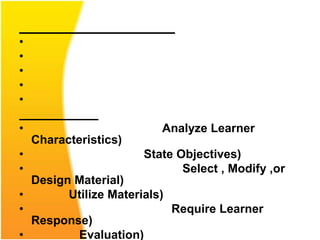
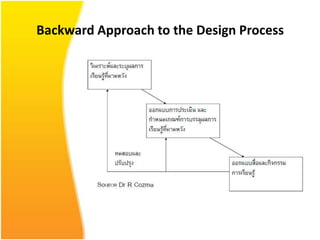
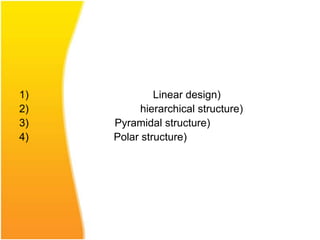
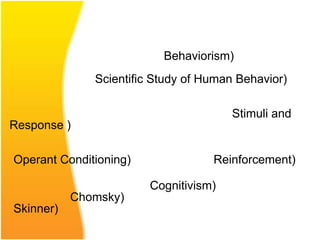
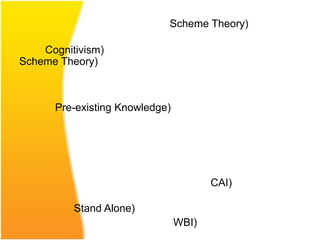
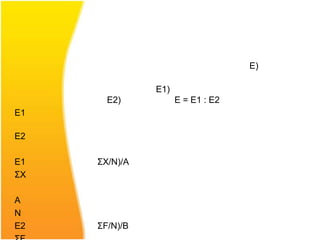
The document discusses various aspects of designing effective learning objects (LOs) for teaching mathematics at the secondary school level. It covers topics like LO metadata, instructional design approaches, storyboarding, feedback mechanisms, usability testing, and technical considerations. The key goals of LOs are to transition students from passive to active learning, bridge the digital divide, and close gaps in understanding through interactive, personalized instructional experiences.