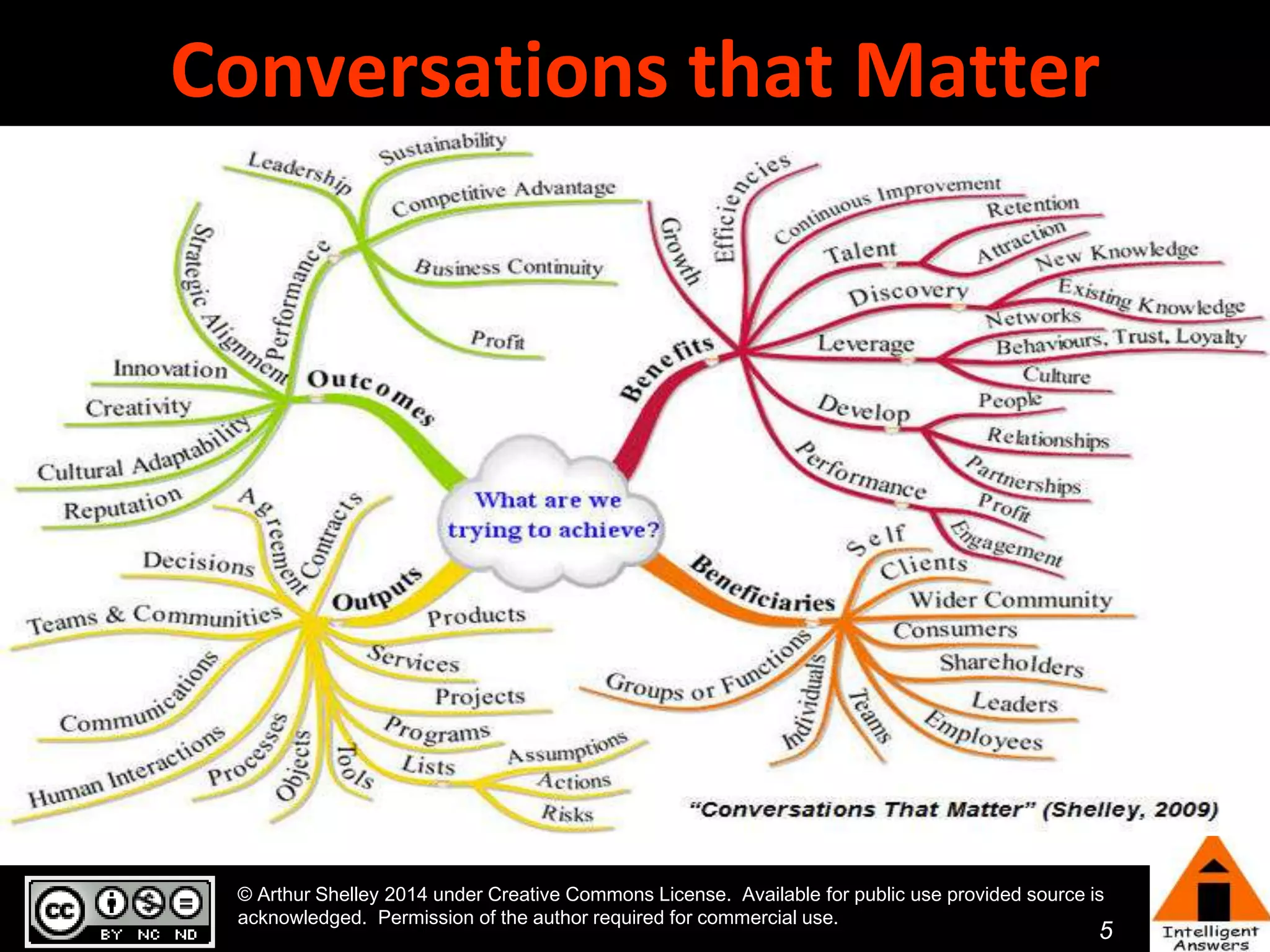
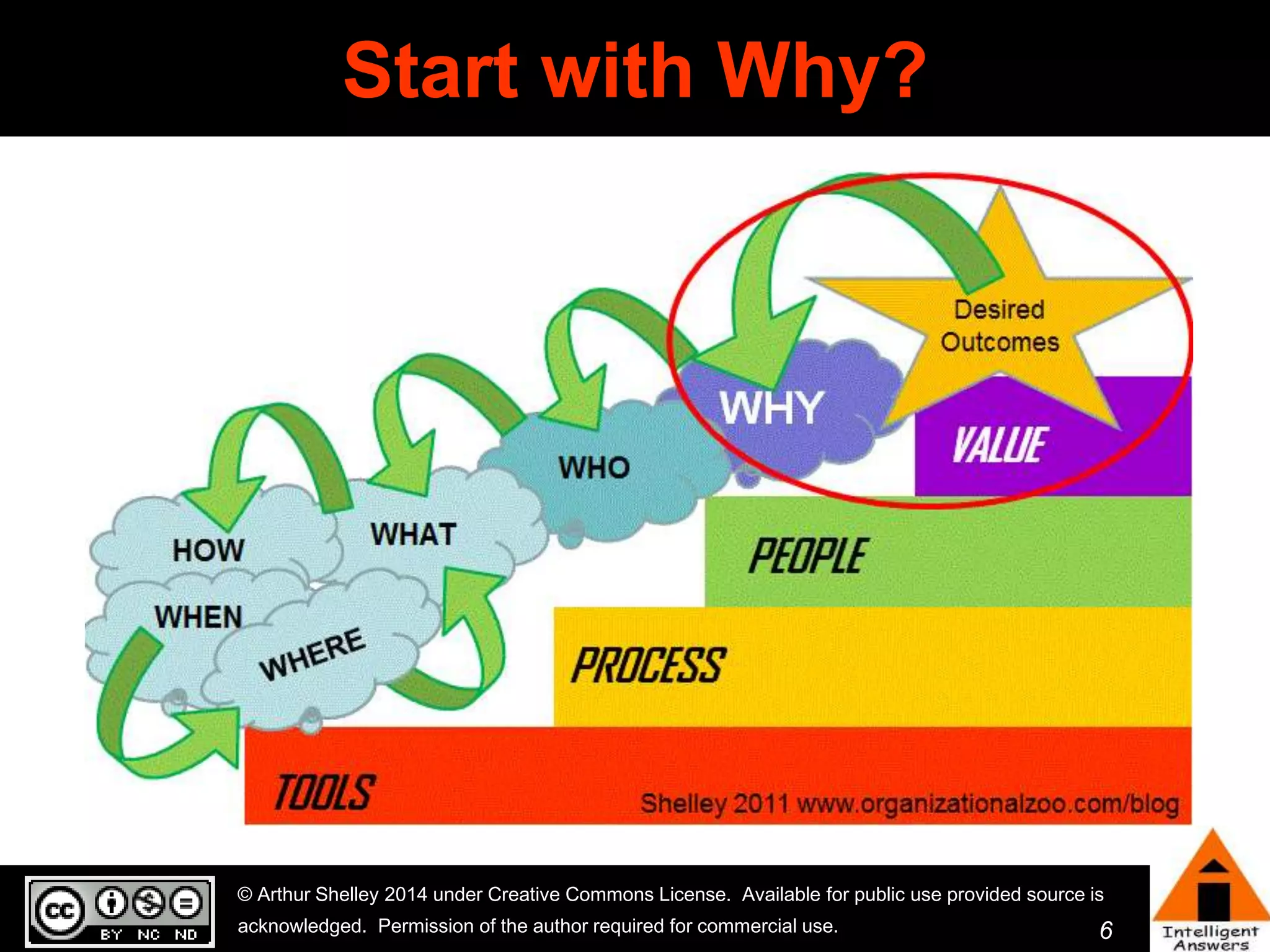
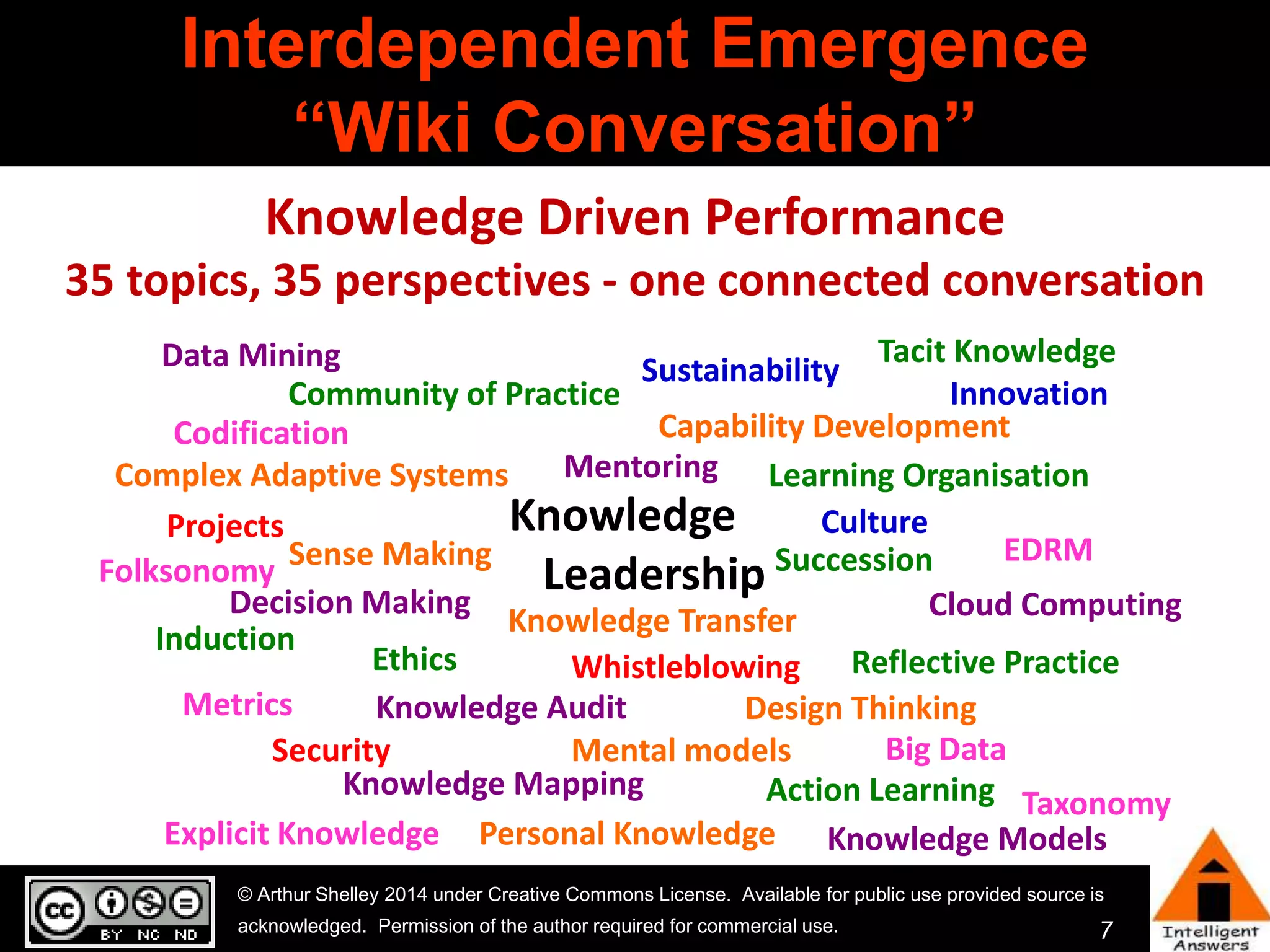
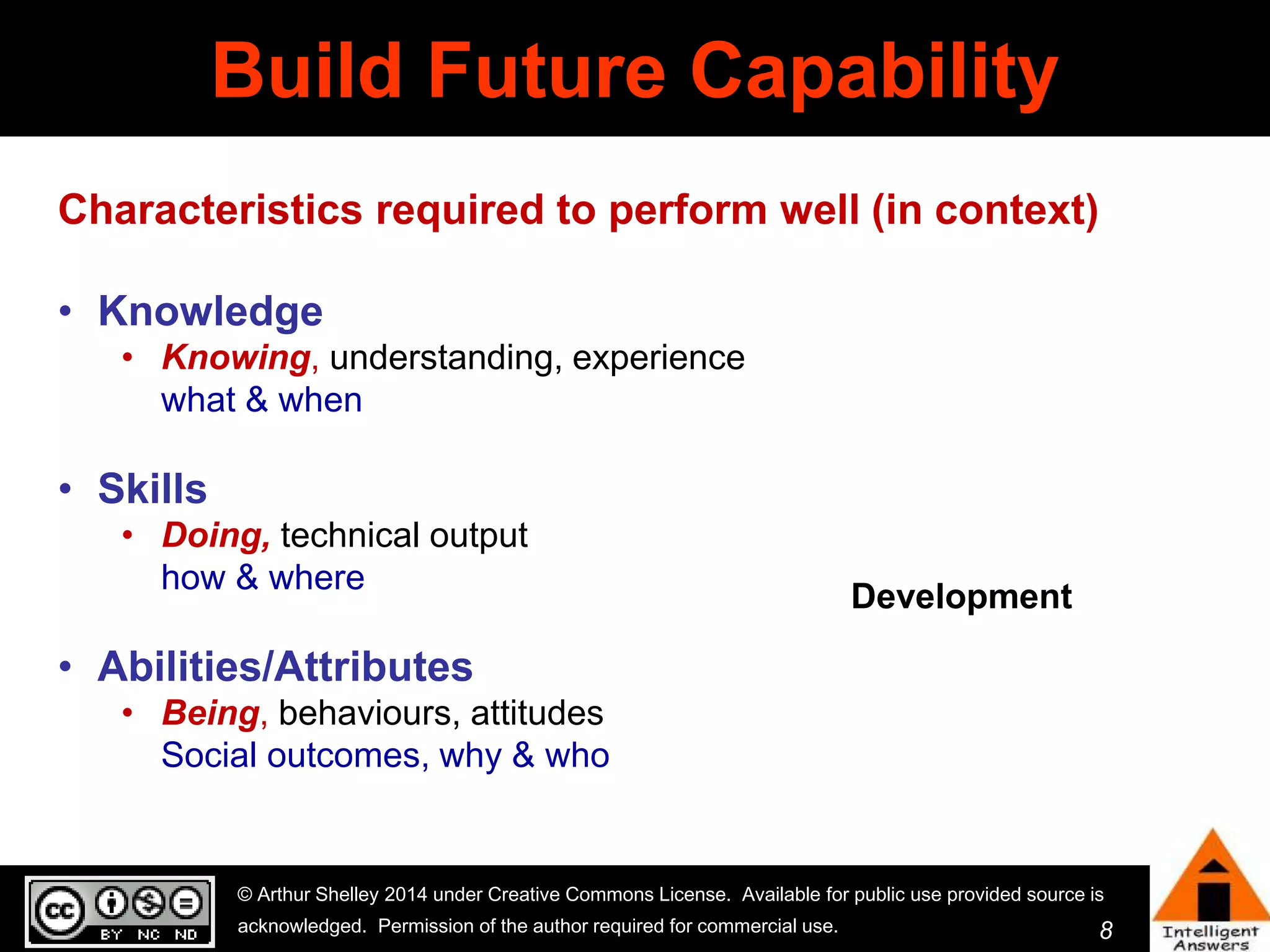
