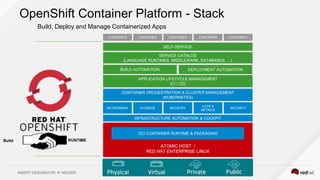
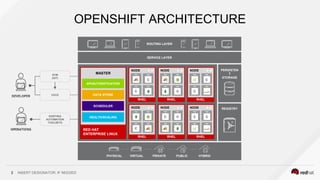
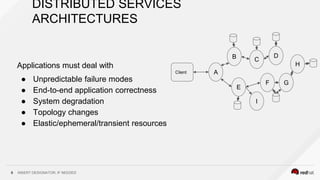
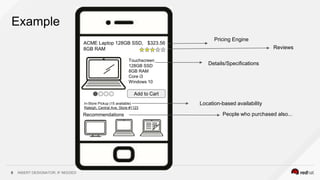
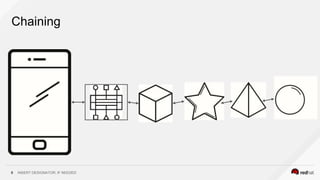
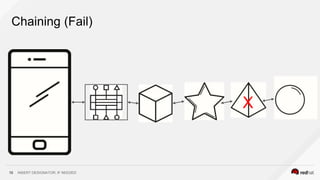
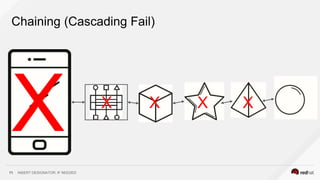
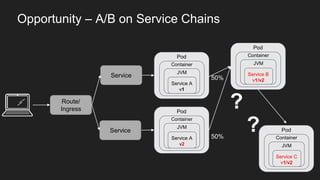
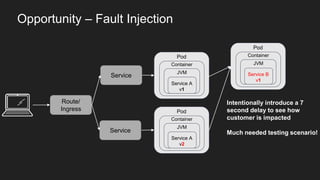
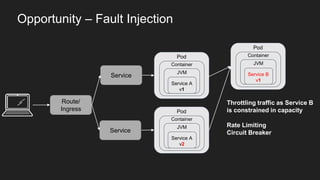
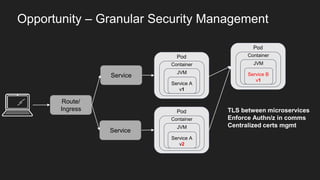
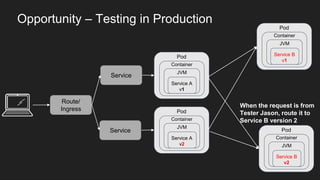
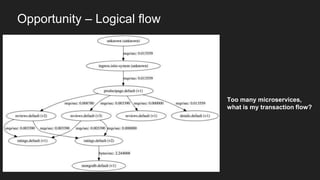
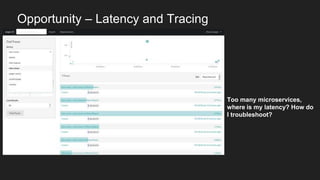
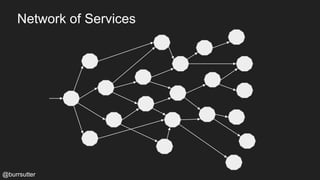
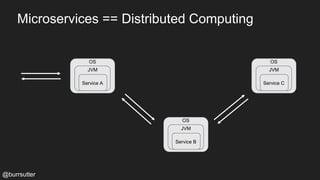
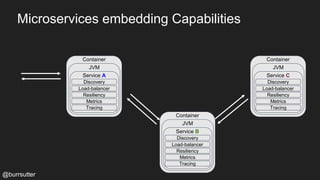
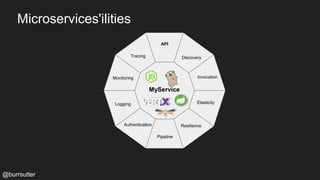
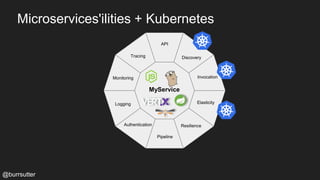
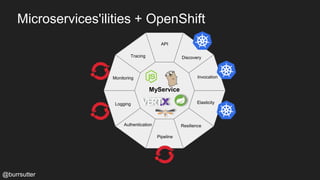
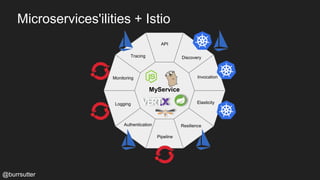
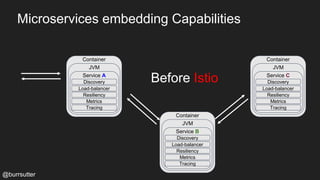
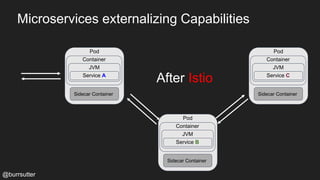
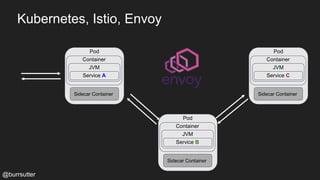
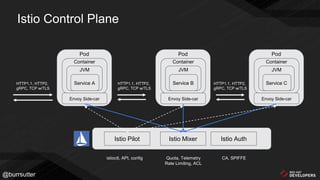
This document discusses using a service mesh like Istio to manage microservices. It describes how Istio uses the Envoy proxy deployed as a sidecar to each microservice pod to provide capabilities like discovery, load balancing, resiliency, metrics and tracing across the network of microservices. These capabilities help govern microservice behavior at runtime, enforce policies, and improve observability of traffic between microservices. The document also outlines some use cases for a service mesh like traffic shaping, fault injection for testing resilience, and improved security and visibility across the distributed application.