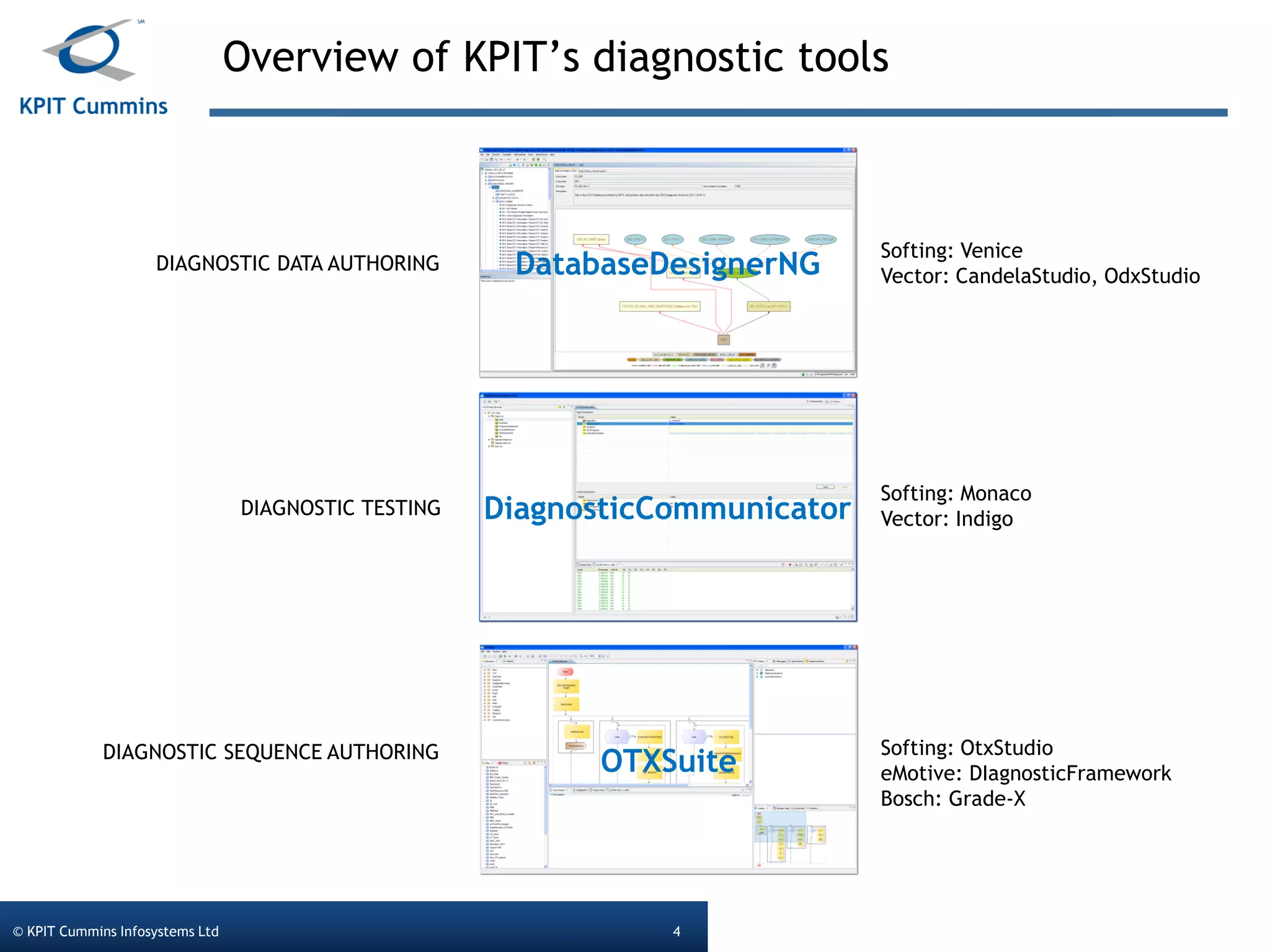
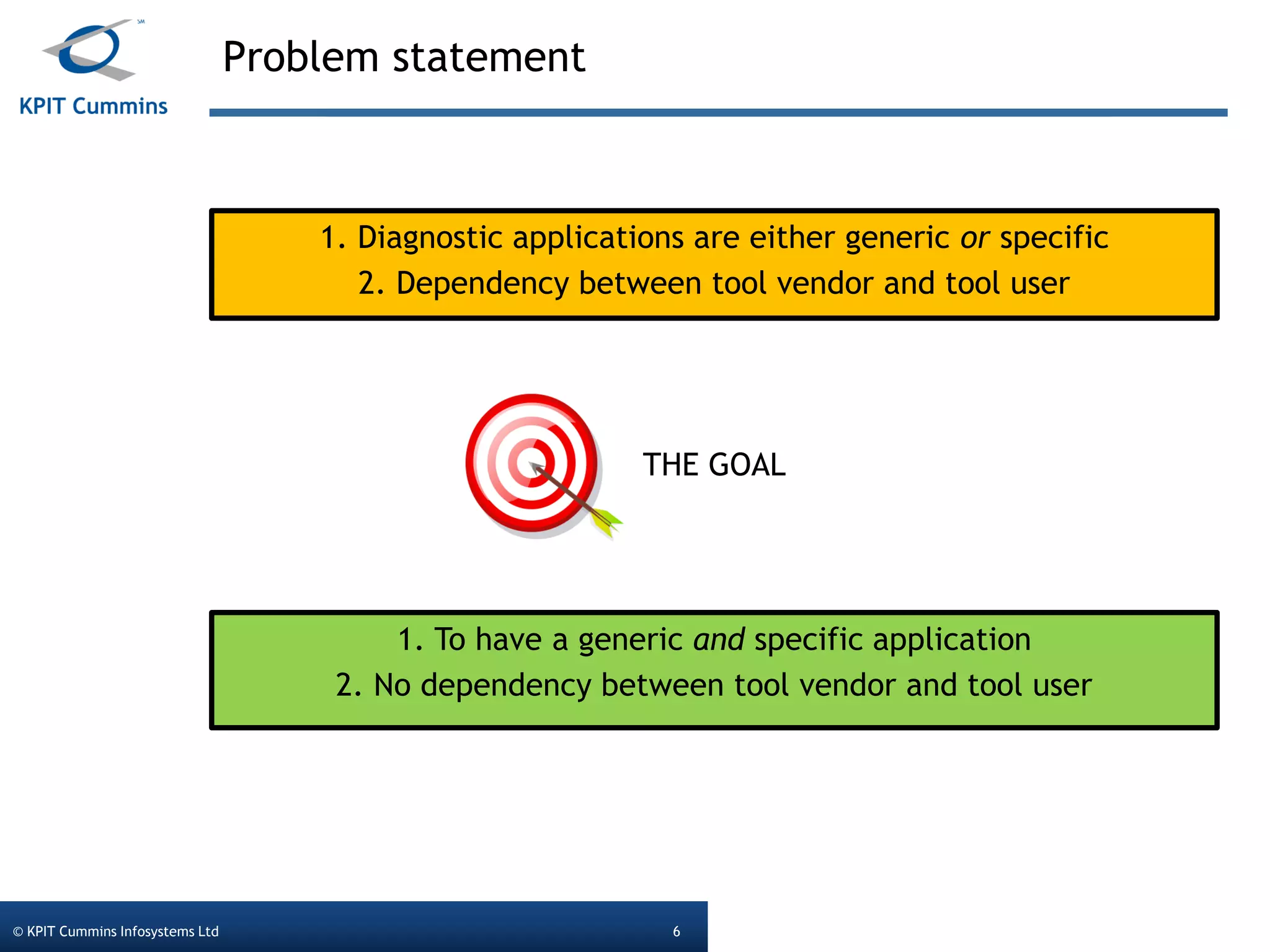
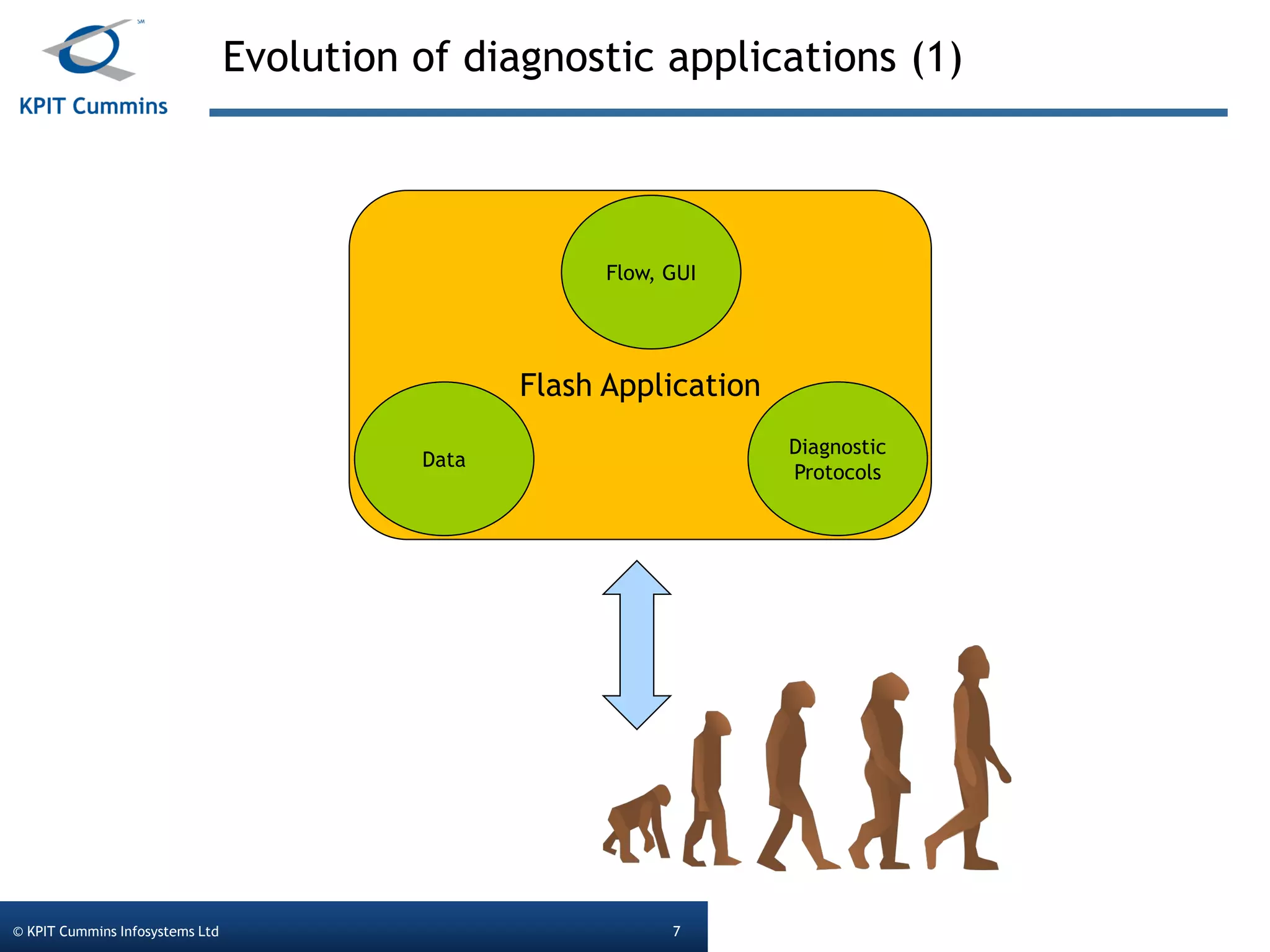
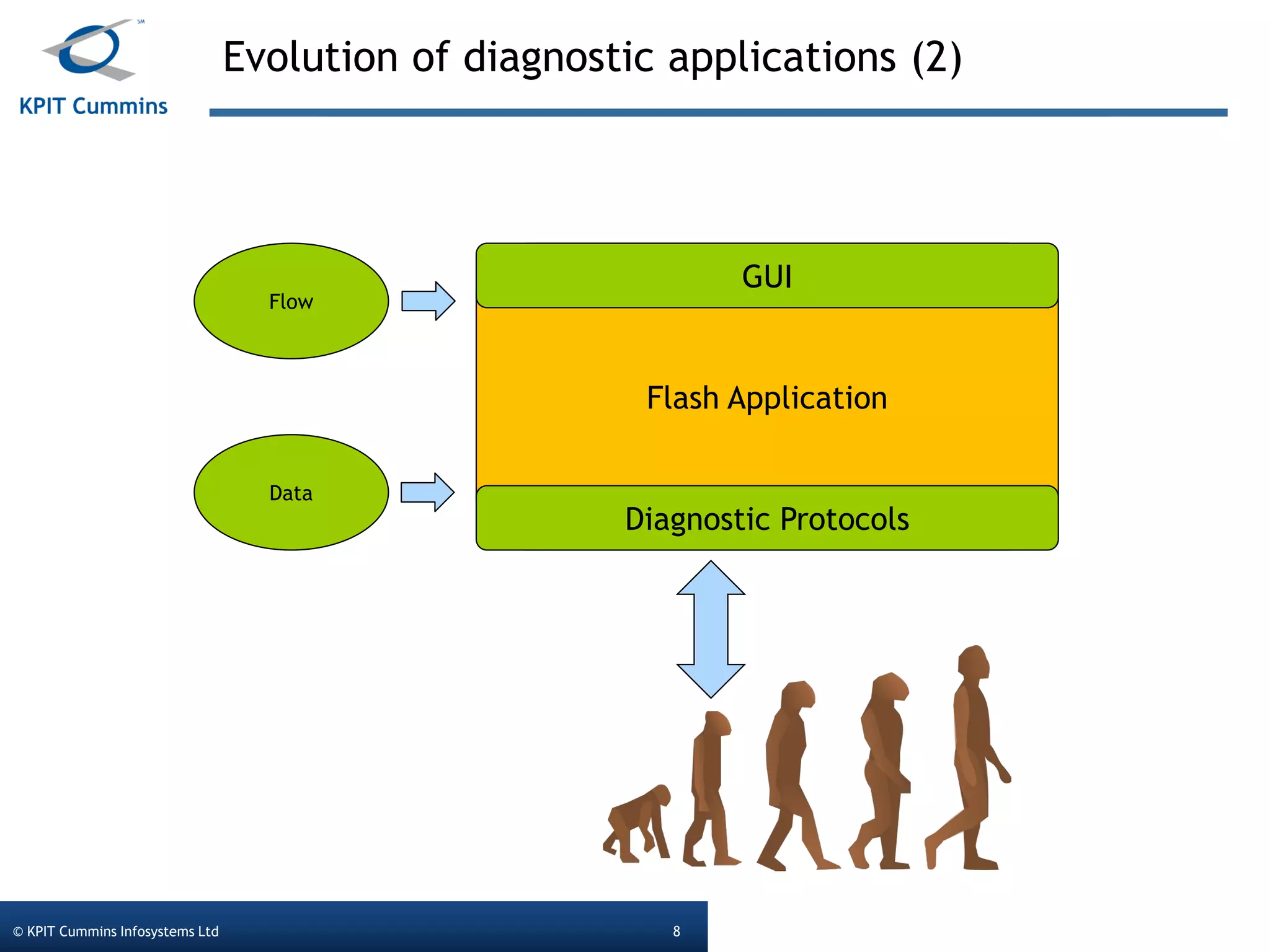
