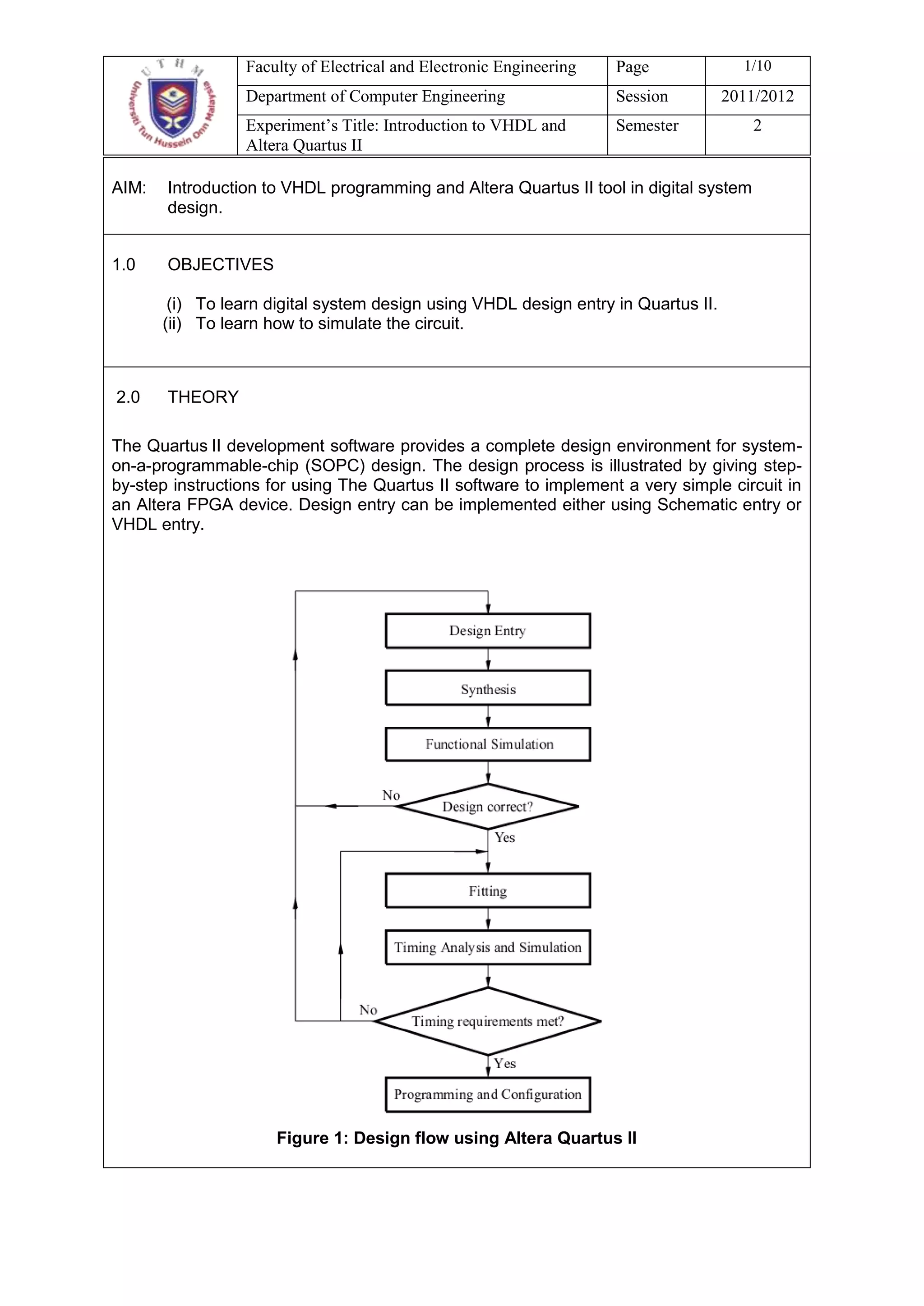
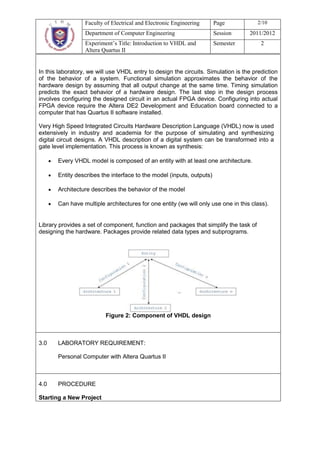
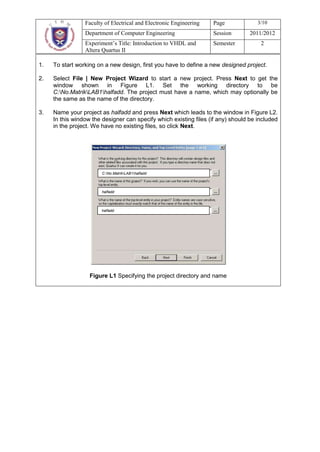
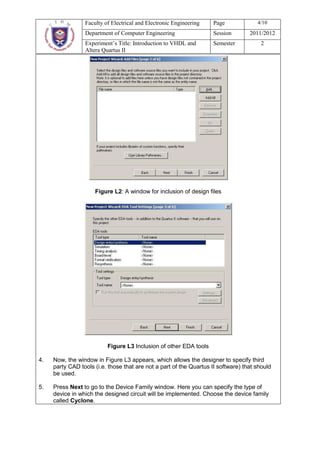
This document describes an experiment on digital circuit design using VHDL and the Altera Quartus II software. The objectives are to learn VHDL design entry and simulation in Quartus II. It outlines designing a half adder and full adder circuit in VHDL, including obtaining the truth tables, deriving the Boolean expressions, writing the VHDL code, and simulating the designs functionally and for timing. Students are asked questions about the half adder and full adder designs, as well as general questions about digital design flows and VHDL.