Embed presentation
Downloaded 53 times




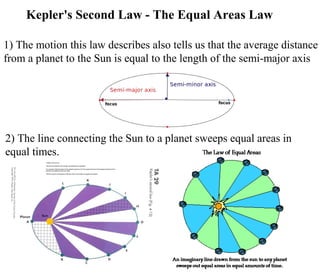

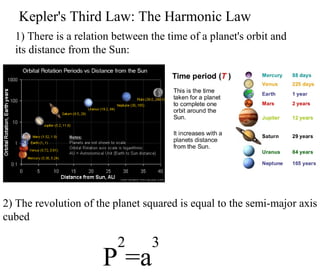
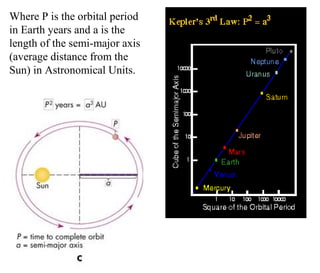
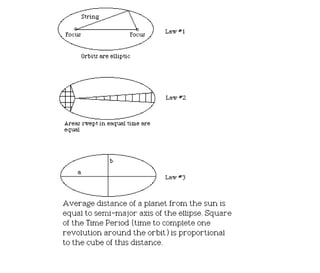
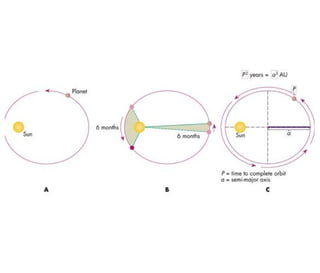

Kepler's laws describe the motion of planets: 1) Planets orbit the sun in ellipses with the sun at one focus. 2) A line connecting a planet to the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times. 3) The square of a planet's orbital period is proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis of its orbit.









