LAYERS OF EPIDERMIS_RHICHA GUPTA.pptx
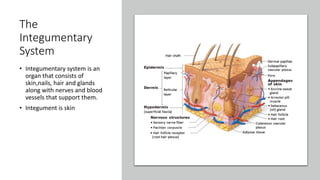
- 1. The Integumentary System • Integumentary system is an organ that consists of skin,nails, hair and glands along with nerves and blood vessels that support them. • Integument is skin
- 2. Skin • Skin is the largest and heaviest organ in the body and covers the entire external surface. • 16% of body weight comes from skin. • Scientific name of skin is derma • The cells in the skin are mainly made of protein keratin. There are two kinds of human skin • Glabrous skin(non-hairy) • Hair –bearing skin
- 3. Functions of the skin Skin has the vital function to keep the physiological and biochemical conditions in the body in optimum state. Regulates body temperature Prevents loss of body fluids and penetration of toxic substances Storage of lipids cholesterol vitamin and synthesis of vitamin D Excretes toxic substances by sweat(salt, water, organic wastes) Protection of body from harmful effects of the sun and radiation Immunological function mediated by Langerhans cells. Sensory organ for touch, pressure, pain , temperature Mechanical support
- 4. Layers of Skin Skin has primarily three layers • Epidermis • Dermis • Hypodermis
- 5. EPIDERMIS – The first layer of Skin • Strong superficial layer of skin serves of first line of protection against outer environment from interior body. • Composed of keratinized ,stratified, squamous, epithelial cells • Continually renewing cells that keratinizes and gives rise to derivative appendages(hair,nails,sebaceous and sudoriferous gland) • Oxygen and nutrients diffuse from underlying dermis . • It is avascular-no blood supply • The thickness of epidermis varies 0.4 to 1.5mm • It is thickest on the palms and soles.
- 6. Cells of Epidermis • Keratinocytes • Melanocytes • Langerhans cell • Merkel cells • Corneocyte • Basal cells
- 7. Layers of Epidermis From below up layers are: • Stratum Basale or Germinativum(deepest layer)- (BASAL LAYER) • Stratum Spinosum or Prickle Layer (SPINOUS LAYER) • Stratum Granulosum(GRANULAR LAYER)) • Stratum Corneum (Horny Layer) • Stratum Lucidum(CLEAR CELL LAYER) is extra layer below Horny Layer found in thick skin of palms and soles.
- 8. Stratum Basale • Also known as Stratum Germinativum • The cells are cuboidal or columnar in shape, with dark staining nuclei and a dense cytoplasm. • It is generally 1-2 cell layers thick • Cells are active in mitosis constantly producing keratinocytes to replenish the cells shed from epidermis • The keratin produced hardens and flattens the cells as it moves outwards and waterproofs the skin. • This layer also has melanocytes and merkel cells. • It is attached to the underlying Dermis by basement membrane(basal lamina) • The melanocytes produces melanin which gives colour to the skin
- 9. Stratum Spinosum Also known as prickle layer It is about 8-10 cell layer, polyhedral cell The cells are shrunken with spine like projection The spine connects to the neighbouring cells with desmosomes Functions as adhesion of epidermal cells and resistance to mechanical stress. Partly responsible for skins strength and flexibility Langerhans cells are found in this layer Keratin synthesis begins in this layer
- 10. Stratum Granulosum • Also known as Granular Layer • It is 3-5 cell layer • Cells are diamond in shape • Cells has keratohyaline granules and lamellar granules • Keratinocytes has keratohyaline granules which clusters to form keratin filament. • Lamellar granules are present in the intercellular space which secretes glycolipids acting as a glue keeping the cells stuck together • Cornified envelope begins to form.
- 11. Stratum Lucidum It has 2-3 cell layers Present in thicker skin of palms and soles, and lips It is a transparent thin layer Translucent protein called eleidin is present in the cell
- 12. Stratum Corneum • Also known as horny layer • The outermost layer of the skin • Made of 15-20 layers of flattened, anucleated squamous cells(dead keratinocytes)or corneocyte • The cells are made of mature protein –keratin • This keratin secretes defensins which immunes our body. • Cornification takes place as keratinization keeps happening • Desquamation takes place continuously • Average duration for cells to replace from basal layer to corneum layer for adults is 4-6 weeks and for babies is 7-10 days.
- 13. To remember • Keratinization • Cornification – development of skin barrier, nails and hair • Desquamation • These are certain processes which keeps happening for proper functioning of integumentary system in the epidermis layer
- 14. Cells of epidermis Keratinocytes • Predominant cell of epidermis • Originates in Basal Layer • Protective barrier by secreting defensins • The mature keratin acts as water barrier by making and secreting lipids • Gives toughness to skin because of hardened keratin • Regulates calcium absorption needed for formation of vitamin D by UVB rays
- 15. Langerhan’s cells • Present in Stratum Spinosum • They are dendritic cells. • It protects the skin by producing antigen presentation through allergic reaction and stimulates the immune cells into action. • It guards the cutaneous membrane(epidermis, dermis&hypodermis)
- 16. Merkel Cells Found in Stratum Basale • Oval shaped mechano receptors for light touch • Found mostly in finger tips, palms, soles, oral. • Has keratin and desmosomes • Desmosomes connects merkel cells to adjoining keratinocytes • Their membrane interacts with free nerve endings
- 17. Melanocytes • Found in Stratum Basale • Produces pigment “Melanin”which gives color to the skin • UVB stimulates melanin secretion which protects skin from harmful UV radiation acts as a built in sunscreen • The amount of melanin transfer to keratinocytes defines the skin color • There are two types of melanin Eu melanin ( brown&black) Pheo melanin ( red and yellow)
- 18. Coloration of skin Combination of three pigments • Melanin • Carotene • Haemoglobin Carotene A yellowish pigment found in epidermal cell and fatty cell of dermis Abundant in skins of Asians Together with melanin accounts for yellowish tan color. Haemoglobin Not a pigment, but its oxygen binding capacity in RBC’s gives pinkish tone to the skin.
Editor's Notes
- What is skin, structure, form, function, cause What would happen if we don’t have skin Cause for its formation
- Stratified- layers, squamous –joined edge to edge like fish scale, cuboidal shape of cube, epithelial – outer covering .
- Physiological-proper functioning of the organs Biochemical-make up of cells and other structures of organisms to carry out life processes Touch-socio-sexual and emotional sensations
- Dendritic-type of immune cell, antigen presenting cell
- Corneocyte-lost the nucleus and organelles,Cornification- hardening, flattening makes the cells die while keratinisation is happening Desquamation – shedding of dead skin cells