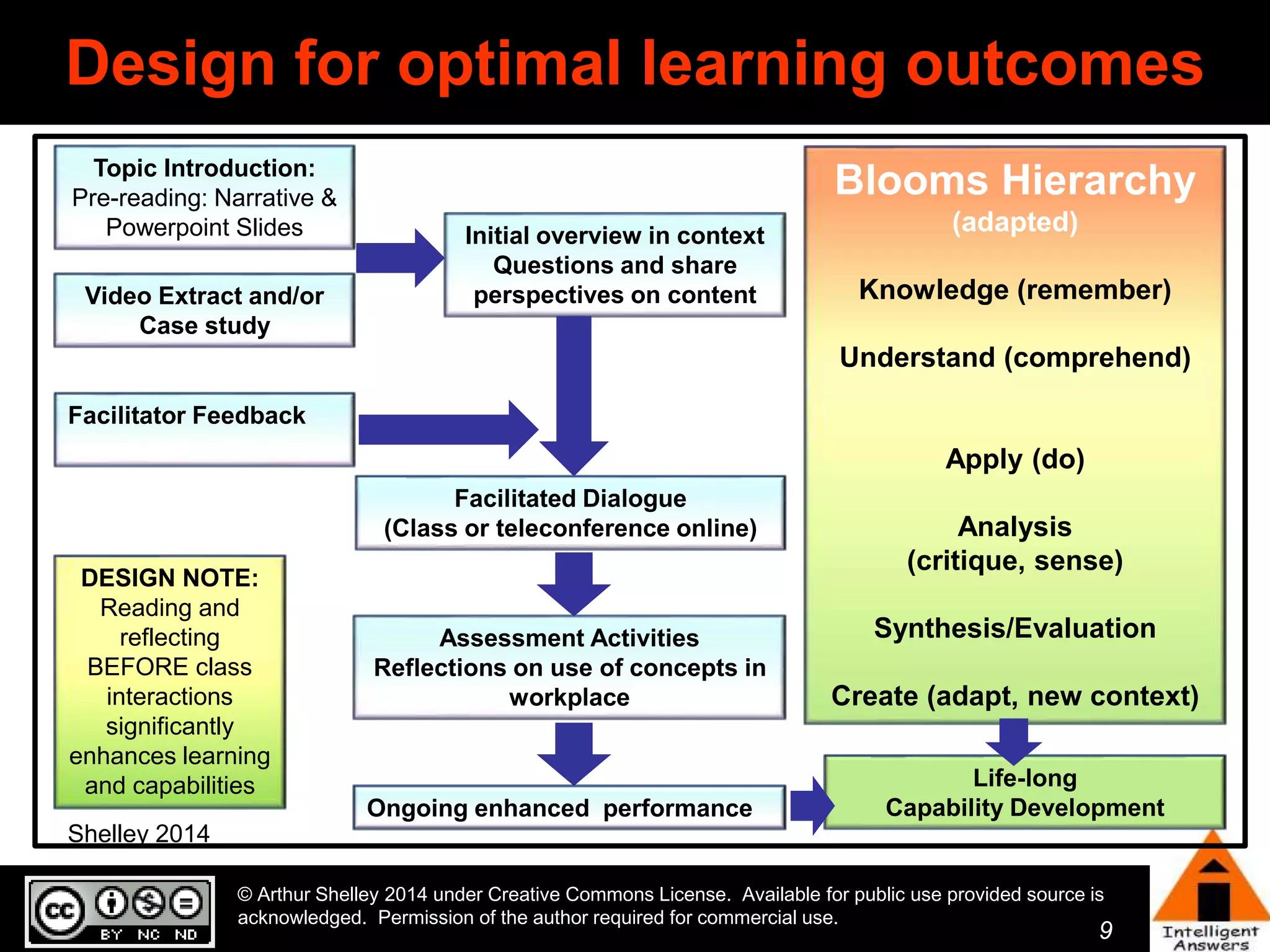
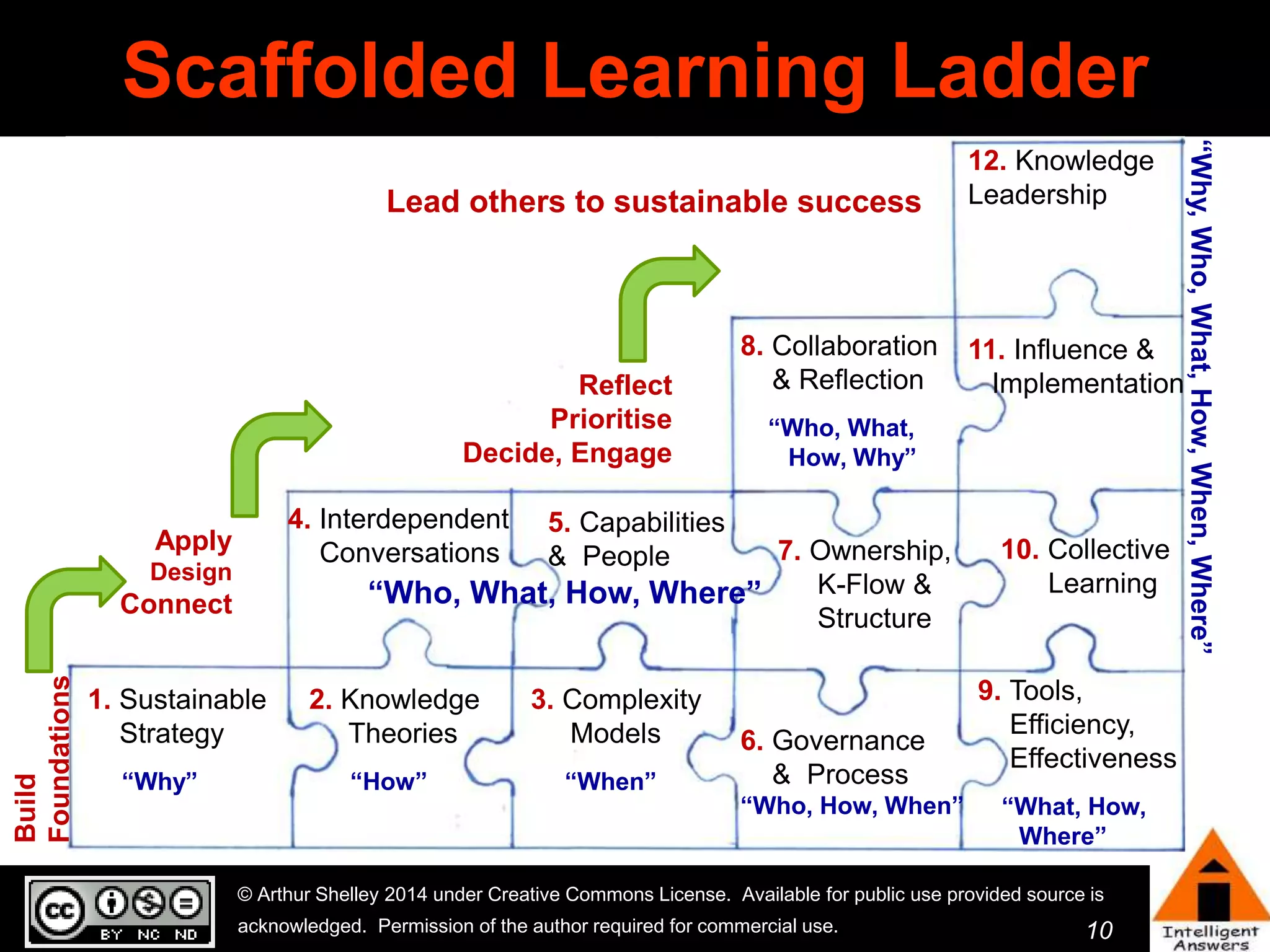
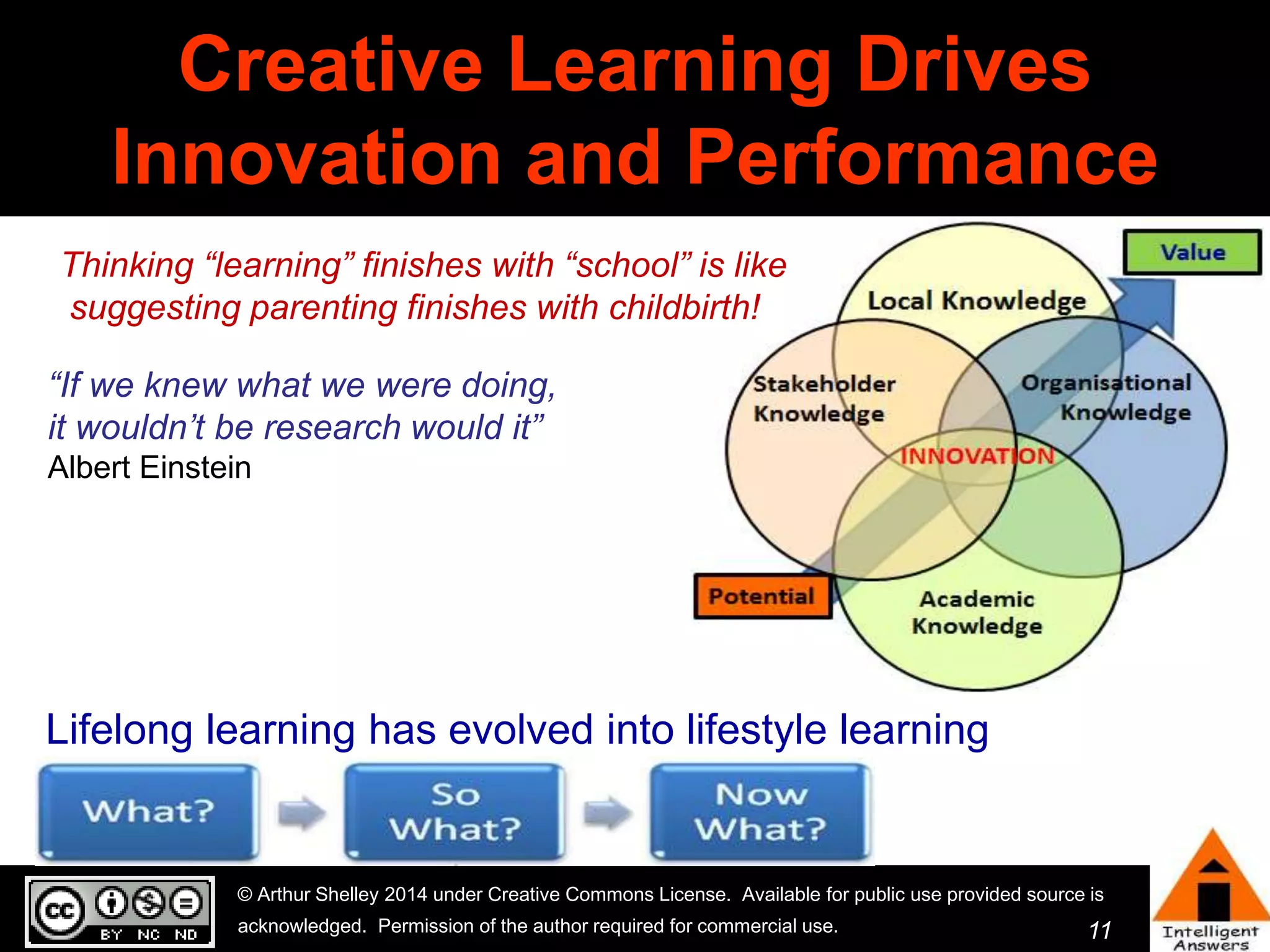
