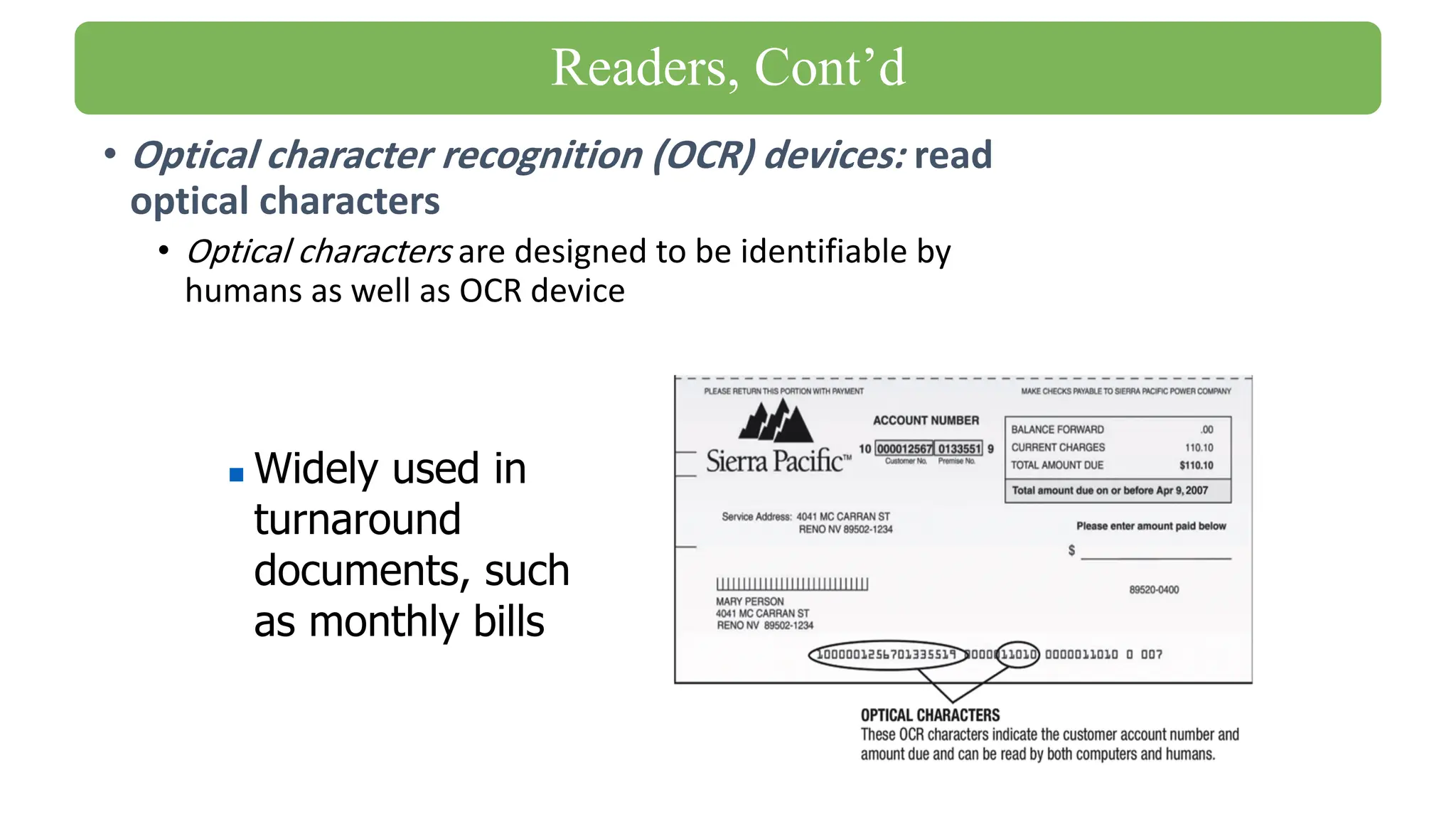
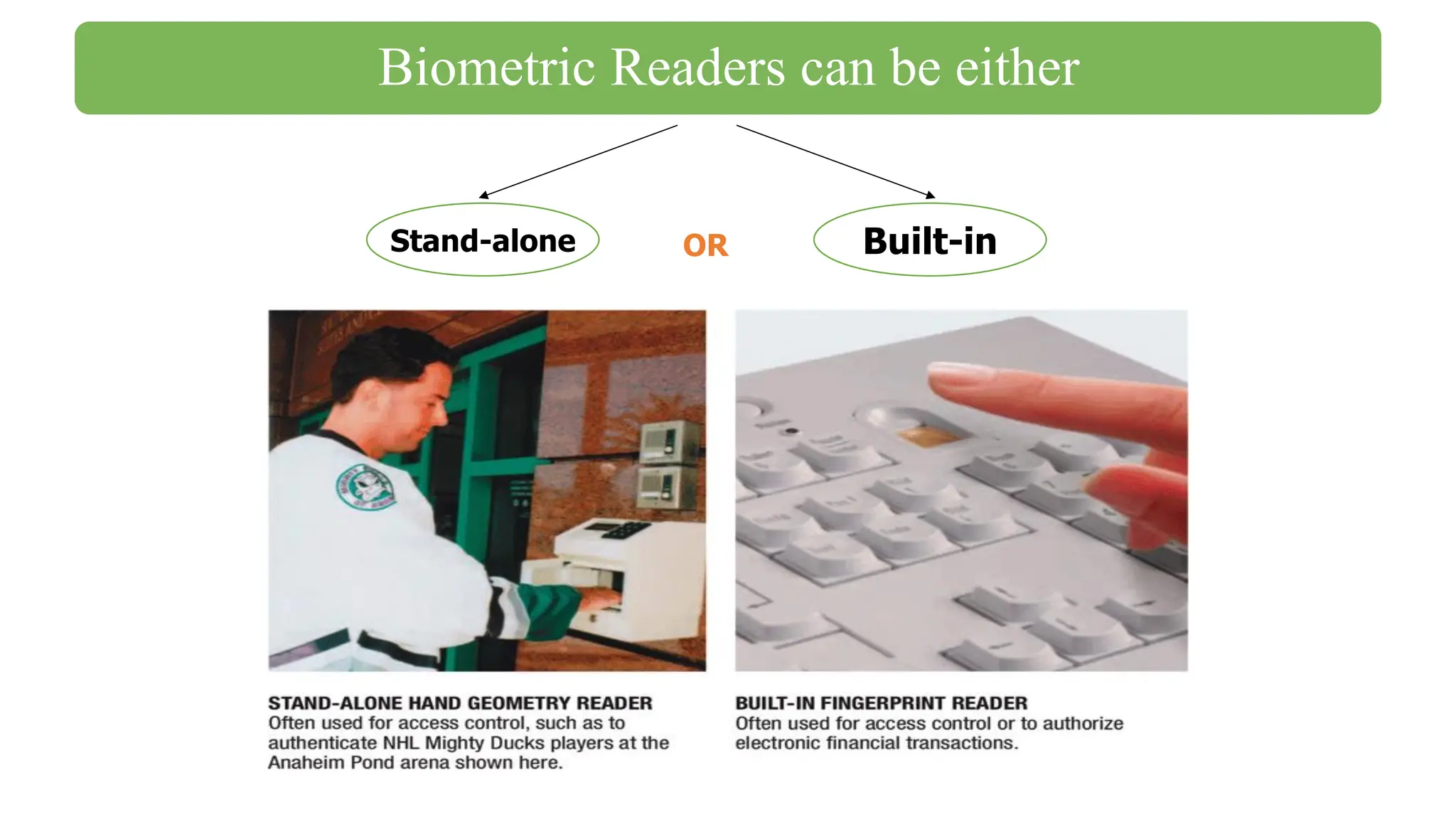
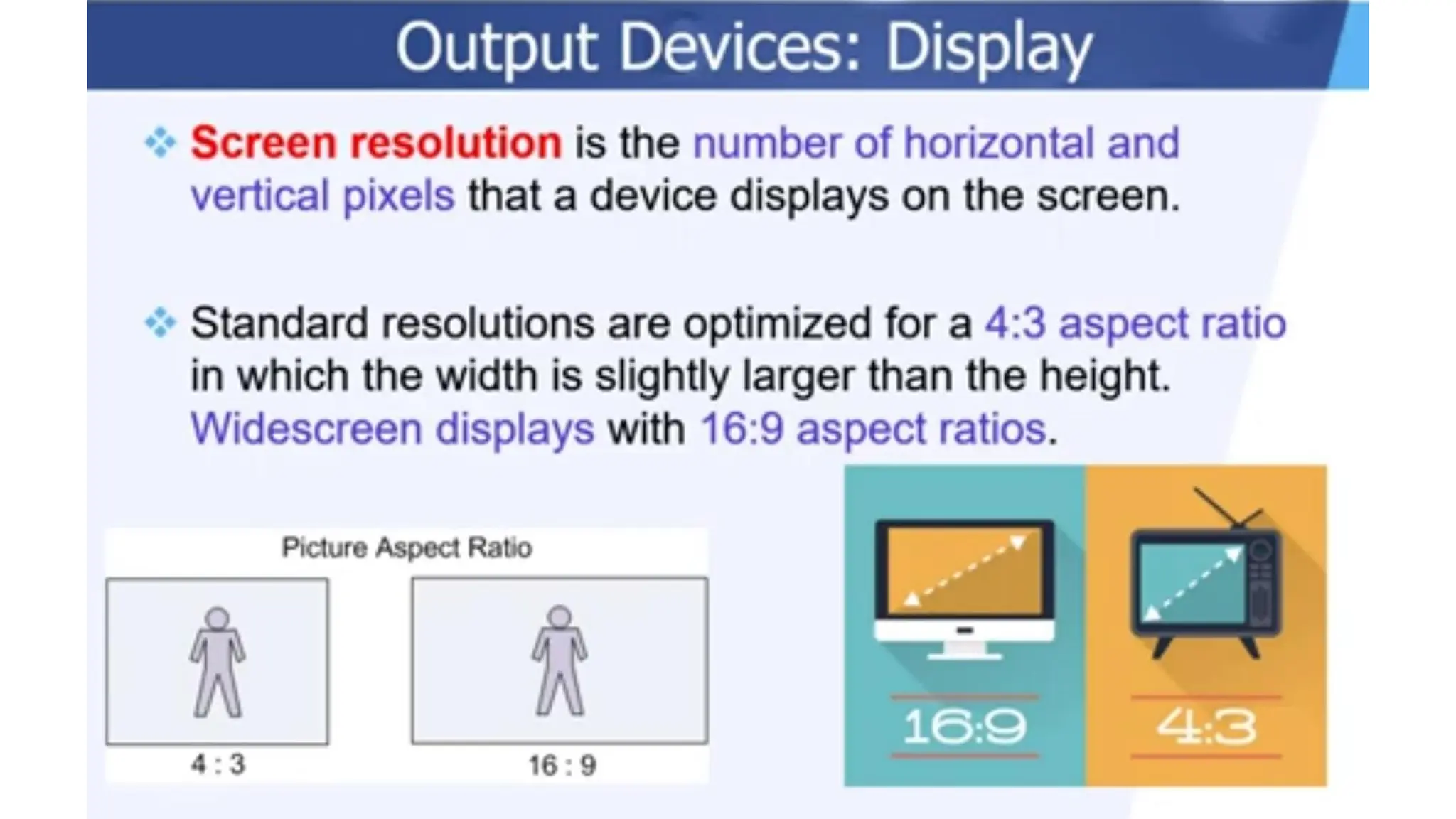
