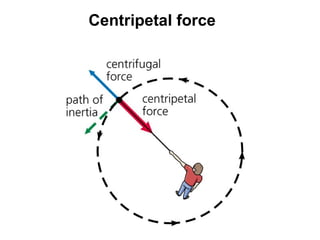
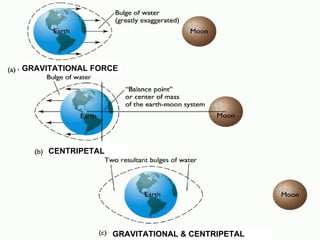
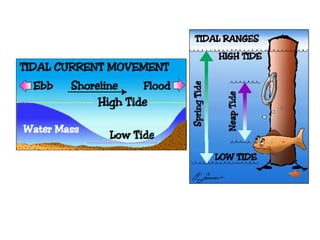
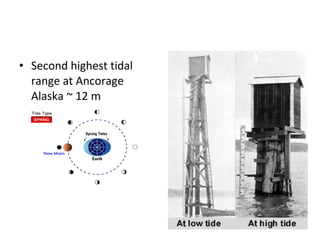
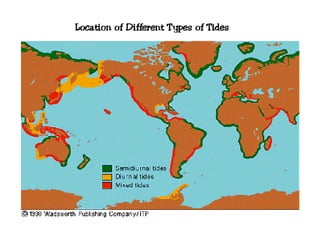
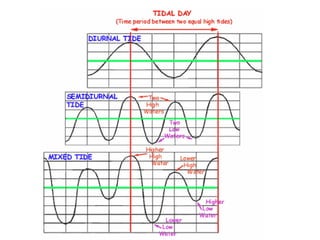
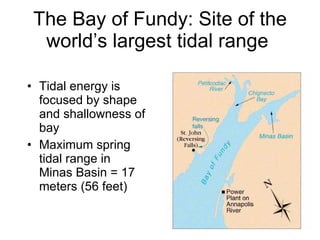
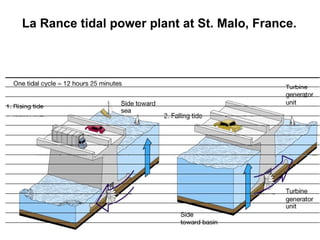
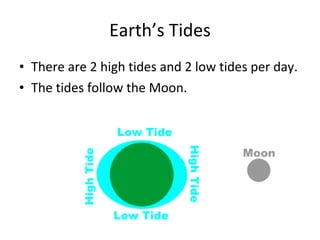
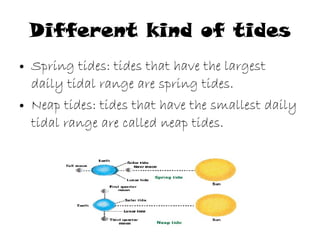
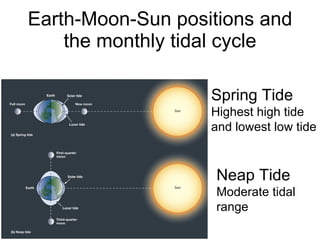
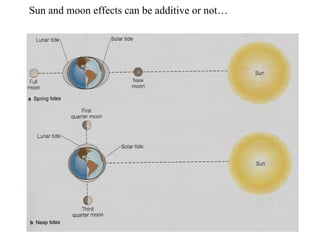
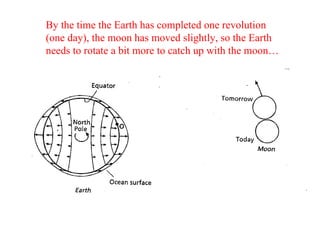
Tides are caused by the gravitational pull of the moon and sun on the Earth's oceans. This causes two high tides and two low tides each day as the Earth rotates. The difference between high and low tides is known as the tidal range, which varies depending on the positions of the moon and sun. Spring tides occur during a full moon or new moon when the sun and moon are aligned, producing the highest tides and greatest tidal range. Neap tides occur during half moons when the sun and moon are at right angles, producing the lowest tides and smallest tidal range.