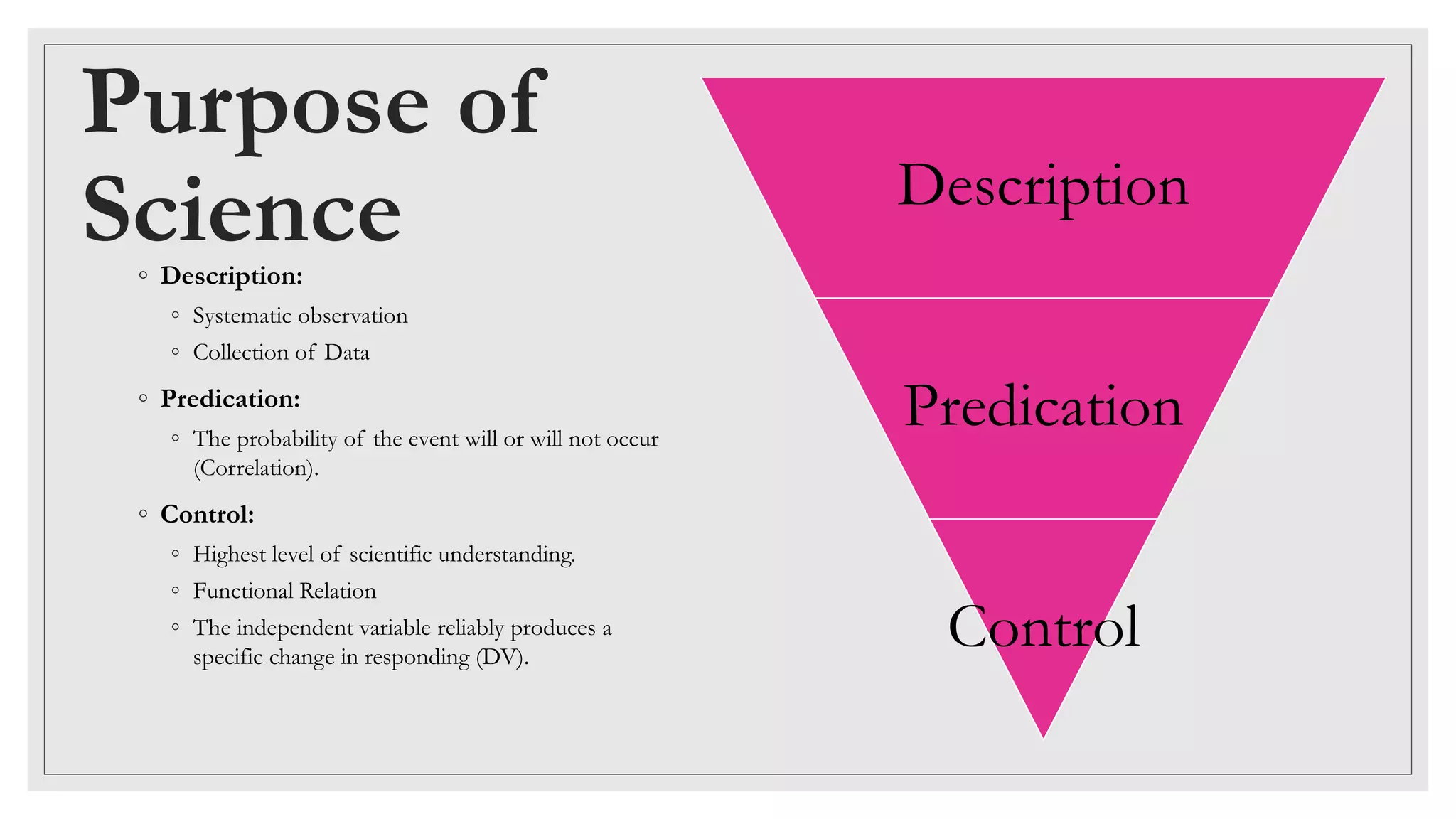
This document discusses the scientific method and applied behavior analysis. It defines science as involving description, prediction, and control based on systematic observation and data collection. Description involves observing and recording data, prediction involves determining what might happen based on correlations, and control involves demonstrating a functional relationship where a change in an independent variable reliably causes a change in a dependent variable. The document provides an example of using description, prediction, and control to determine if a found baby animal is a mammal or bird by observing its characteristics, predicting what it might need based on those characteristics, and testing those predictions by providing appropriate food and observing the response.