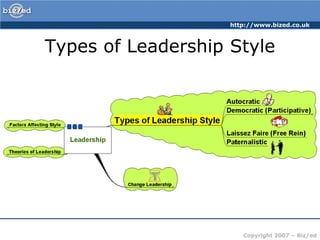
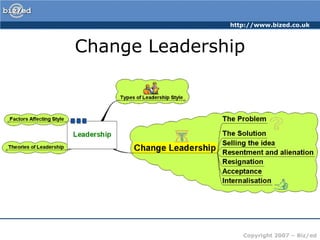
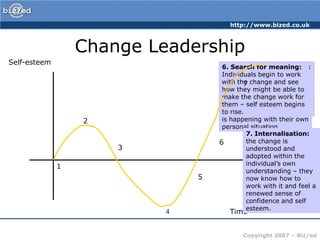
The leaders organized workers into efficient units to clear a road through dense jungle. Progress was excellent as the leaders monitored work and made adjustments. However, one day someone saw the overall situation and shouted that they were going the wrong way. This highlights that management is about efficiency but leadership ensures the overall goal and direction are correct.