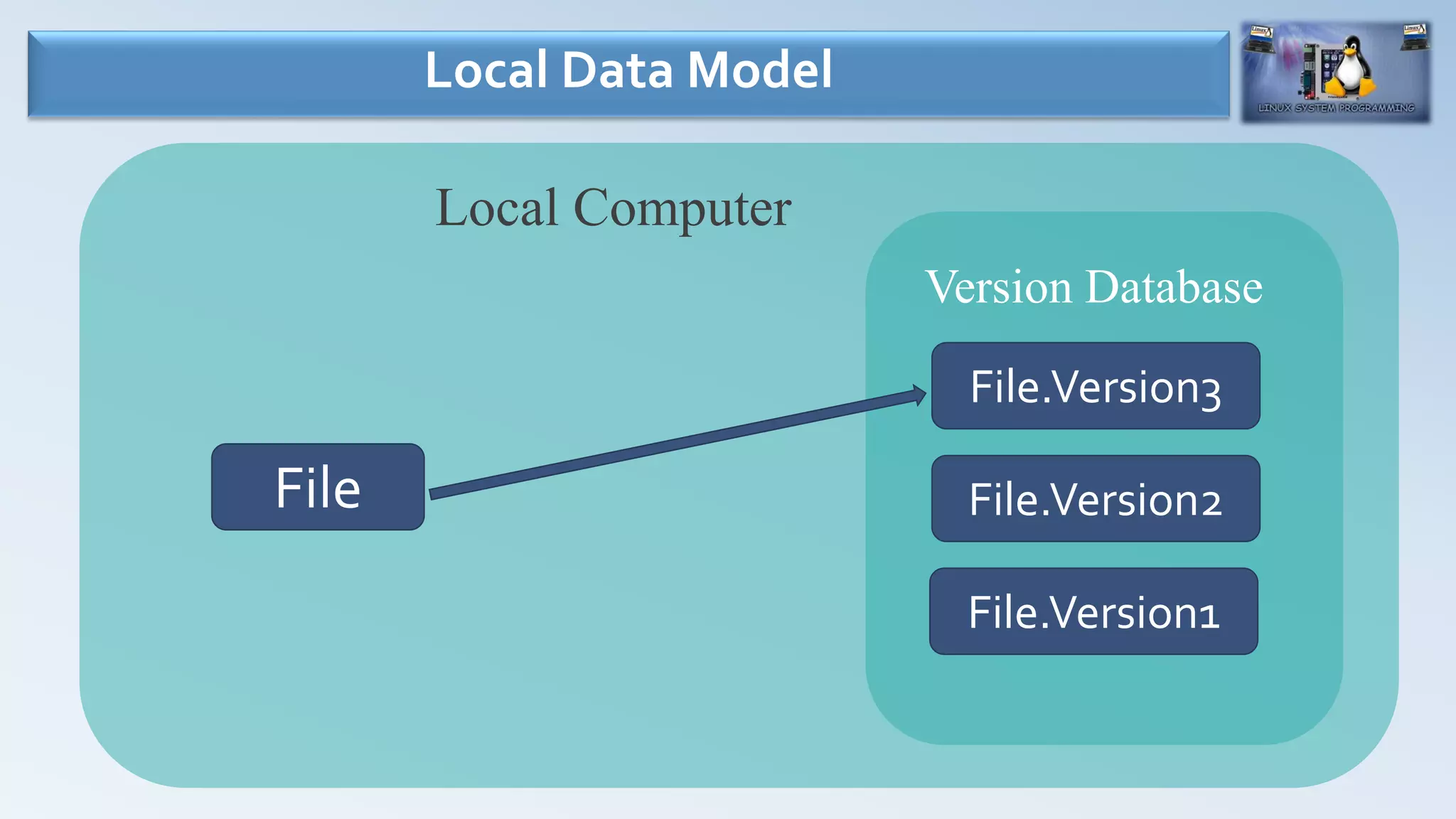
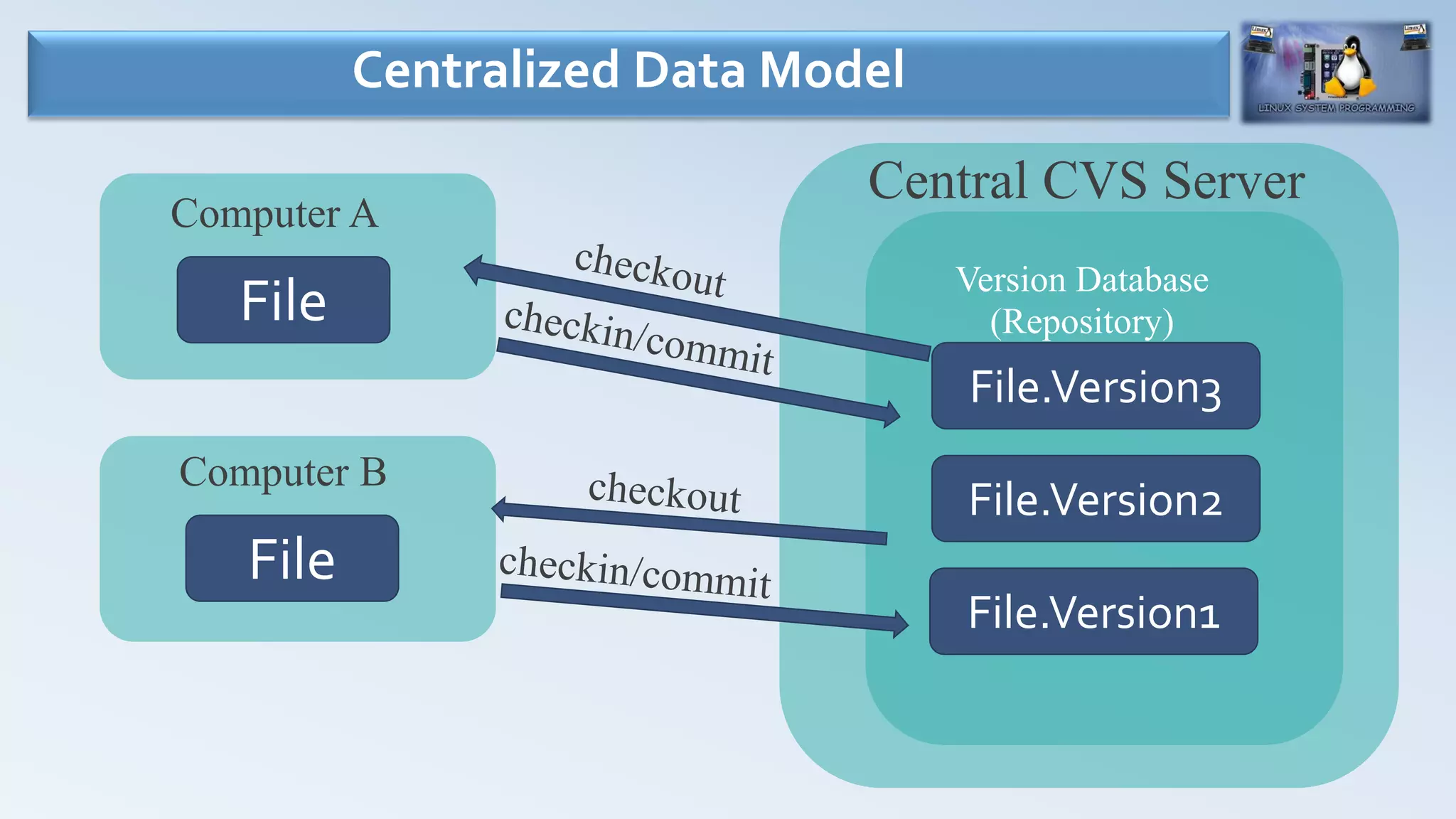
- Version control systems allow users to maintain revisions of files over time and collaborate on projects.