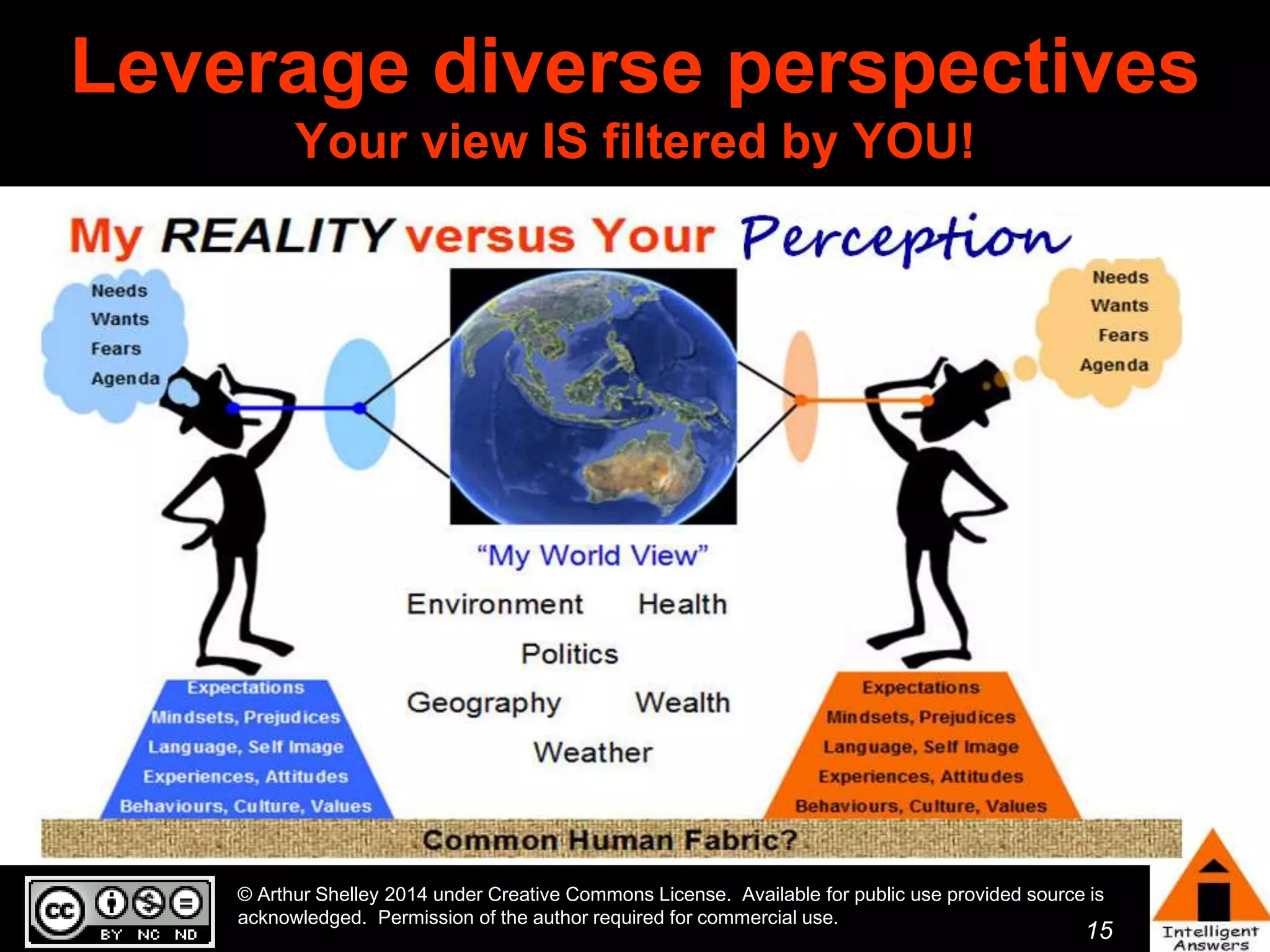
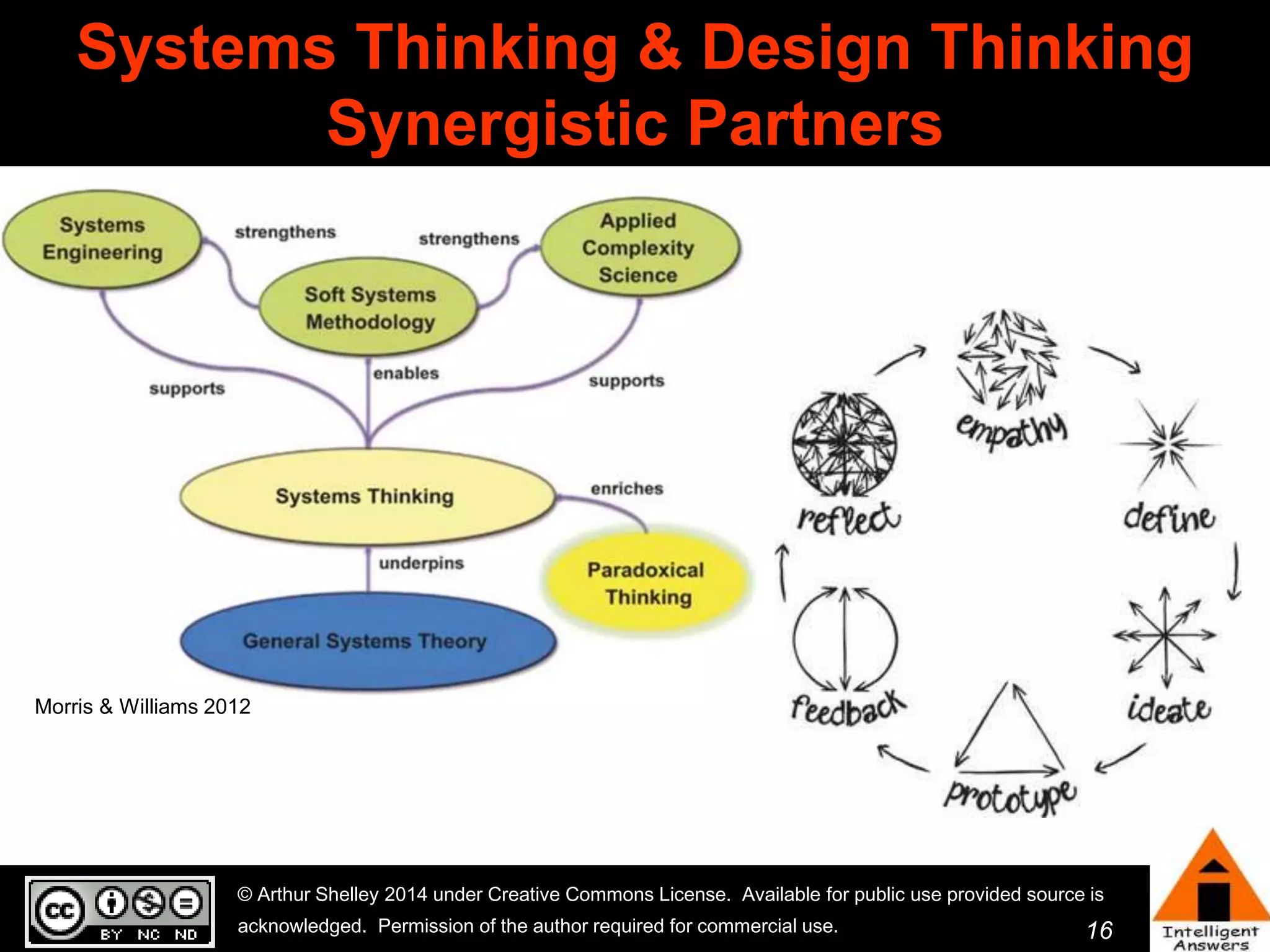
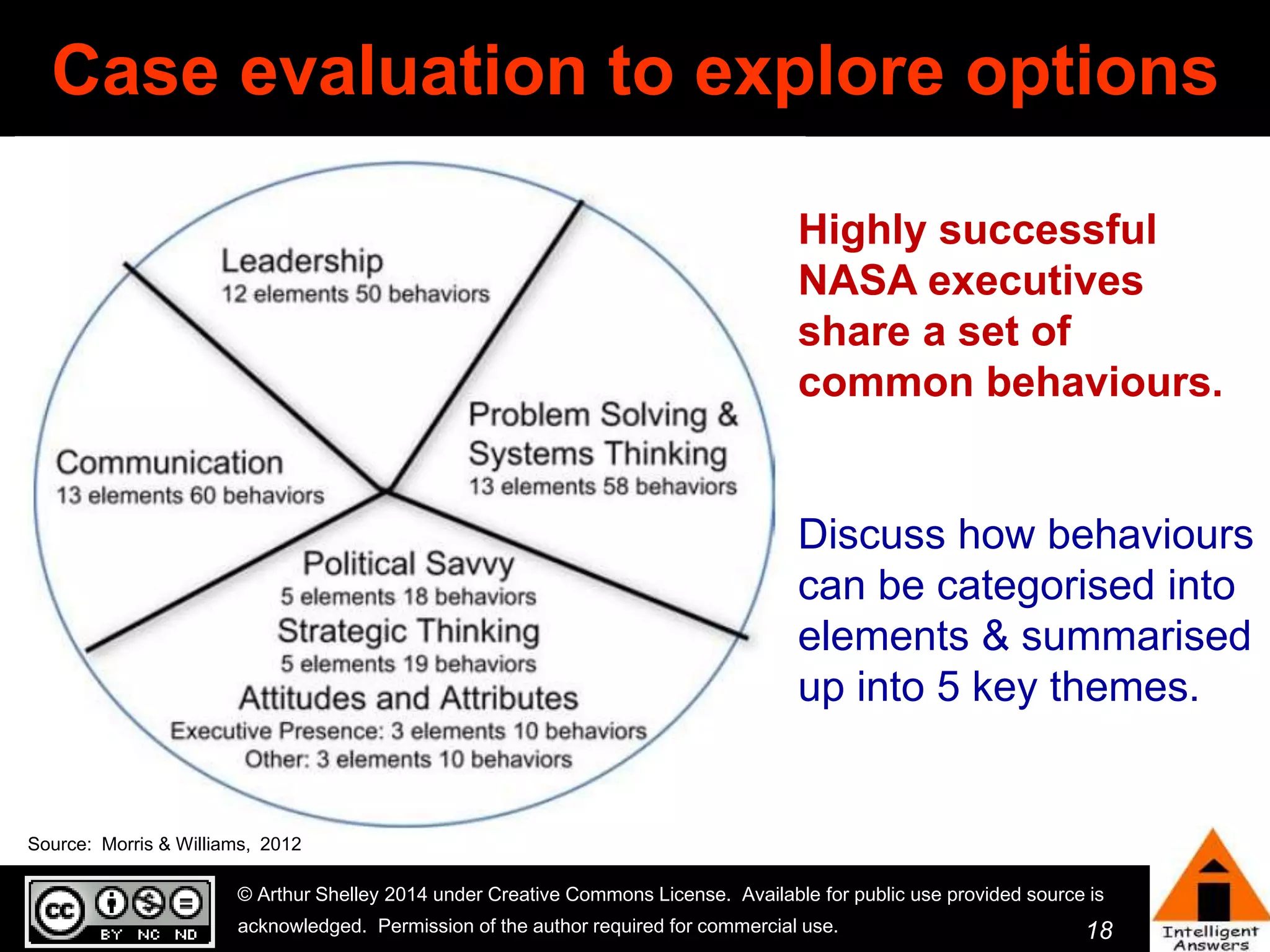
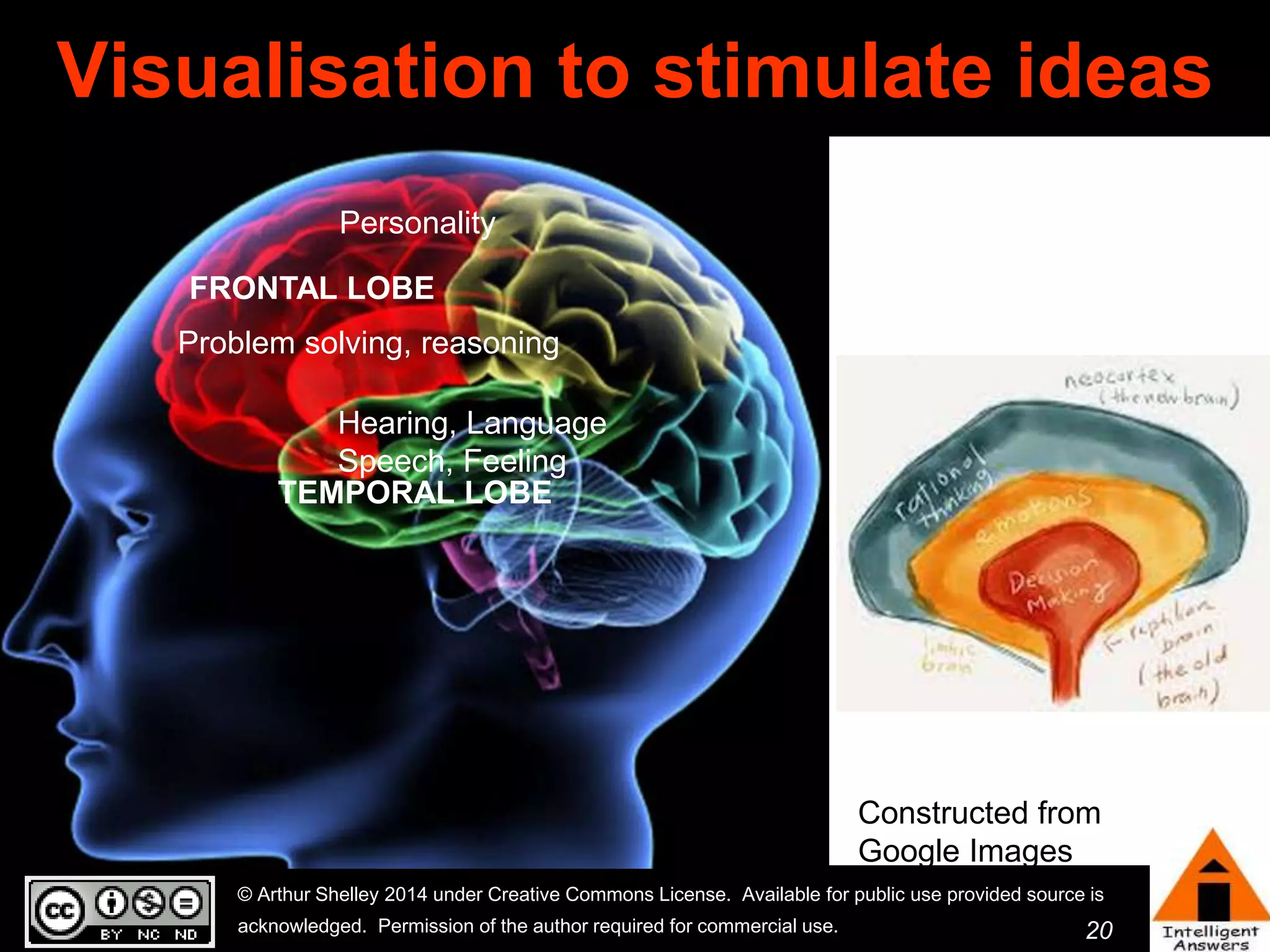
