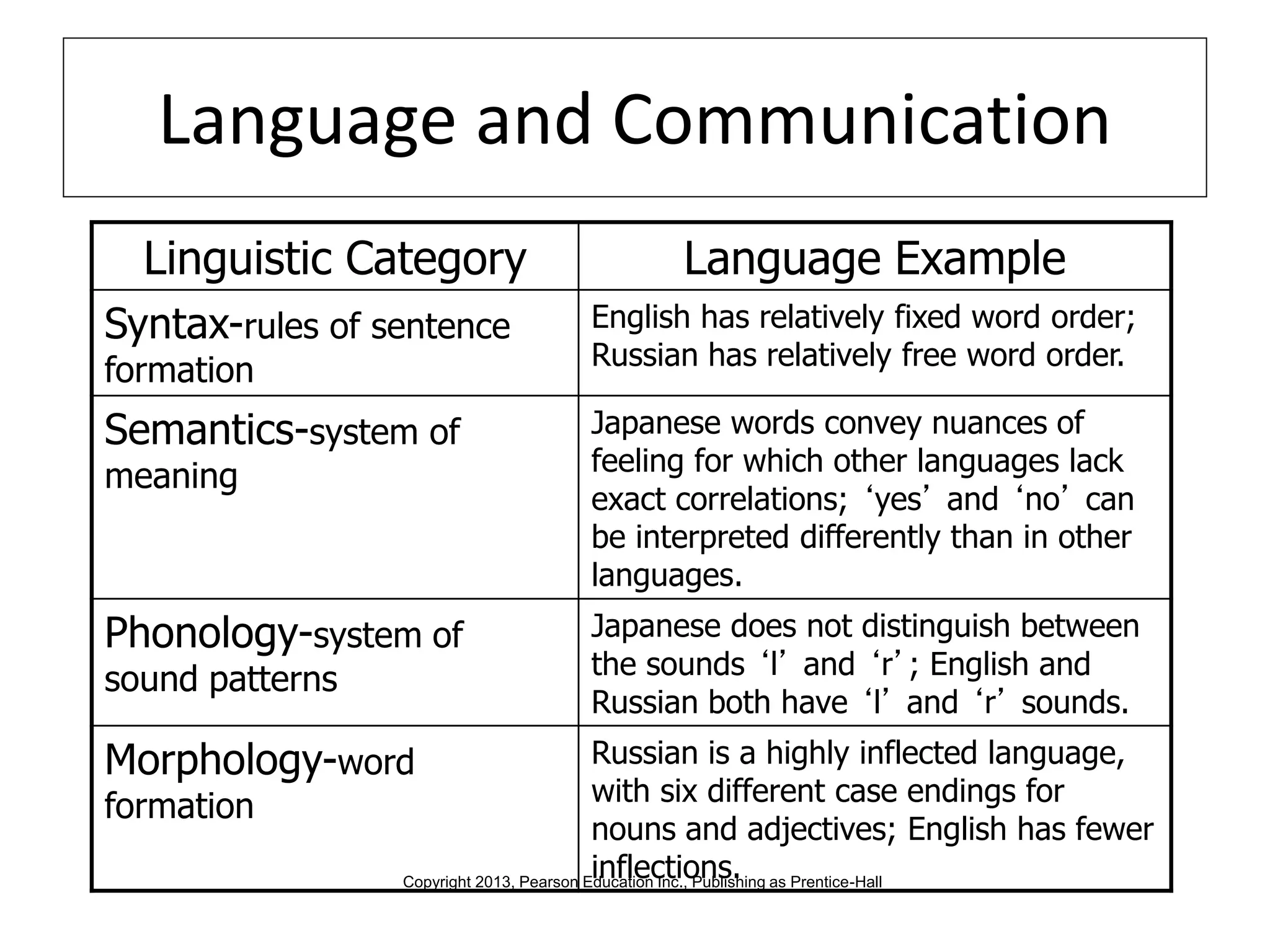
