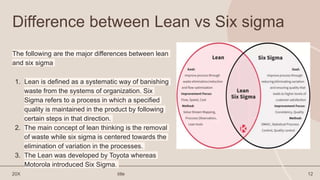
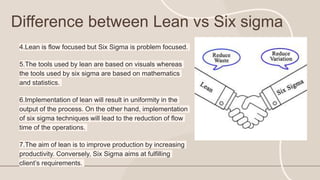
The document provides an overview of Lean Production and related concepts. It discusses that Lean Production aims to eliminate waste in manufacturing through streamlining processes. It identifies seven types of waste - overproduction, defects, waiting, unnecessary inventory, unnecessary motion, overprocessing, and transport. It also outlines five principles and five pillars of Lean Manufacturing. Examples of Lean implementation at Toyota, Saskatchewan and Maruti Suzuki are provided. The document concludes with thanking the presentation creators.