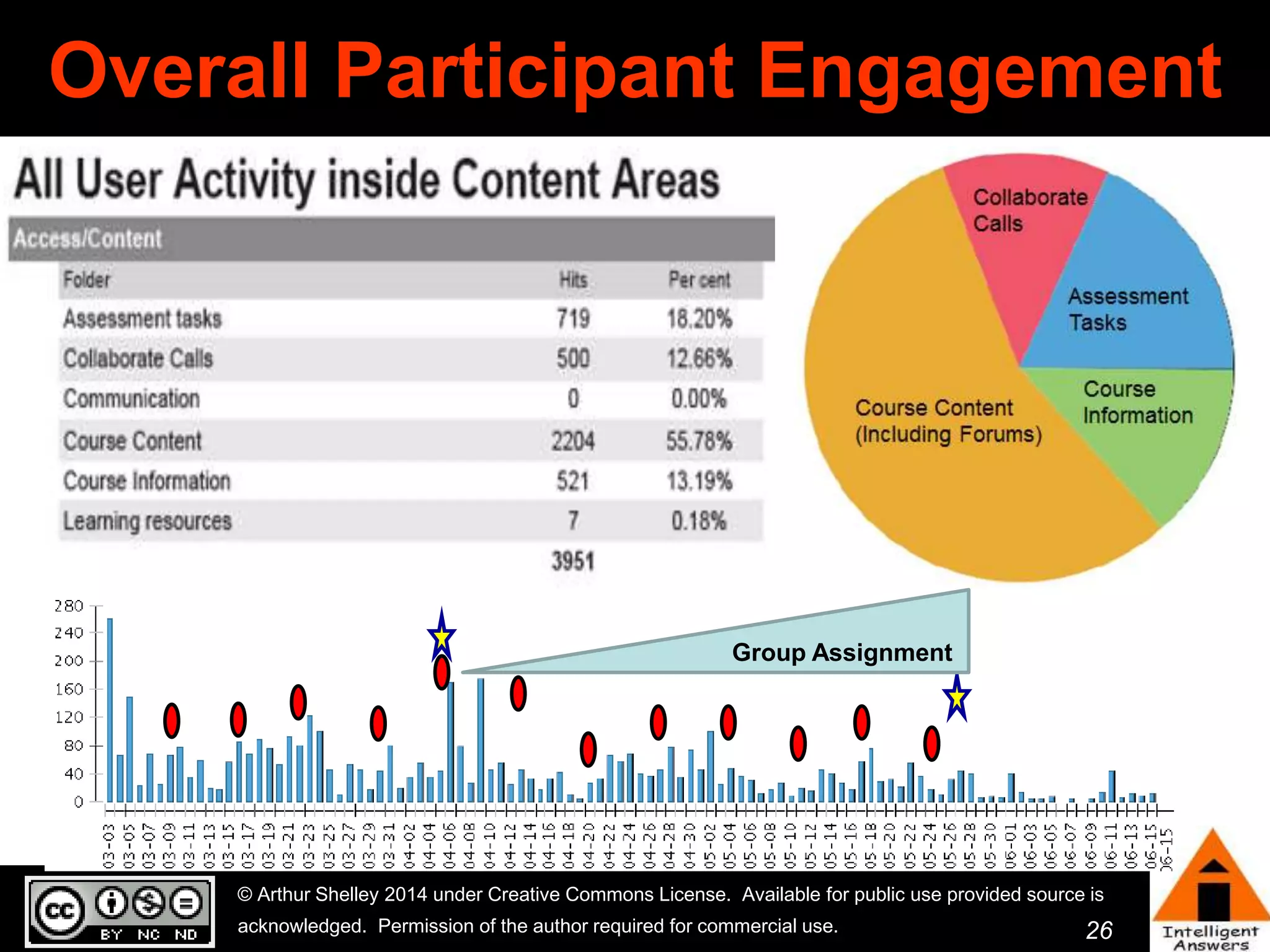
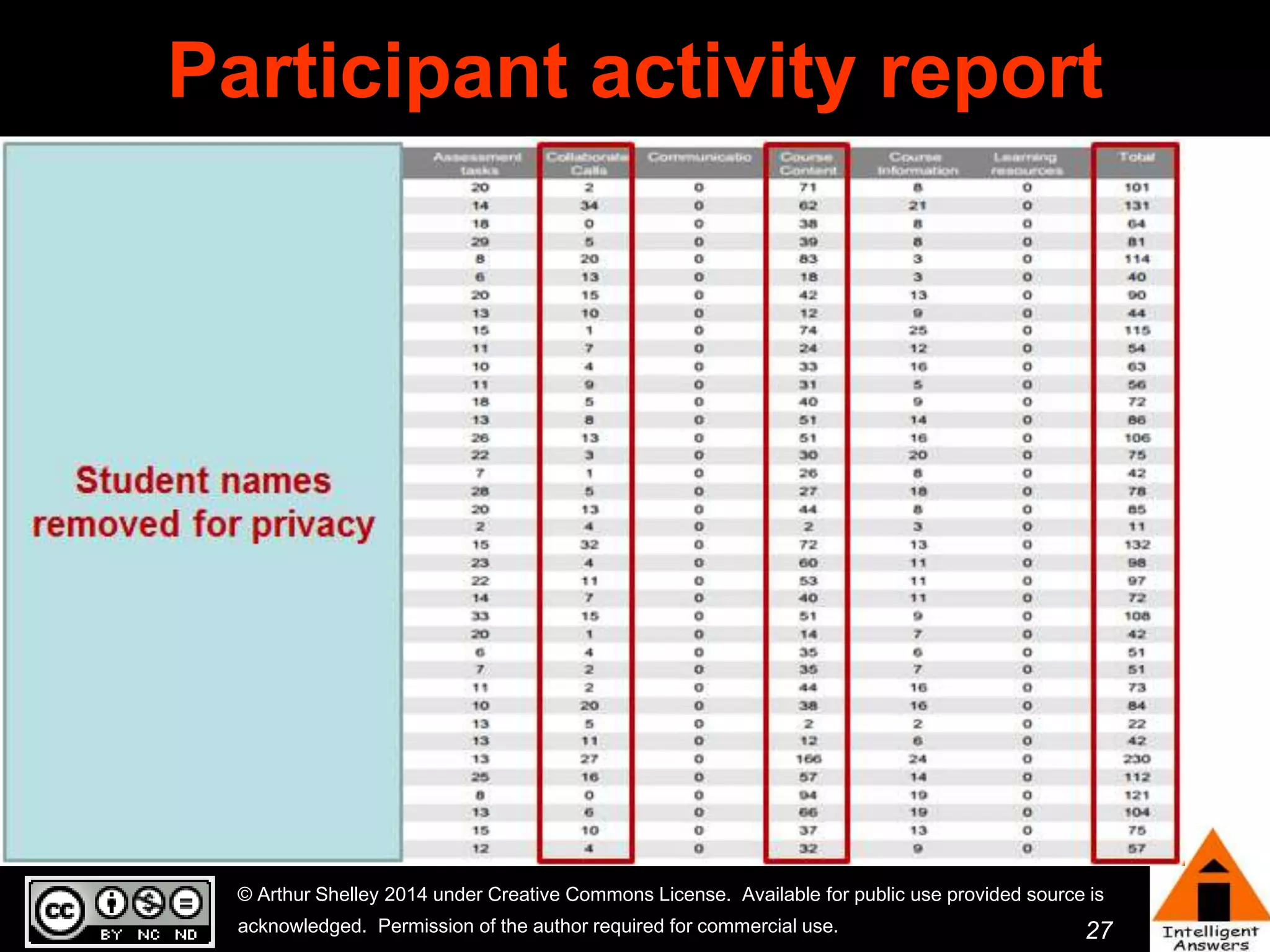
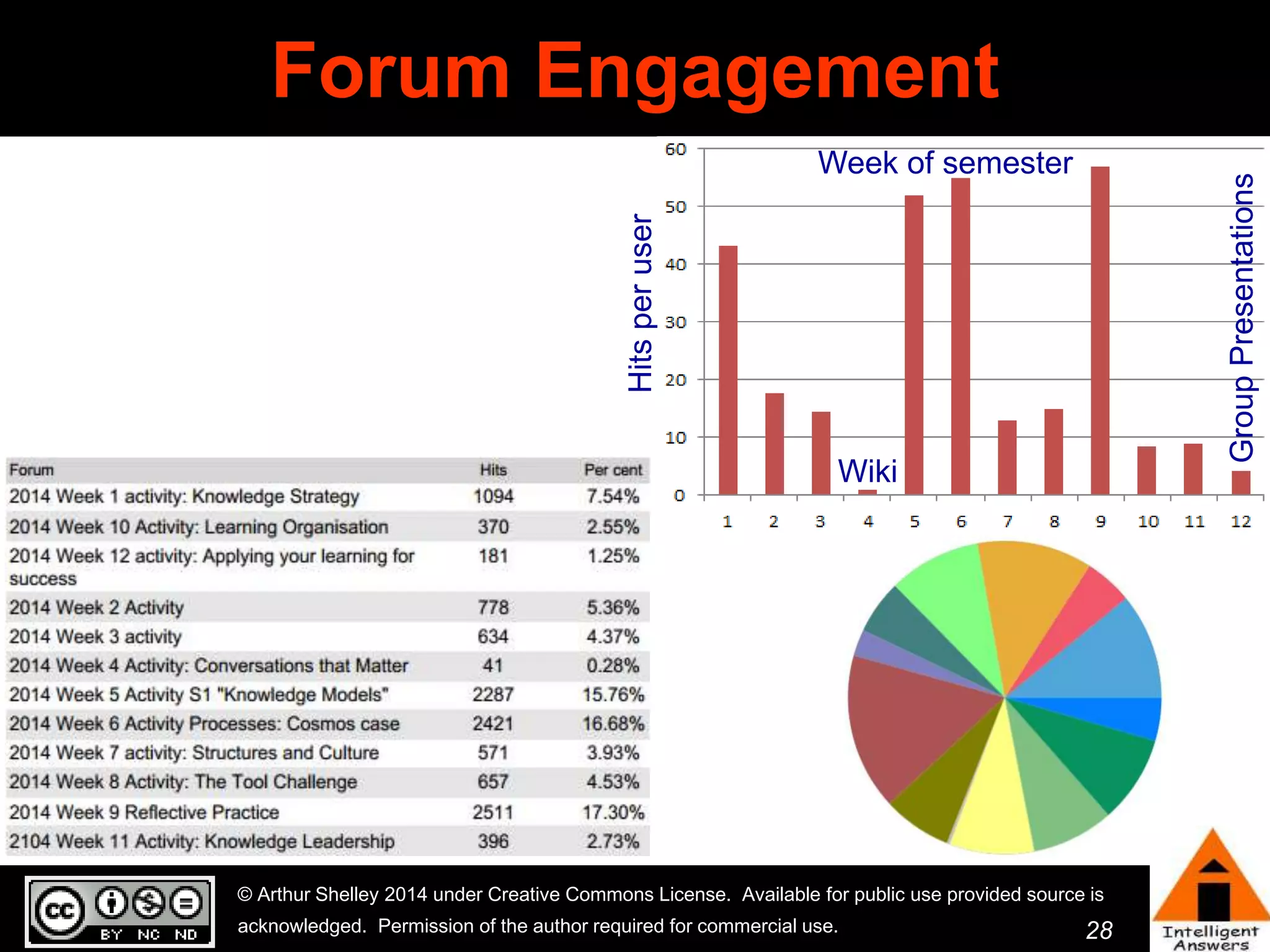
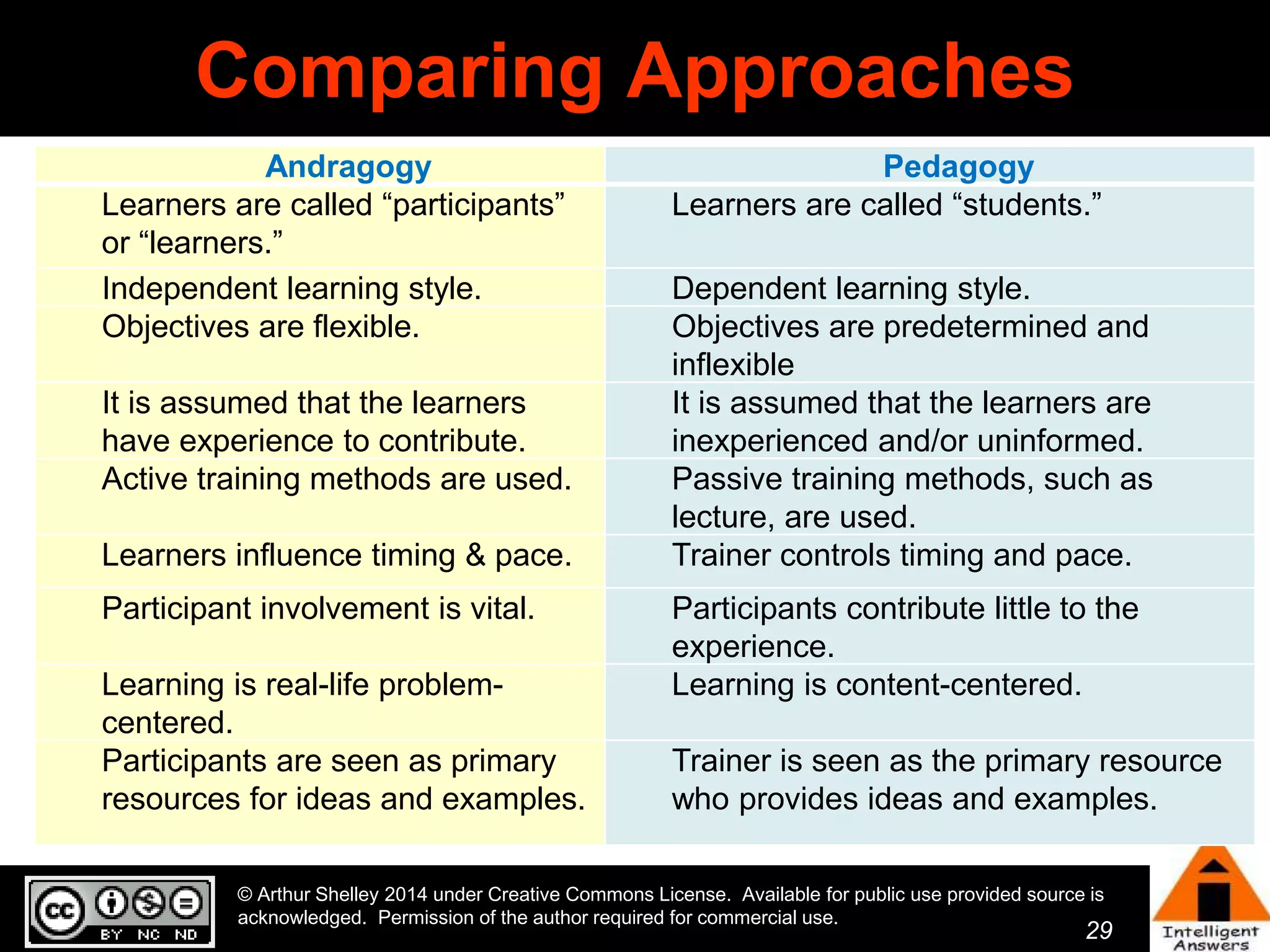
