Embed presentation
Download to read offline


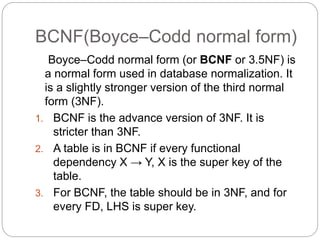
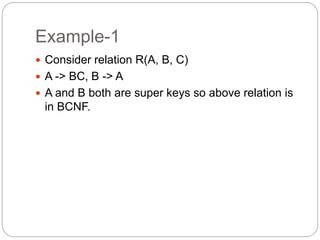


The document discusses Boyce-Codd normal form (BCNF), which is a normal form used in database normalization that is stricter than third normal form (3NF). A table is in BCNF if every functional dependency has a left-hand side that is a super key of the table. Three examples are provided to illustrate the concept: an example of a relation in BCNF, an example of a relation not in BCNF because it violates 2NF, and an example of a relation in BCNF because the left-hand side of each functional dependency is a candidate key.