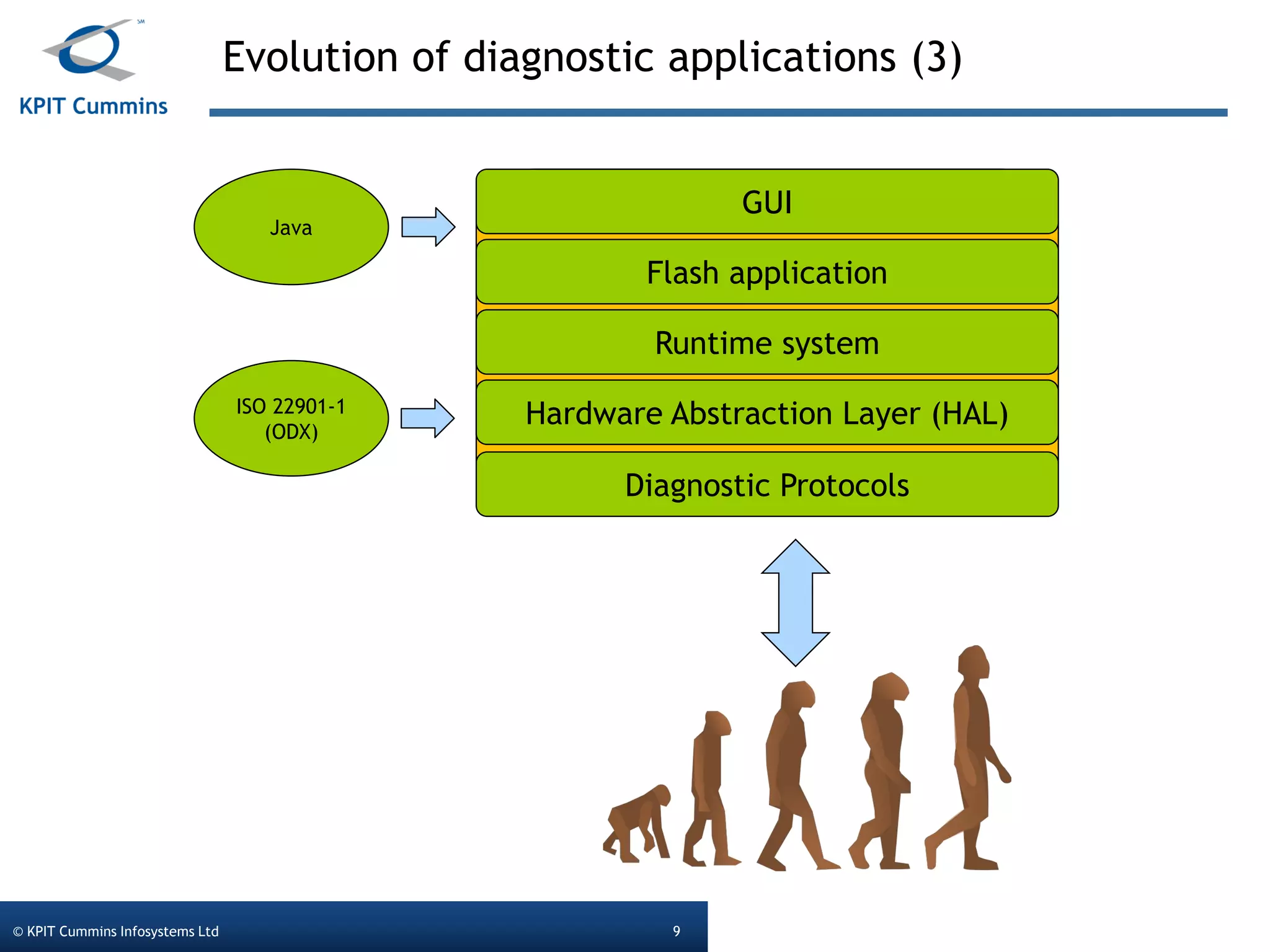
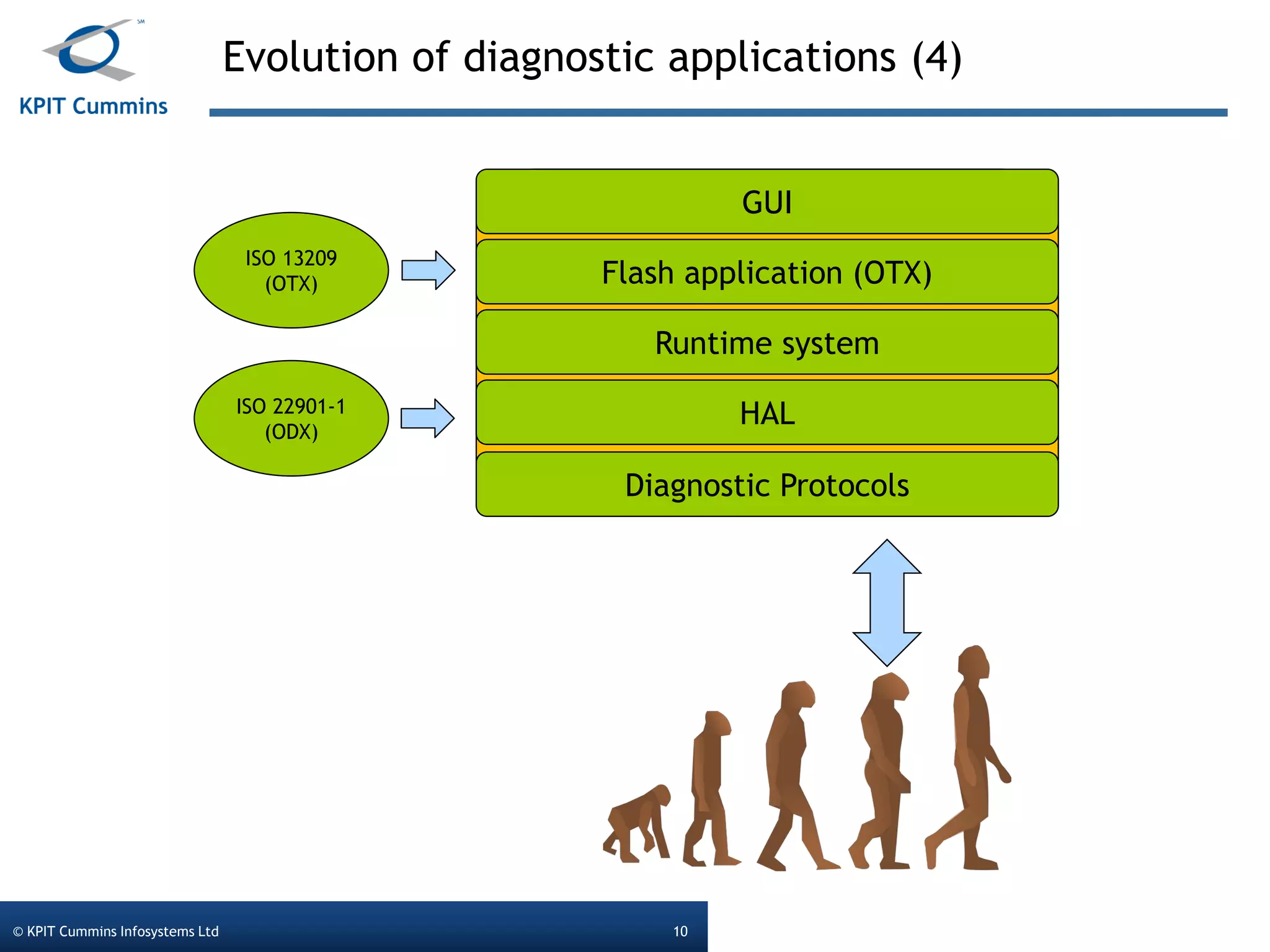
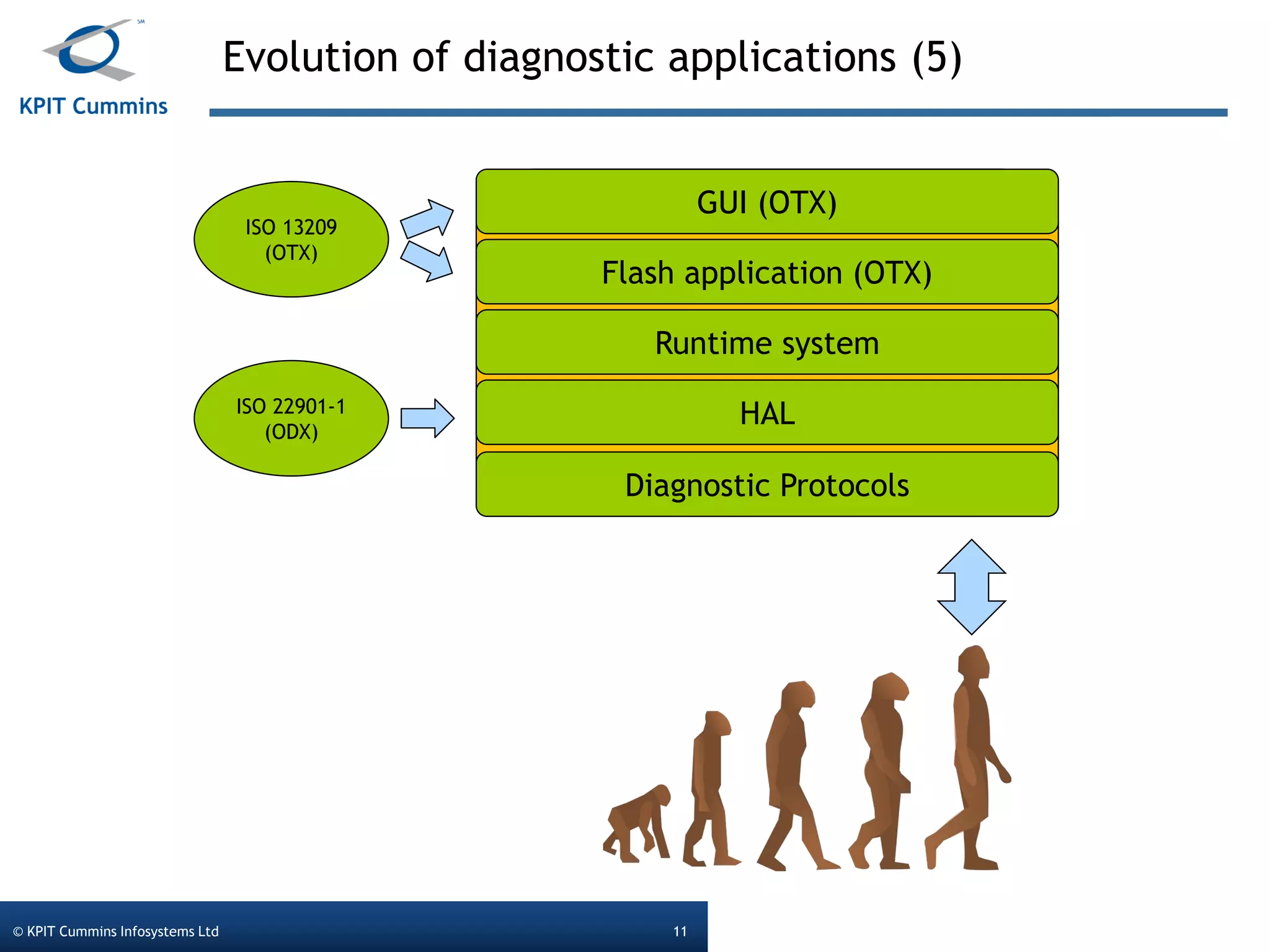
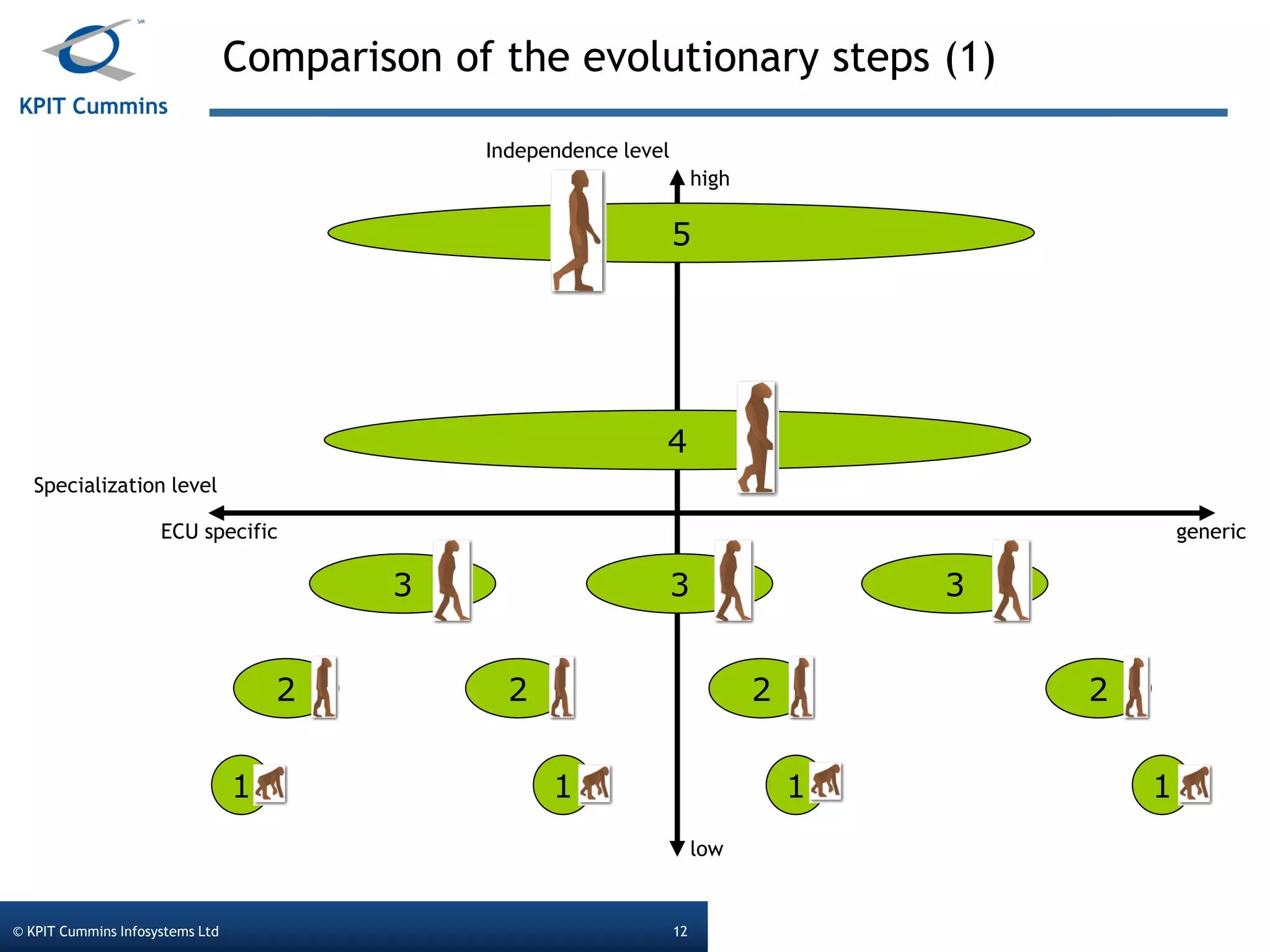
