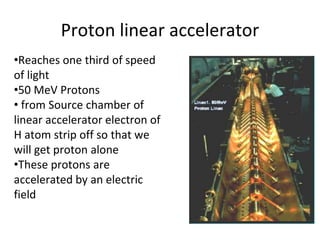
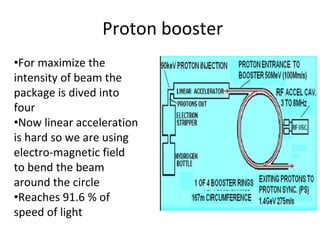
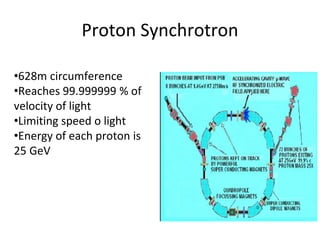
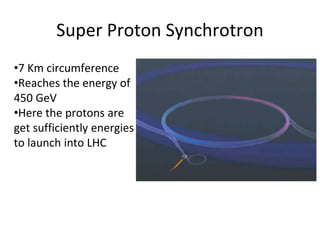
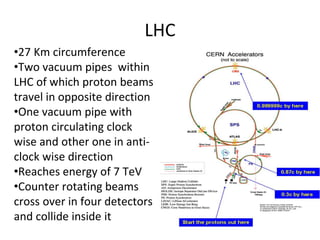
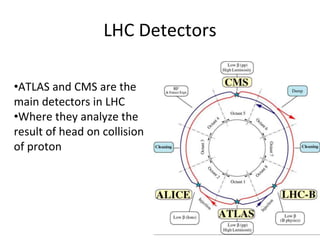
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is a 17-mile long particle accelerator that smashes protons together at nearly the speed of light to recreate conditions shortly after the Big Bang and answer fundamental questions about the universe. It aims to detect elusive particles like the Higgs boson and help explain mysteries like dark matter. The LHC accelerates two beams of protons in opposite directions around its ring and uses powerful magnets to force the beams to collide in four locations, where detectors observe the collision debris to gain insights into physics at the smallest scales.