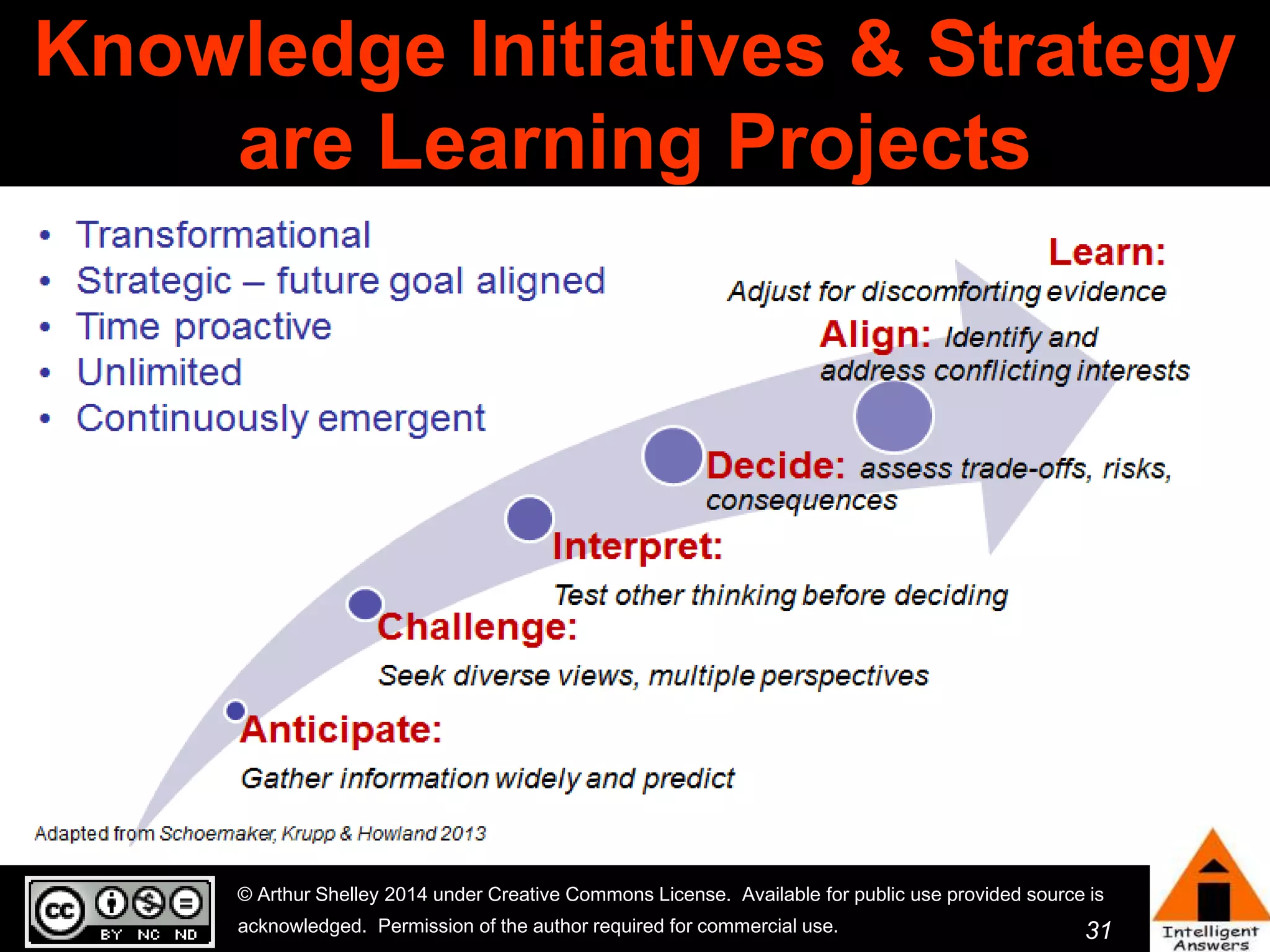
The document outlines a framework for knowledge leadership through interactive learning and knowledge creation, emphasizing the importance of collaborative engagement in enhancing performance and innovation. It discusses essential skills for knowledge workers, such as critical thinking, effective communication, and adaptability to complex environments. The author advocates for lifelong learning as a lifestyle and emphasizes the role of social learning in promoting conversations that foster creativity and trust within organizations.