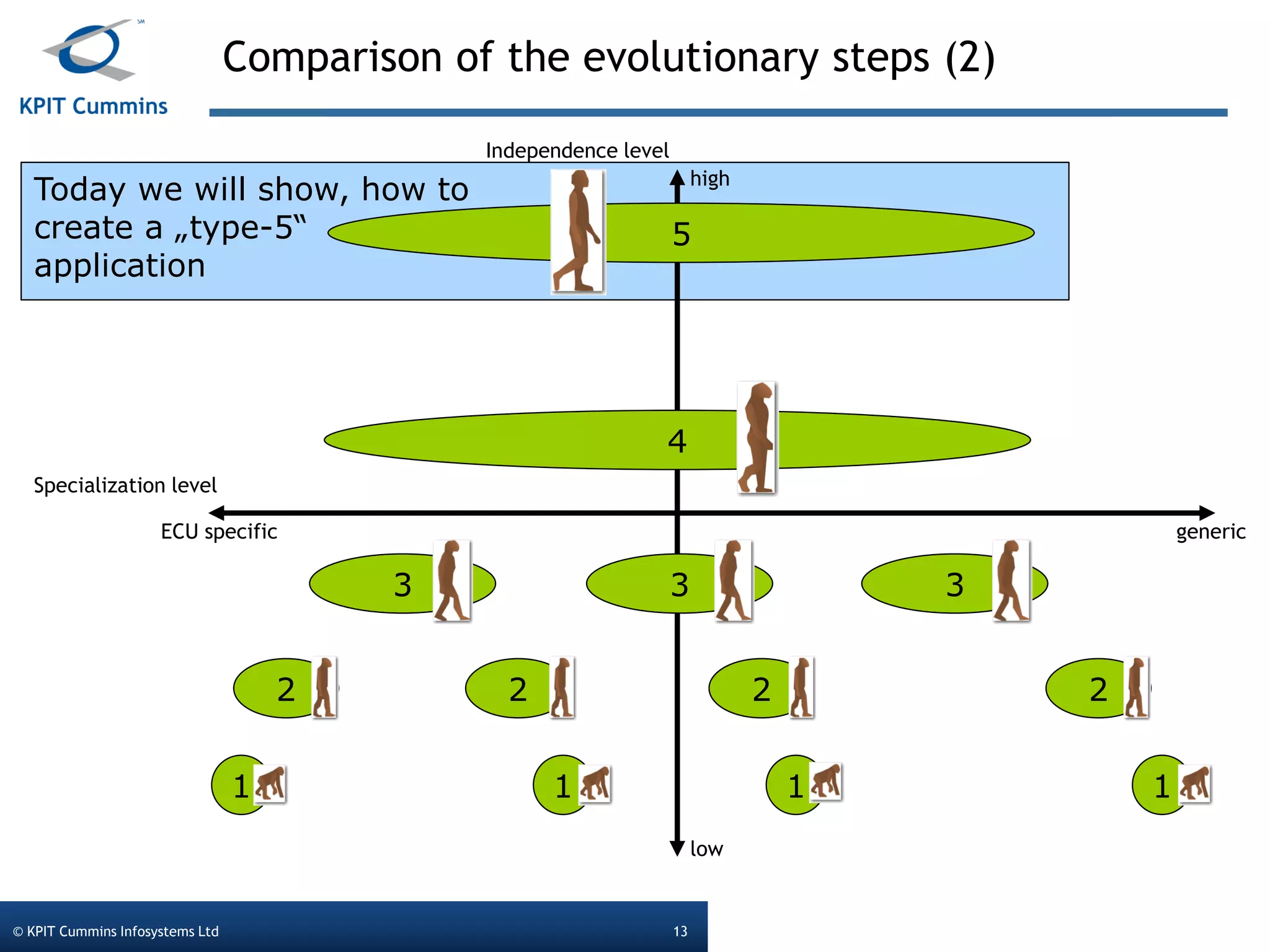
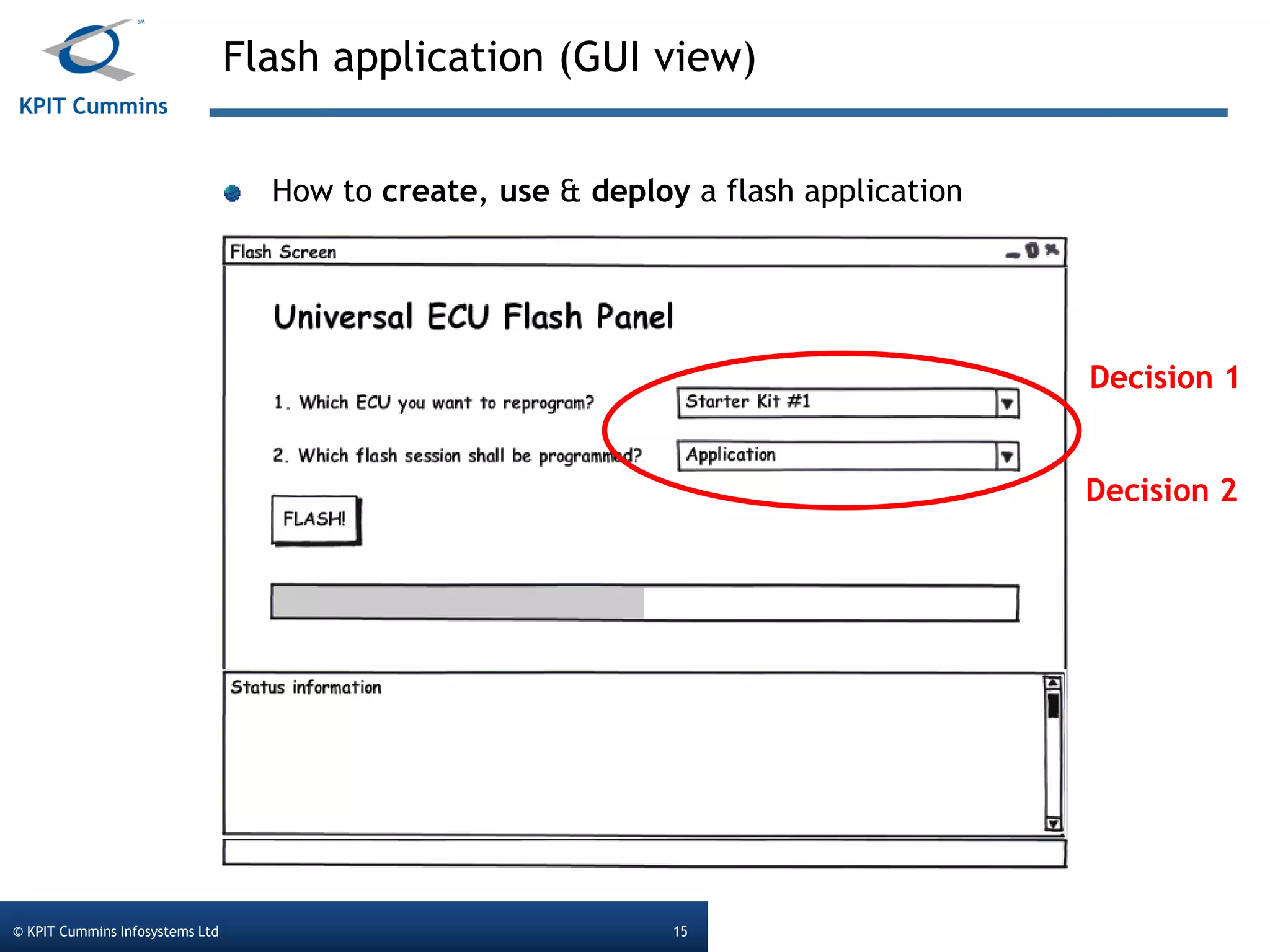
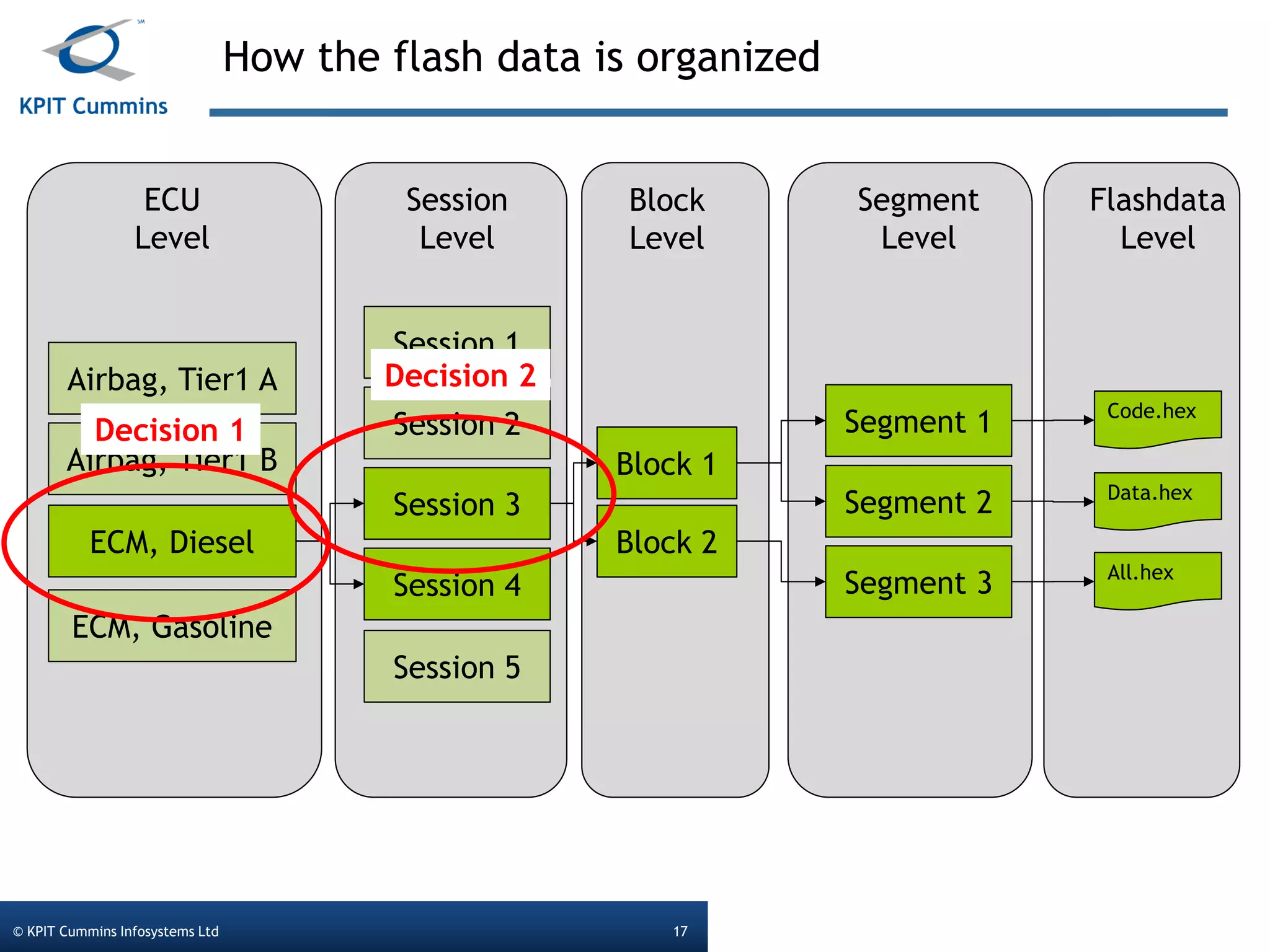