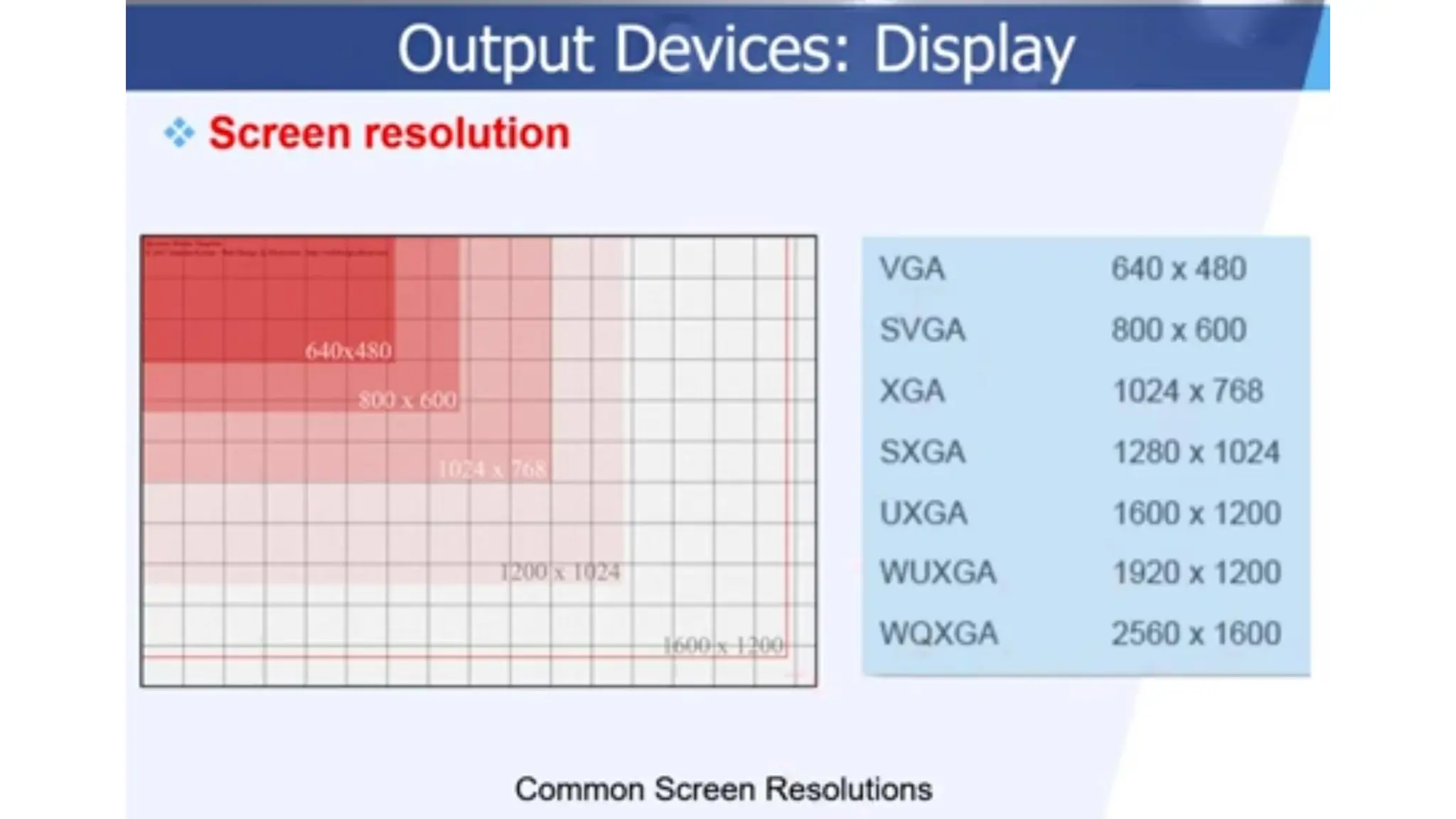
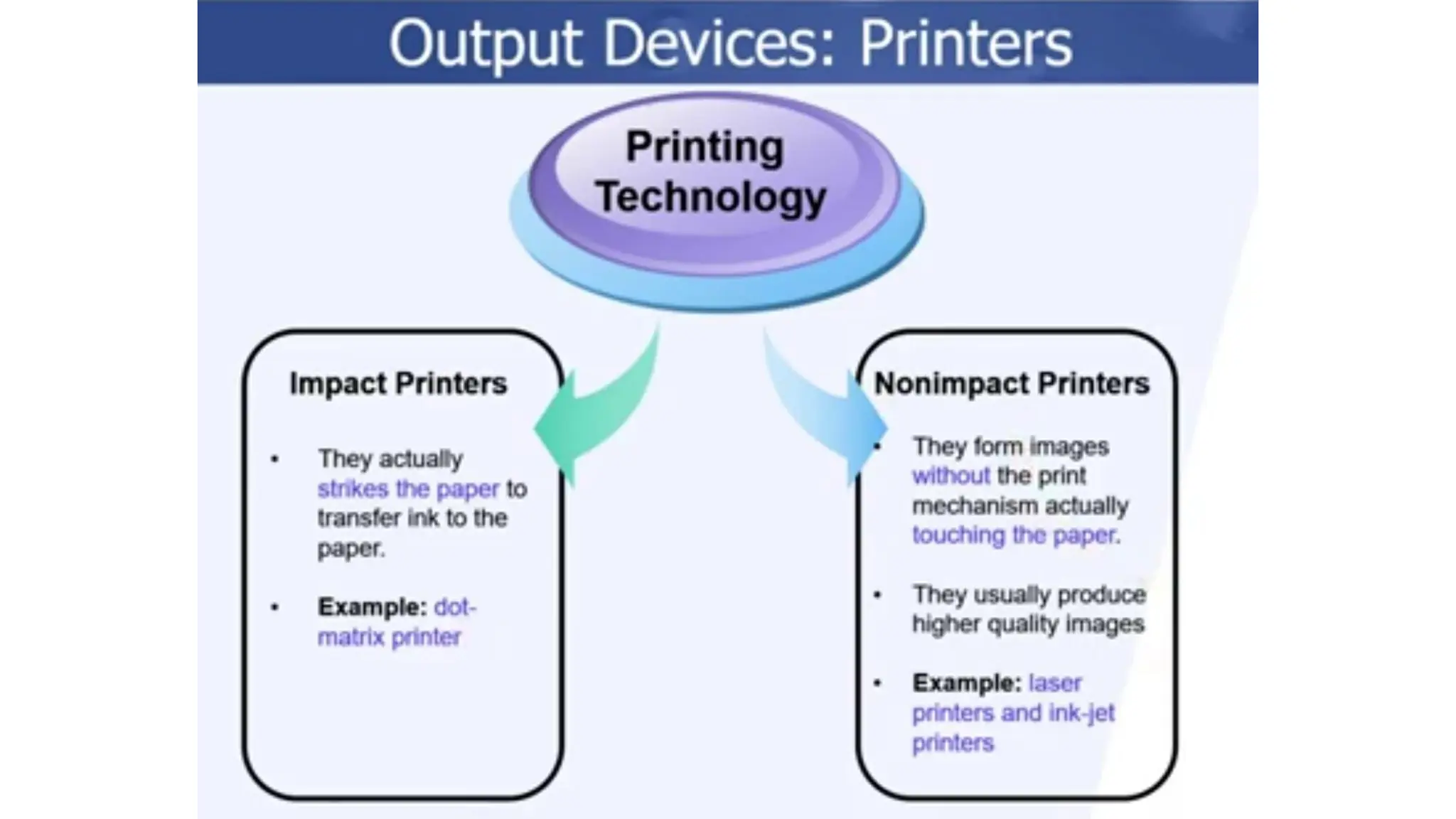
