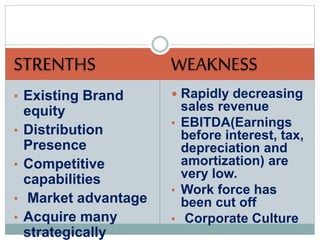
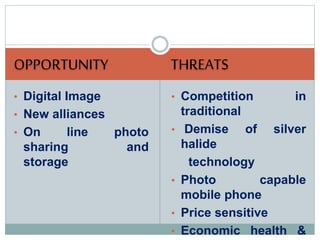
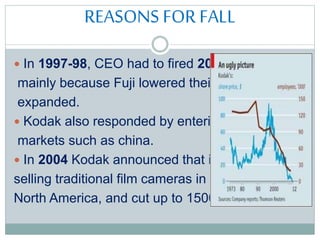
George Eastman founded Eastman Kodak in 1880, pioneering portable cameras and making photography accessible to the public. However, Kodak was slow to transition to digital photography in the late 20th century as technologies like digital cameras and camera-equipped smartphones became popular. By 2012, declining film sales and late entry into digital caused Kodak to file for bankruptcy and exit the photography business altogether.