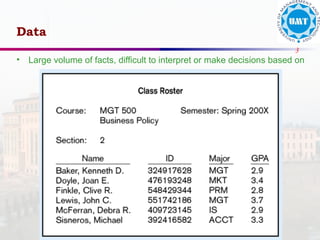
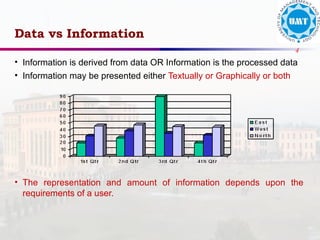
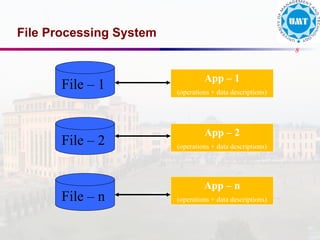
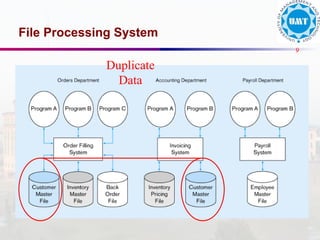
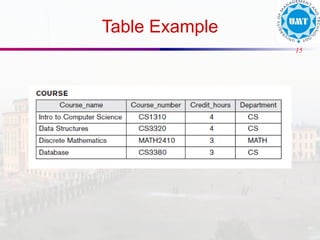
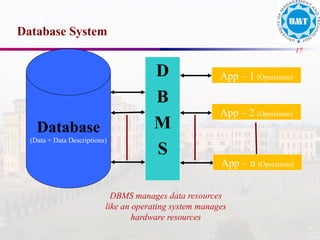
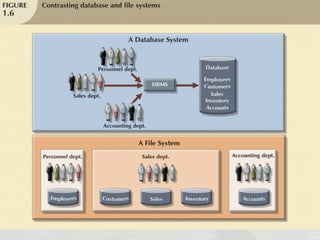
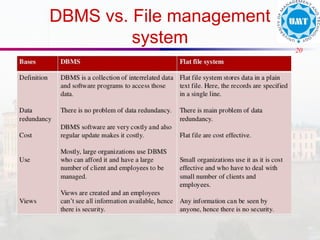
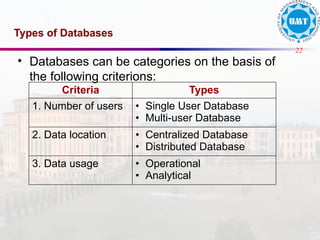
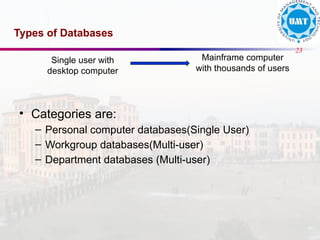
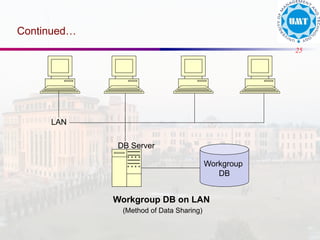
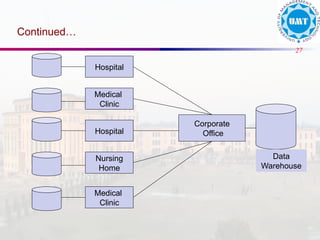
The document discusses the distinctions between data and information, emphasizing how data becomes meaningful through processing and representation. It explores various record-keeping techniques, particularly contrasting manual systems with computerized database systems, highlighting the drawbacks of manual record systems like redundancy and inefficiency. It introduces database management systems (DBMS), which facilitate the management of large data collections, and categorizes different types of databases based on users, data location, and usage.