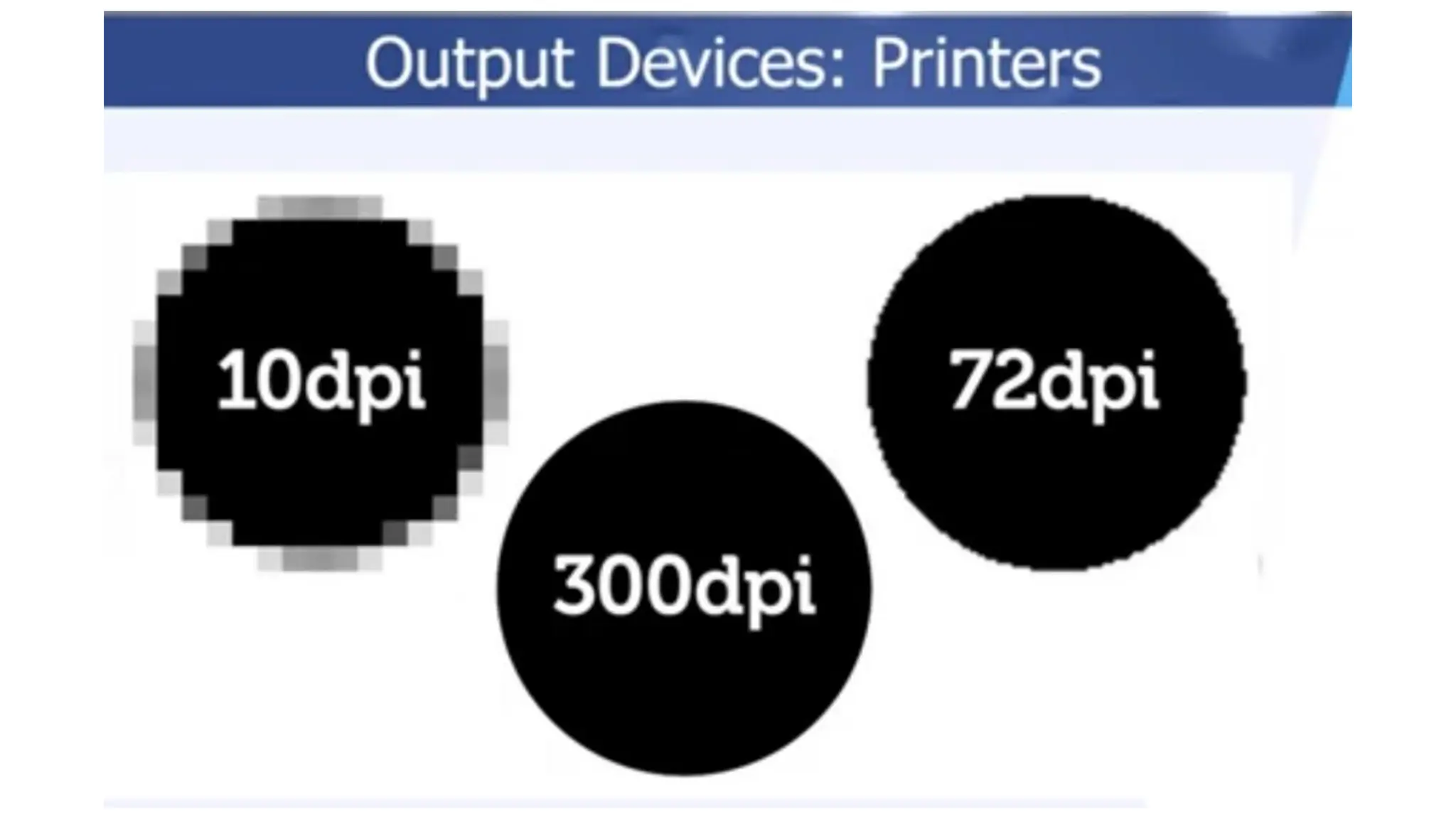
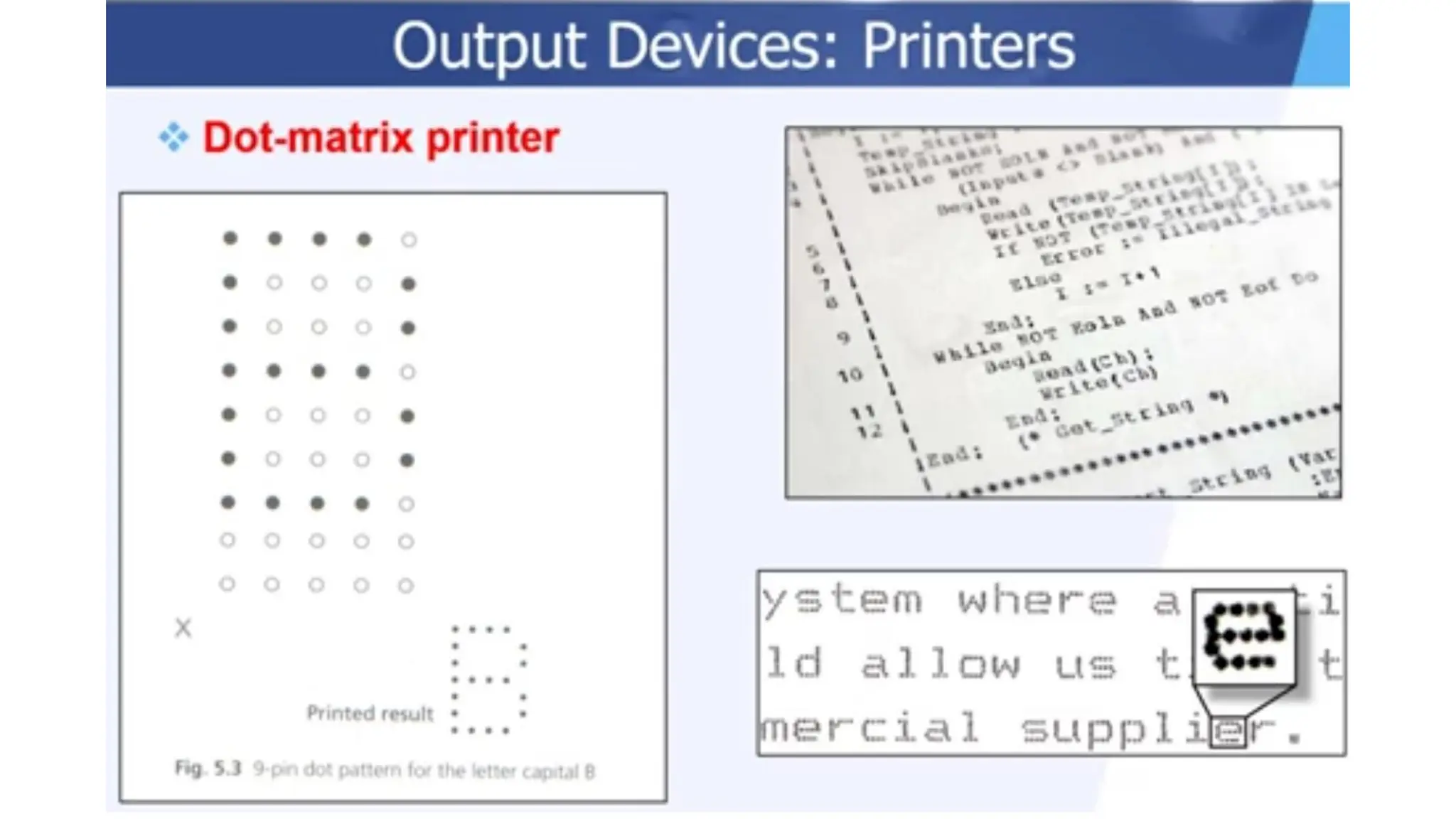
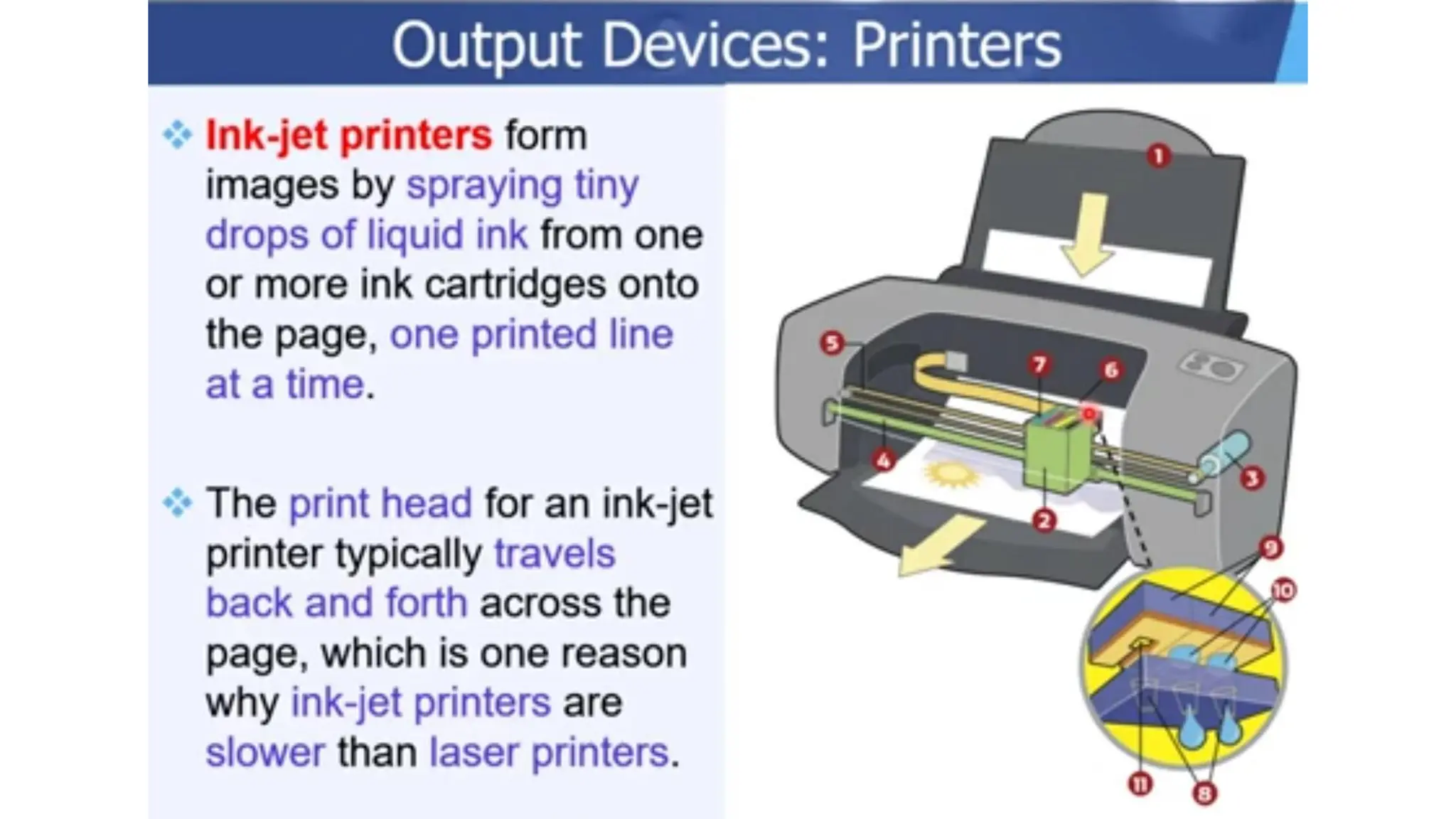
