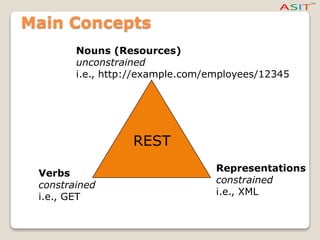
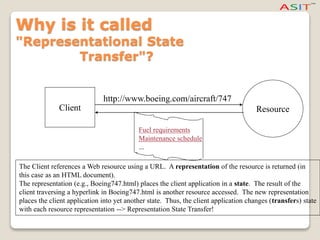
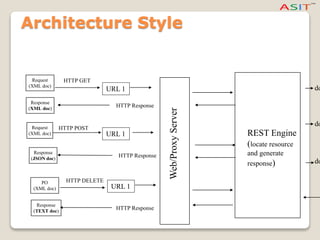
The document explains Representational State Transfer (REST) and Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), highlighting how they facilitate communication over the World Wide Web by leveraging URIs and standard HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. It details the principles and abstraction of resources in REST, how data is represented and transferred, and the significance of representation state transfer in web applications. Additionally, it notes that REST is not a formal standard but relies on established protocols, and showcases well-known examples of RESTful web services.