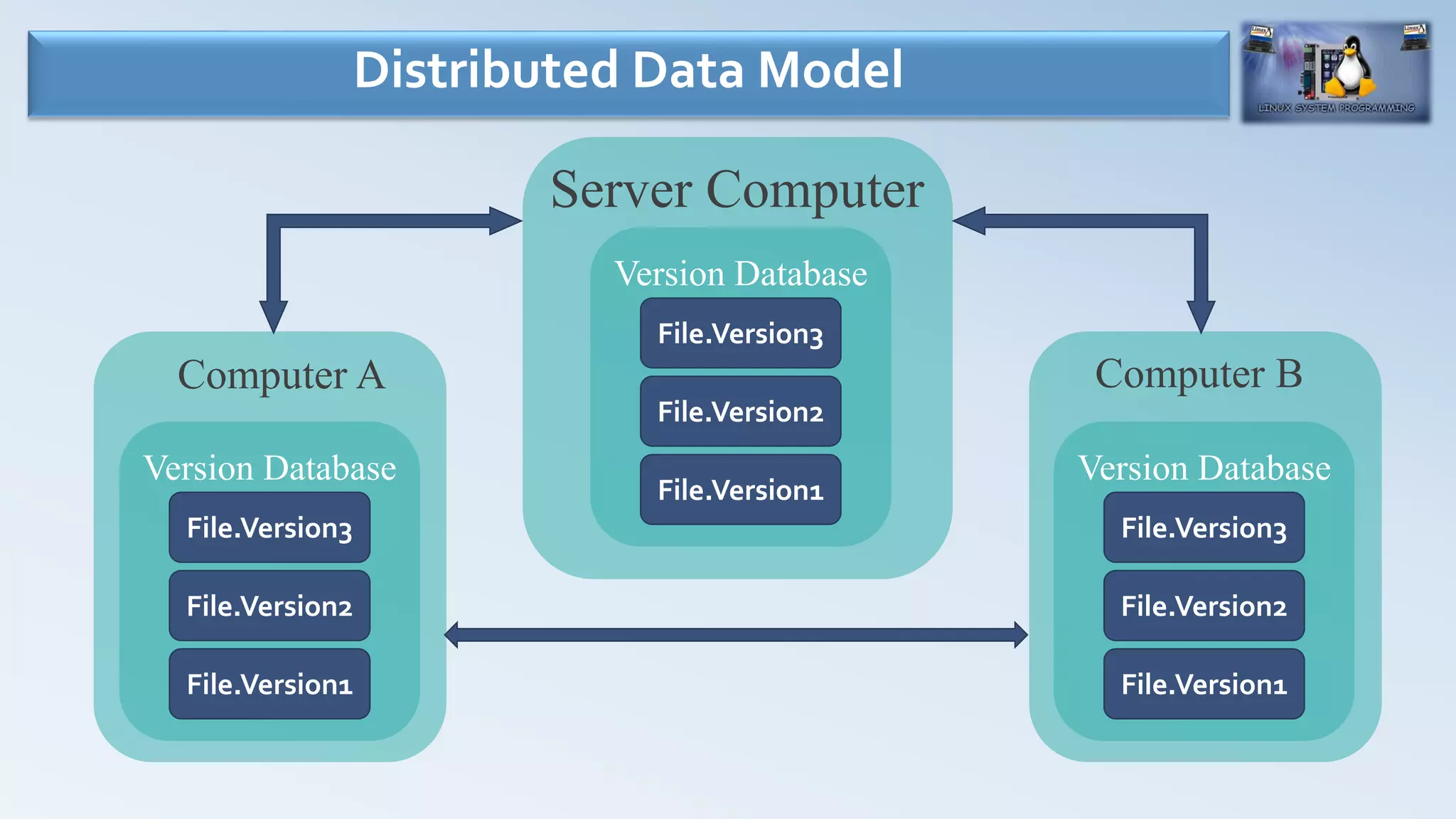
- There are three main types of version control systems: local data model (SCCS, RCS), centralized data model (CVS, SVN), and distributed data model (BitKeeper, Git, Mercurial).
- Git is a free, open source distributed version control system that was created in 2005 and is very popular today. It allows for local repositories that can be synced and shared.