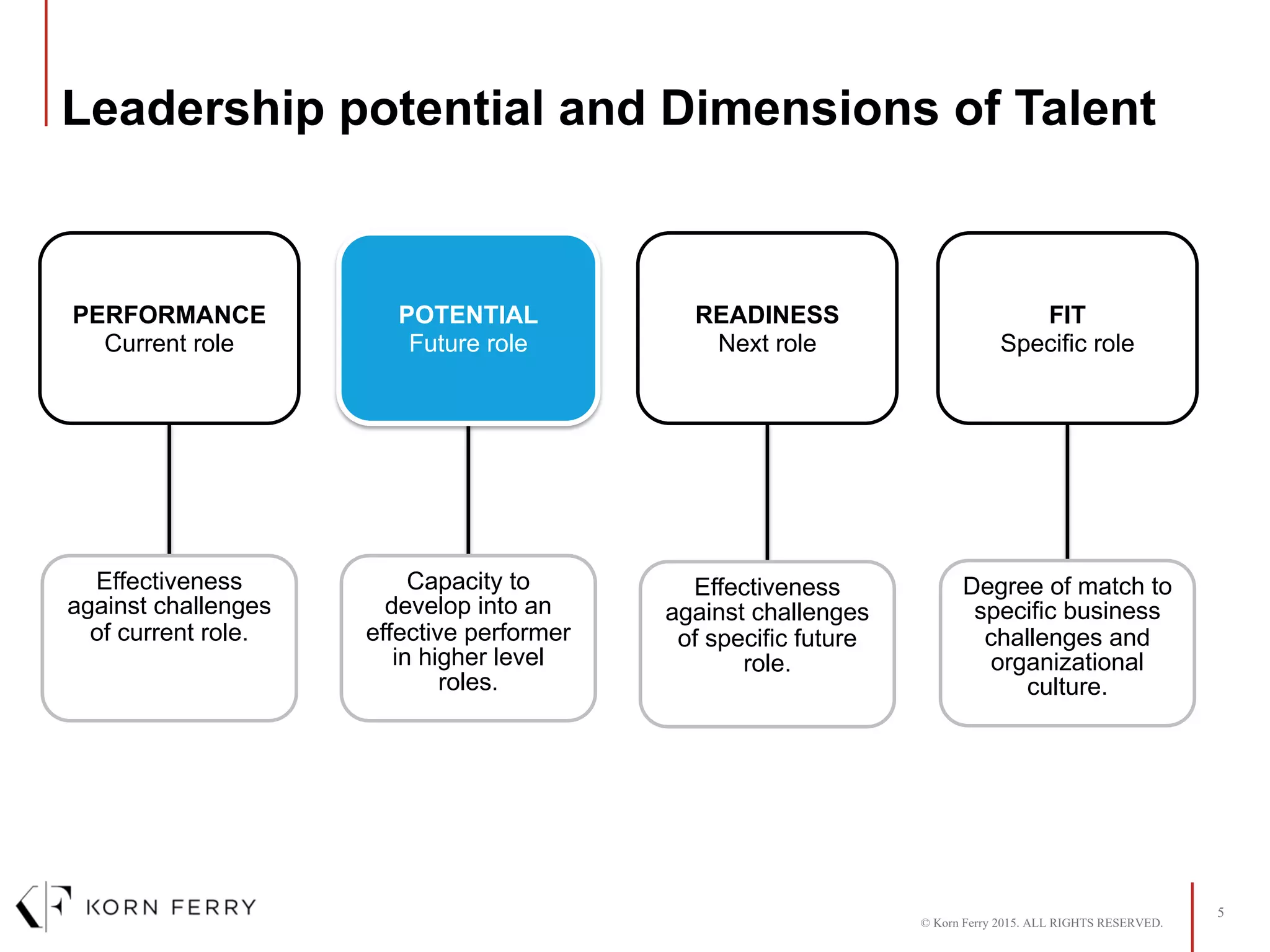
The document provides an overview of Korn Ferry's Assessment of Leadership Potential. The assessment evaluates an individual's leadership potential and readiness for more senior roles. It measures six signposts of leadership potential: drivers, experience, awareness, learning agility, leadership traits, and derailment risks. For each signpost, it assesses dimensions and provides the individual's results compared to target level leaders. The report identifies top development priorities and provides a summary to facilitate action planning.