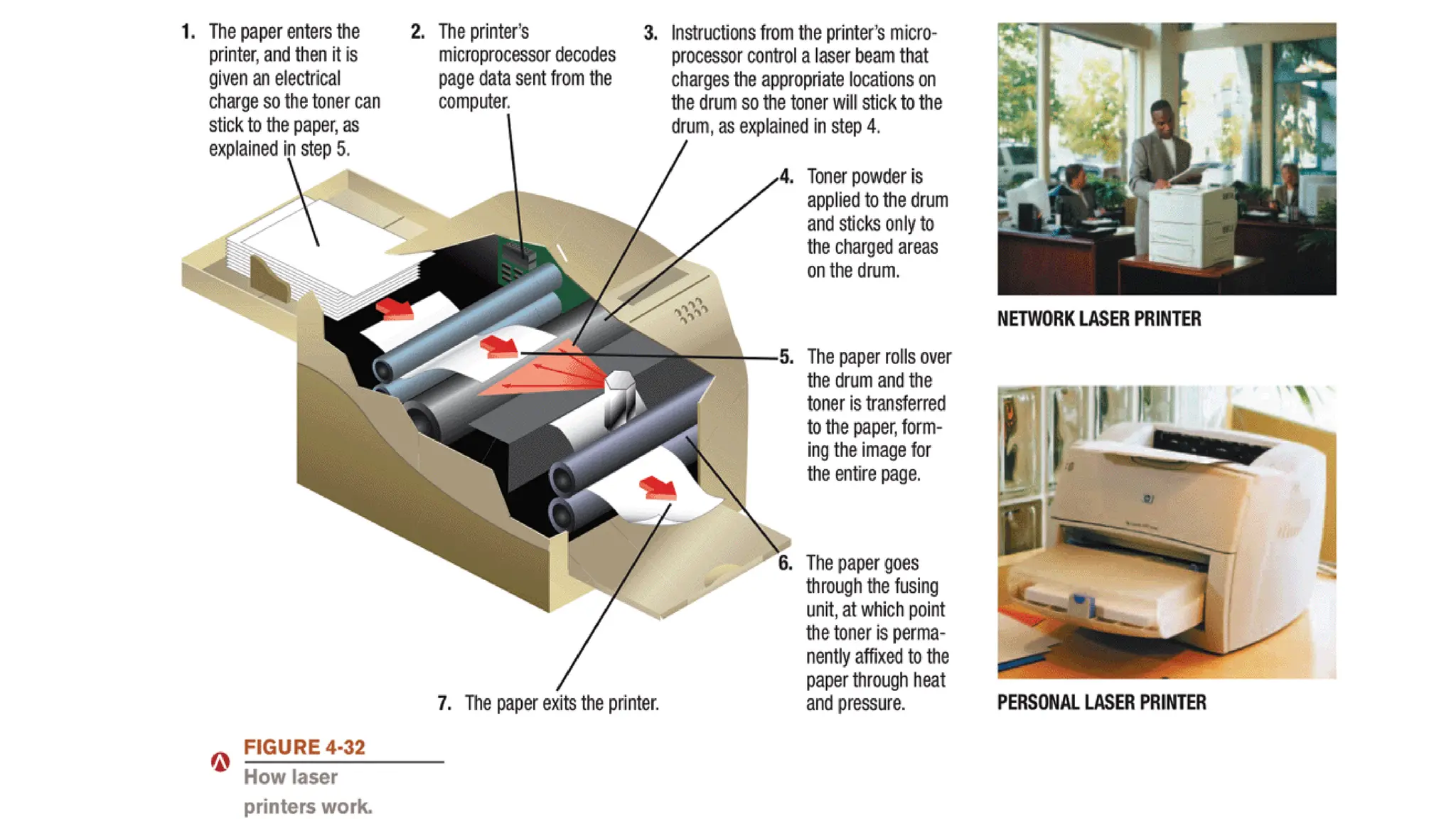
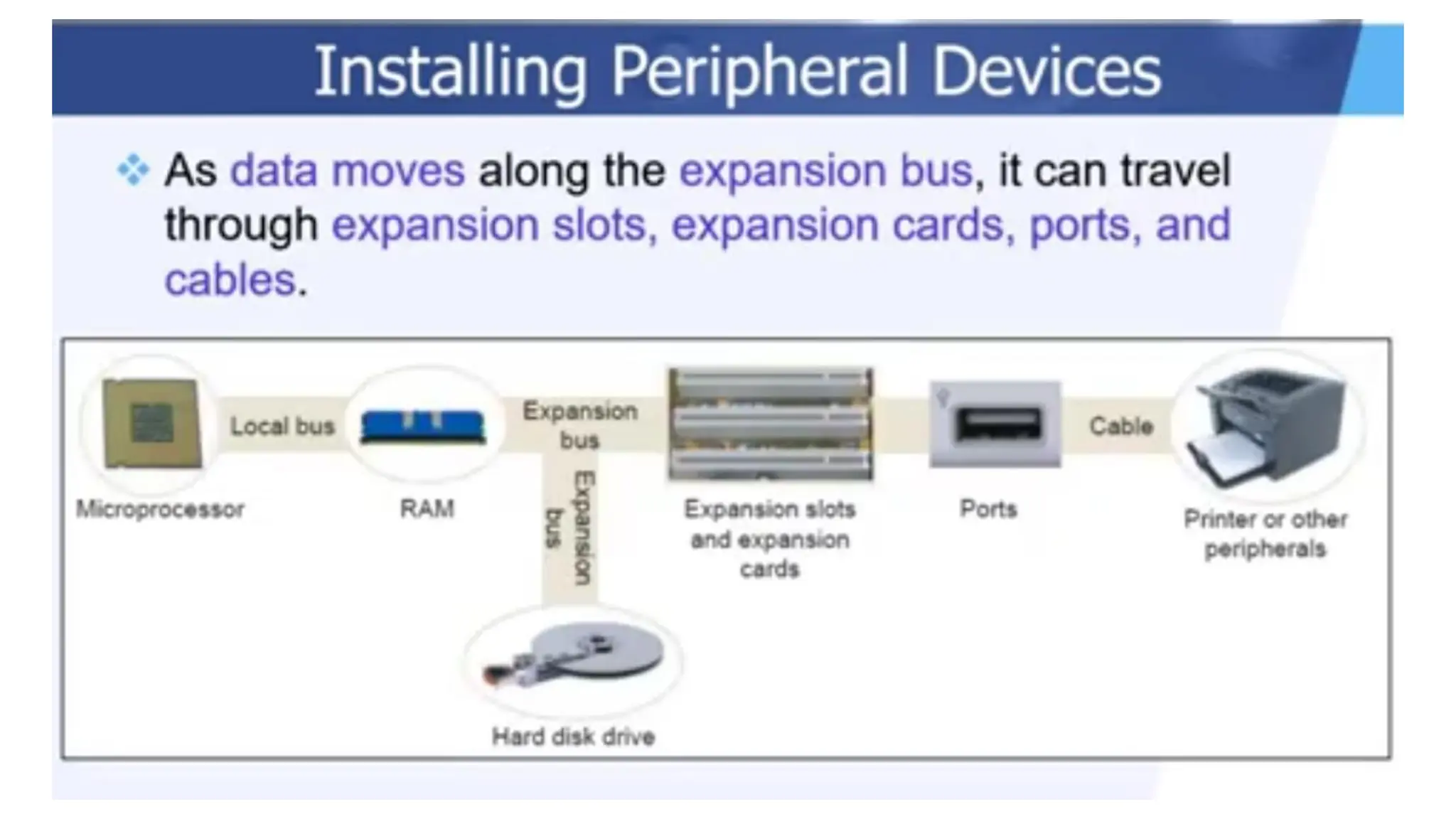
The document outlines the structure and content of the CS 101 course at the Modern Academy for Computer Science & Management Technology, focusing on input and output devices. It covers various input devices like keyboards, pointing devices, scanners, and digital cameras, along with their functionalities. Additionally, it discusses output devices, particularly printers, emphasizing the distinctions between different types and their operational characteristics.