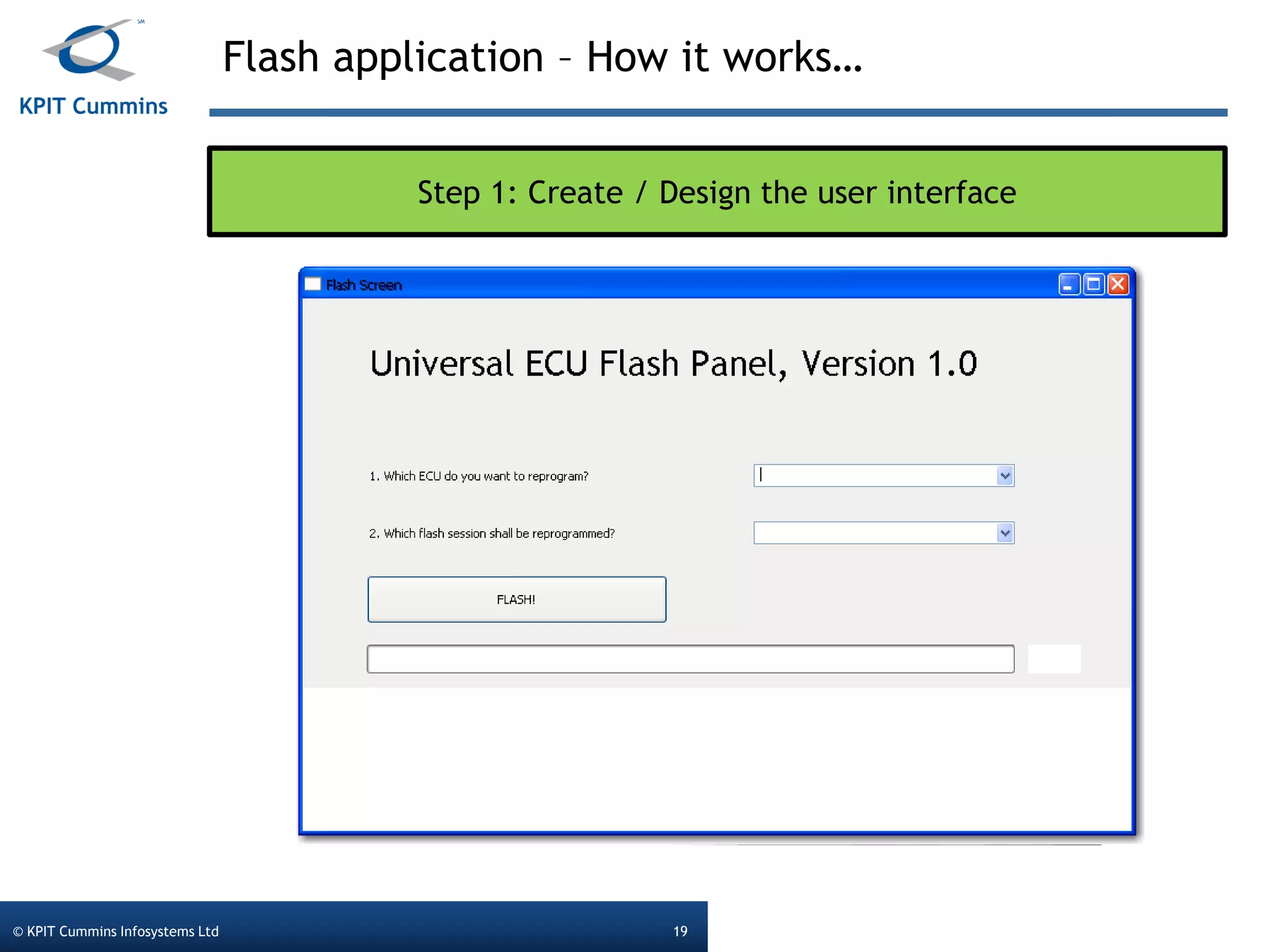
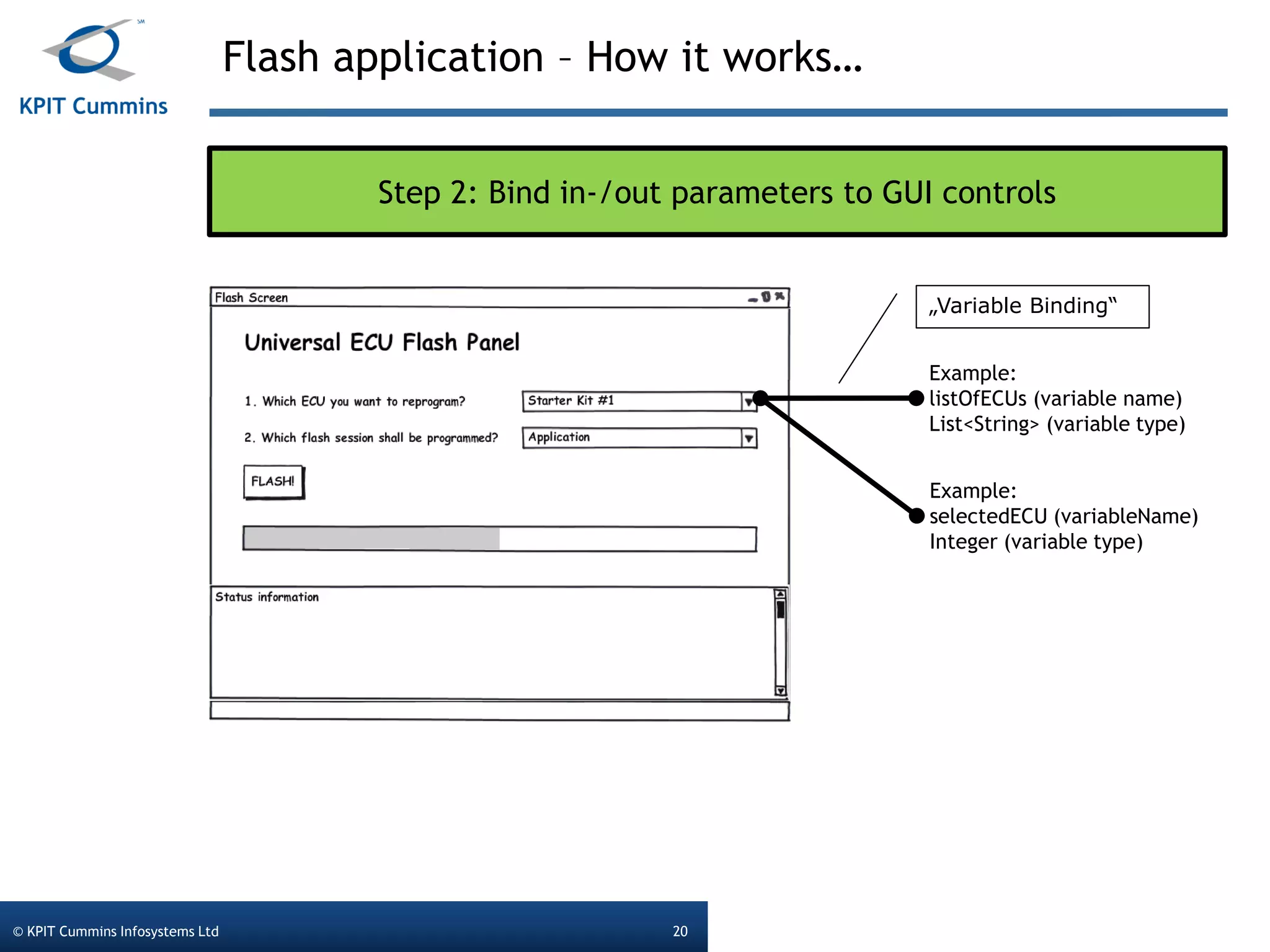
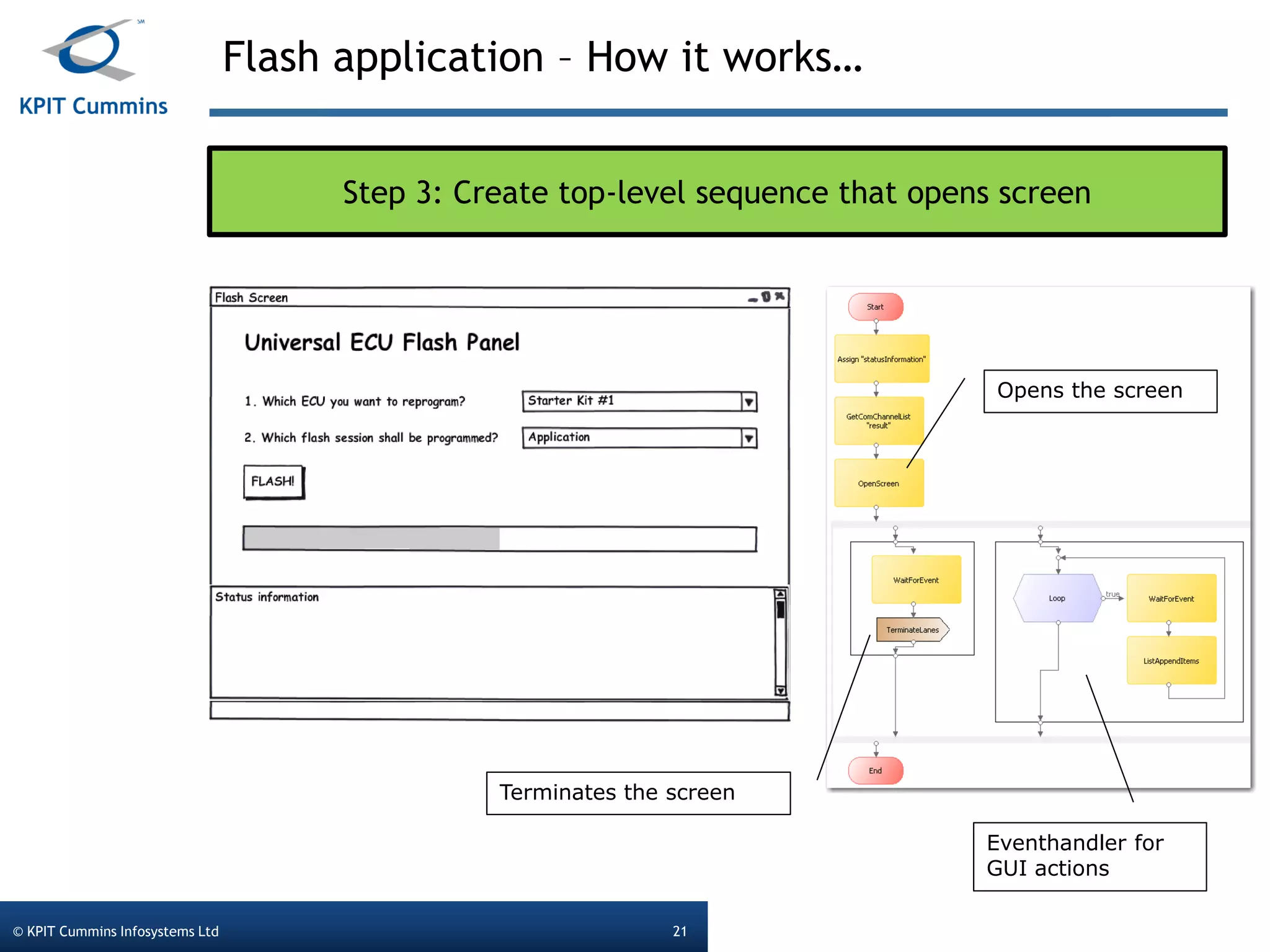
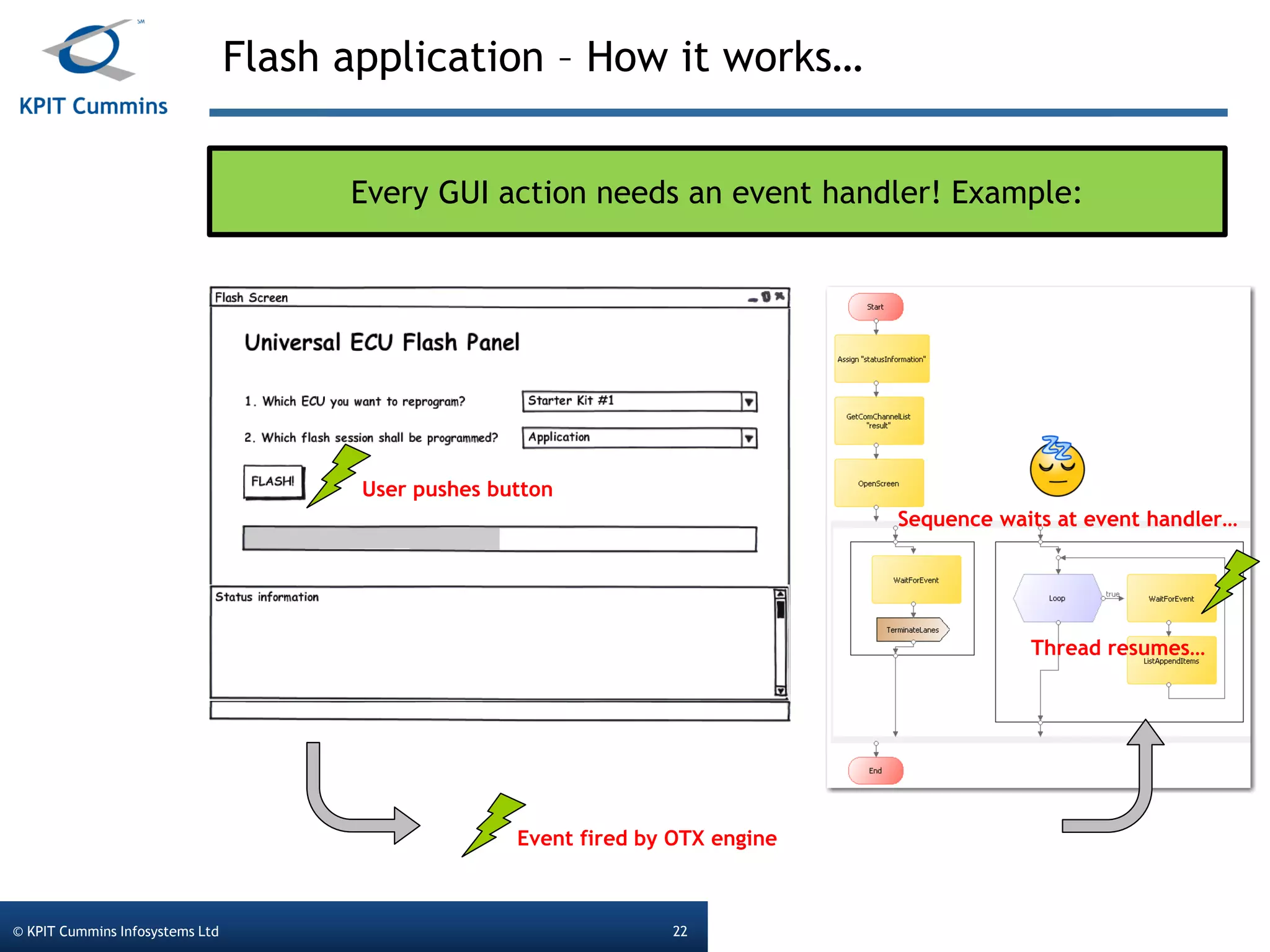
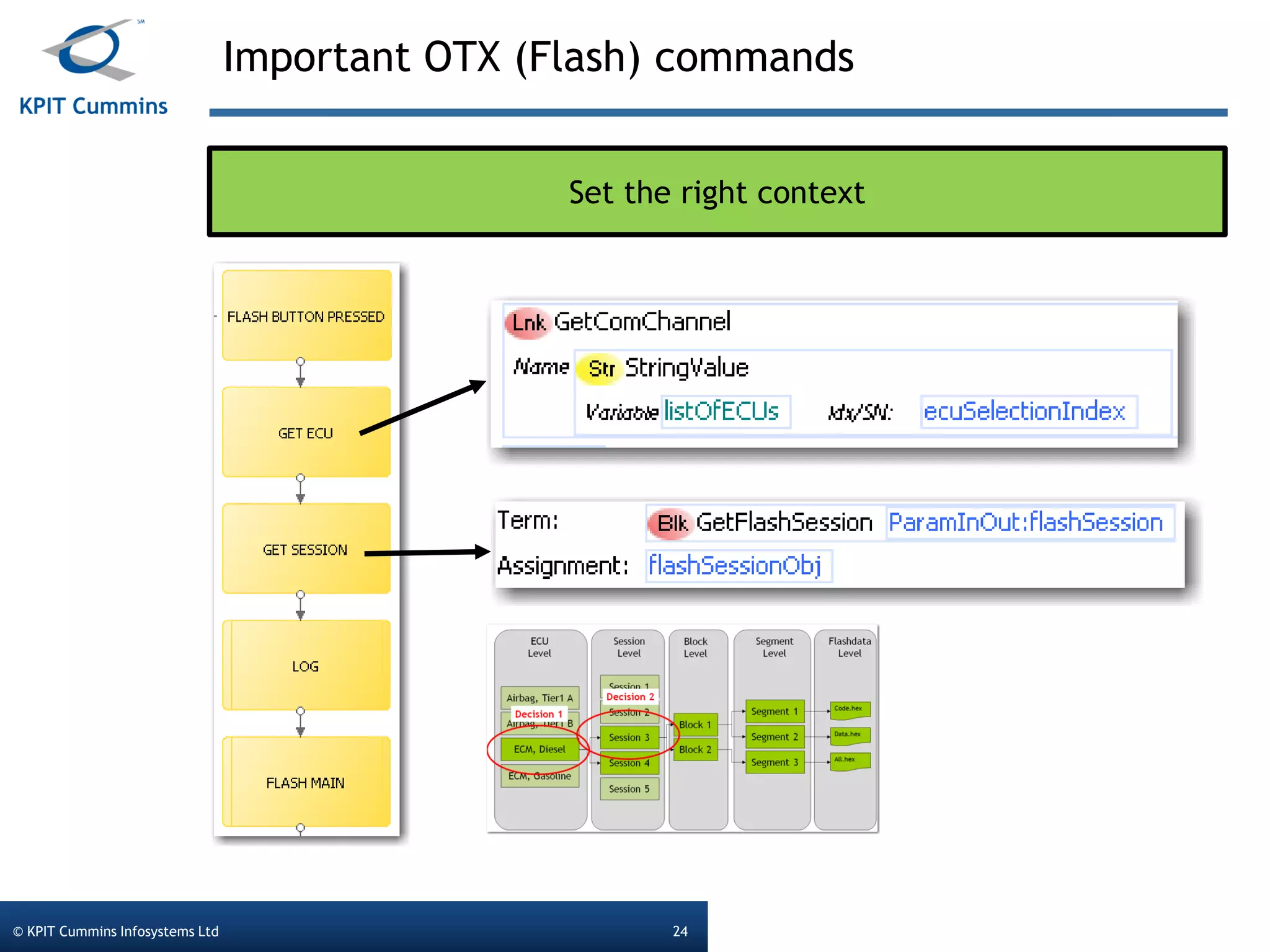
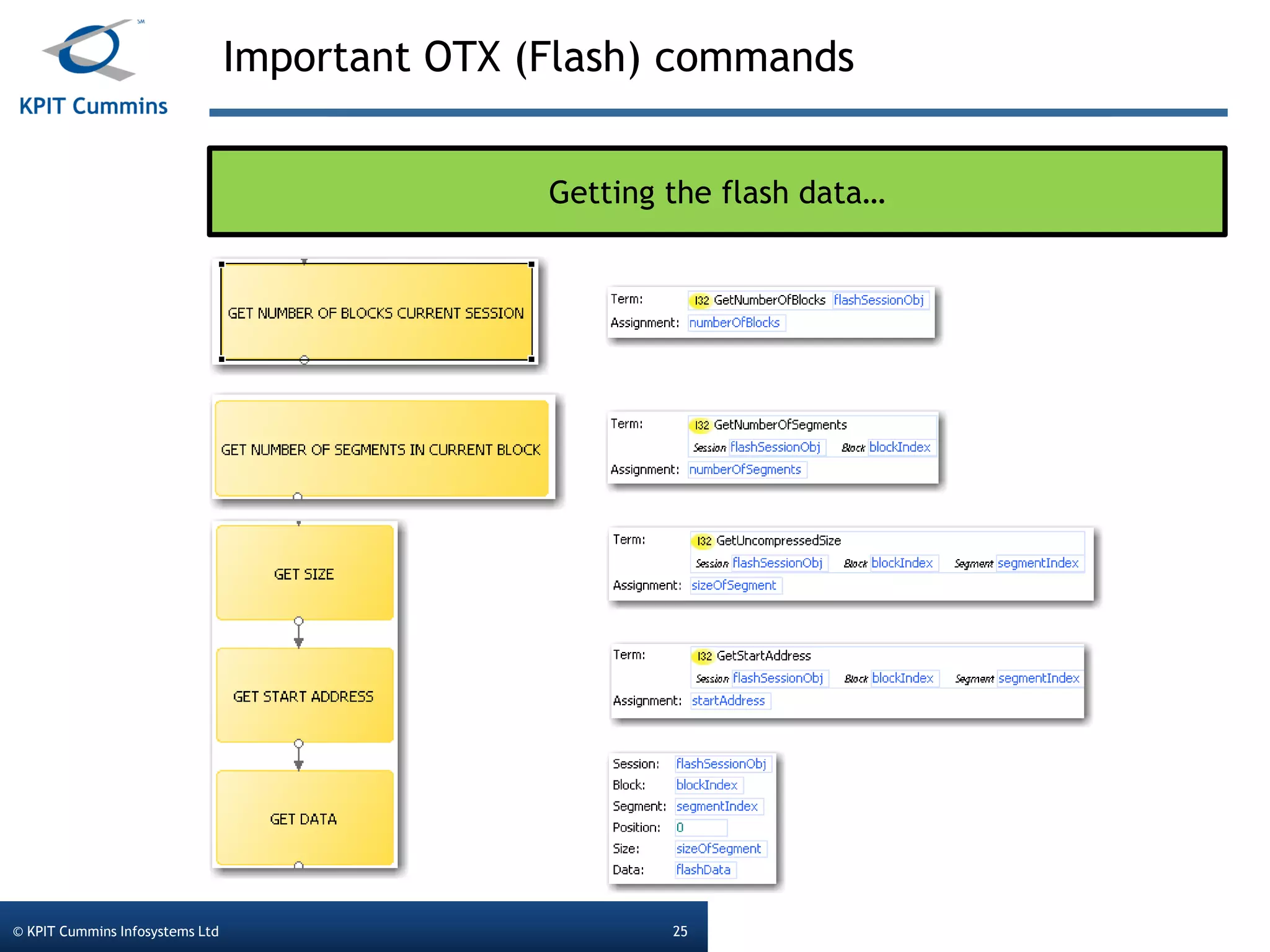
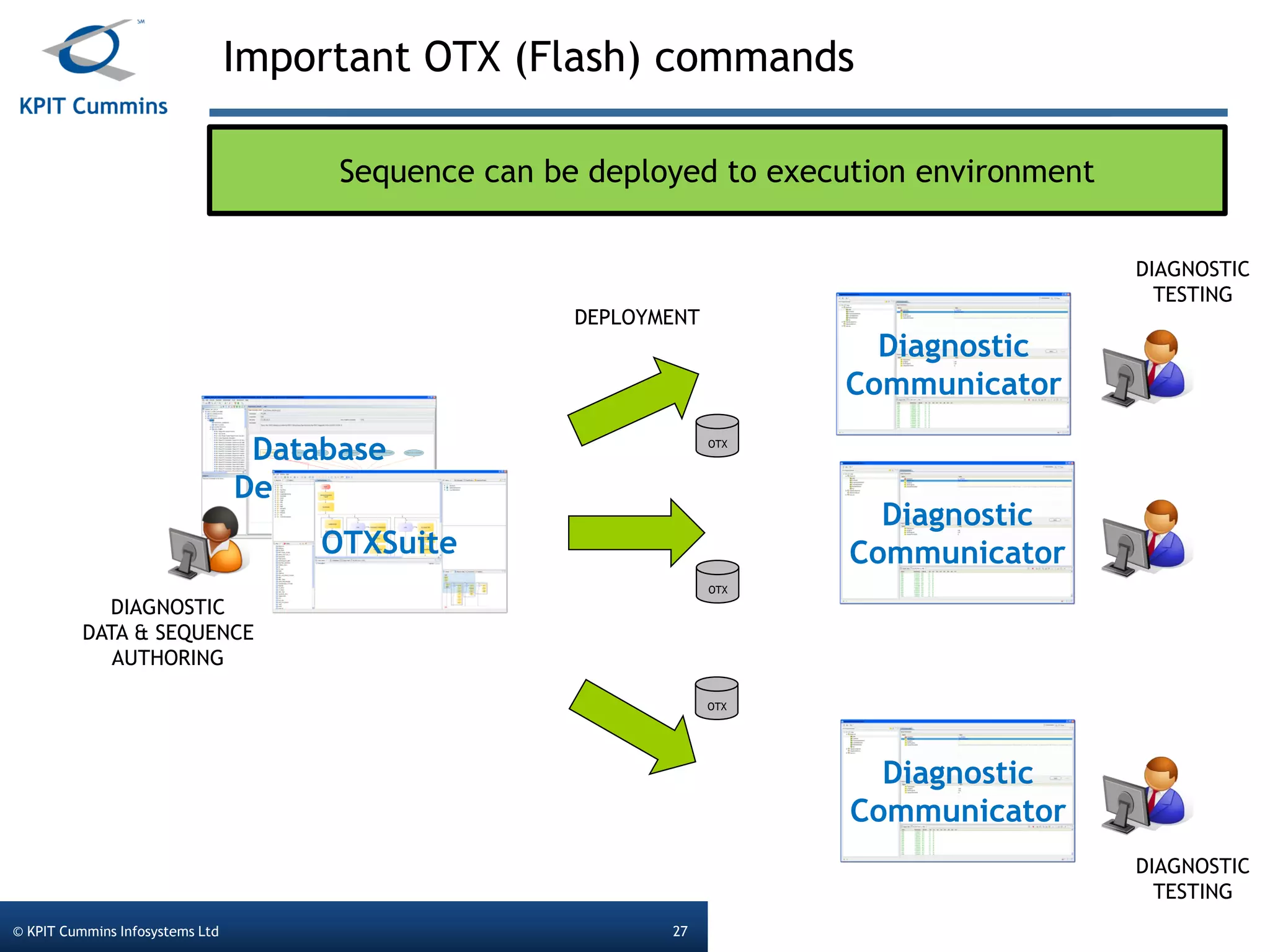
The document outlines a webinar on a diagnostic flash application introduced by KPIT Cummins Infosystems, highlighting the evolution and goals of diagnostic applications aimed at reducing dependency between tool vendors and users. It covers the architecture of the diagnostic toolchain, including various tools and protocols, as well as detailed steps on creating and deploying a flash application. Key topics include the organization of flash data, GUI design processes, and the handling of diagnostic commands.