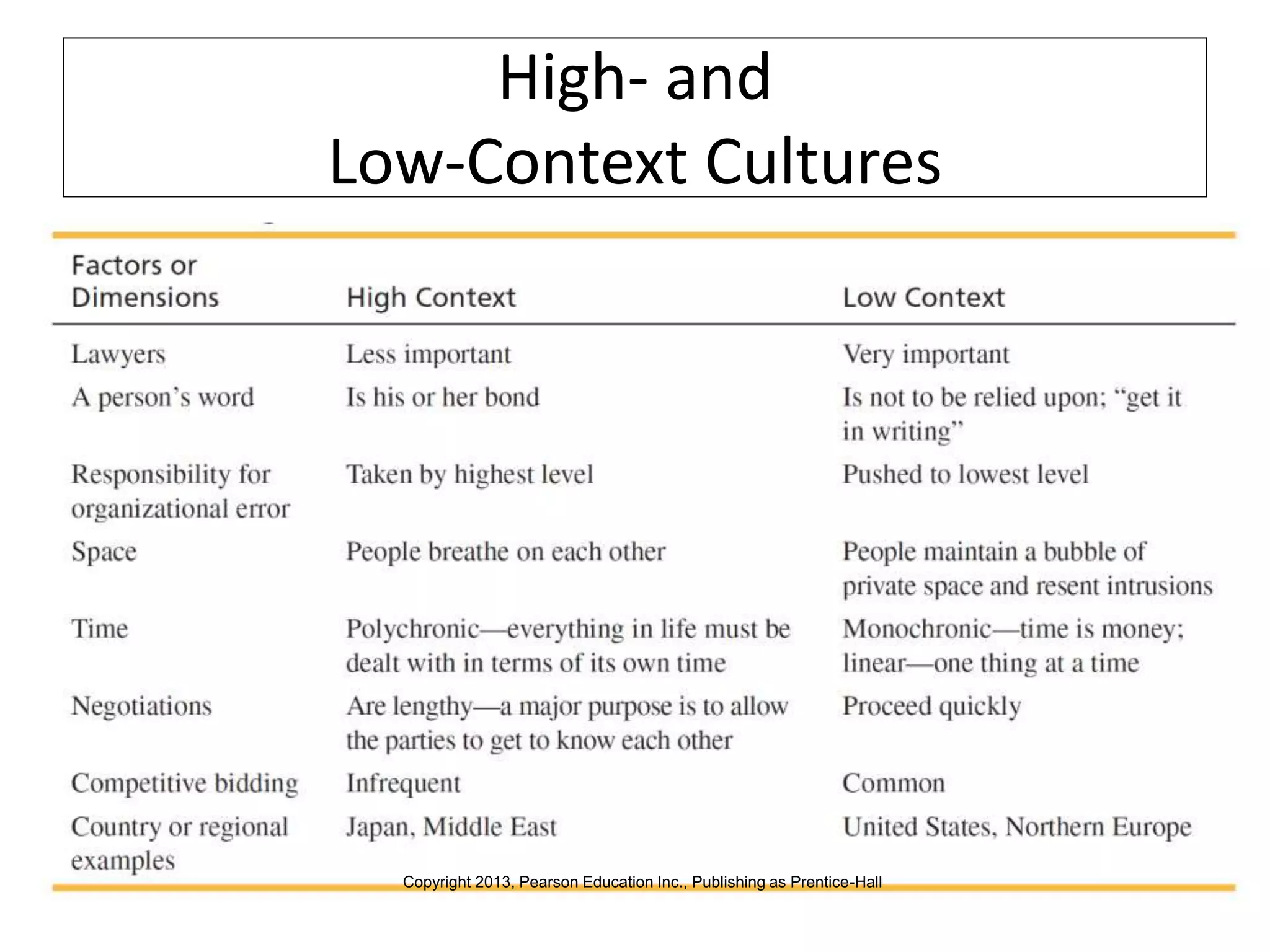
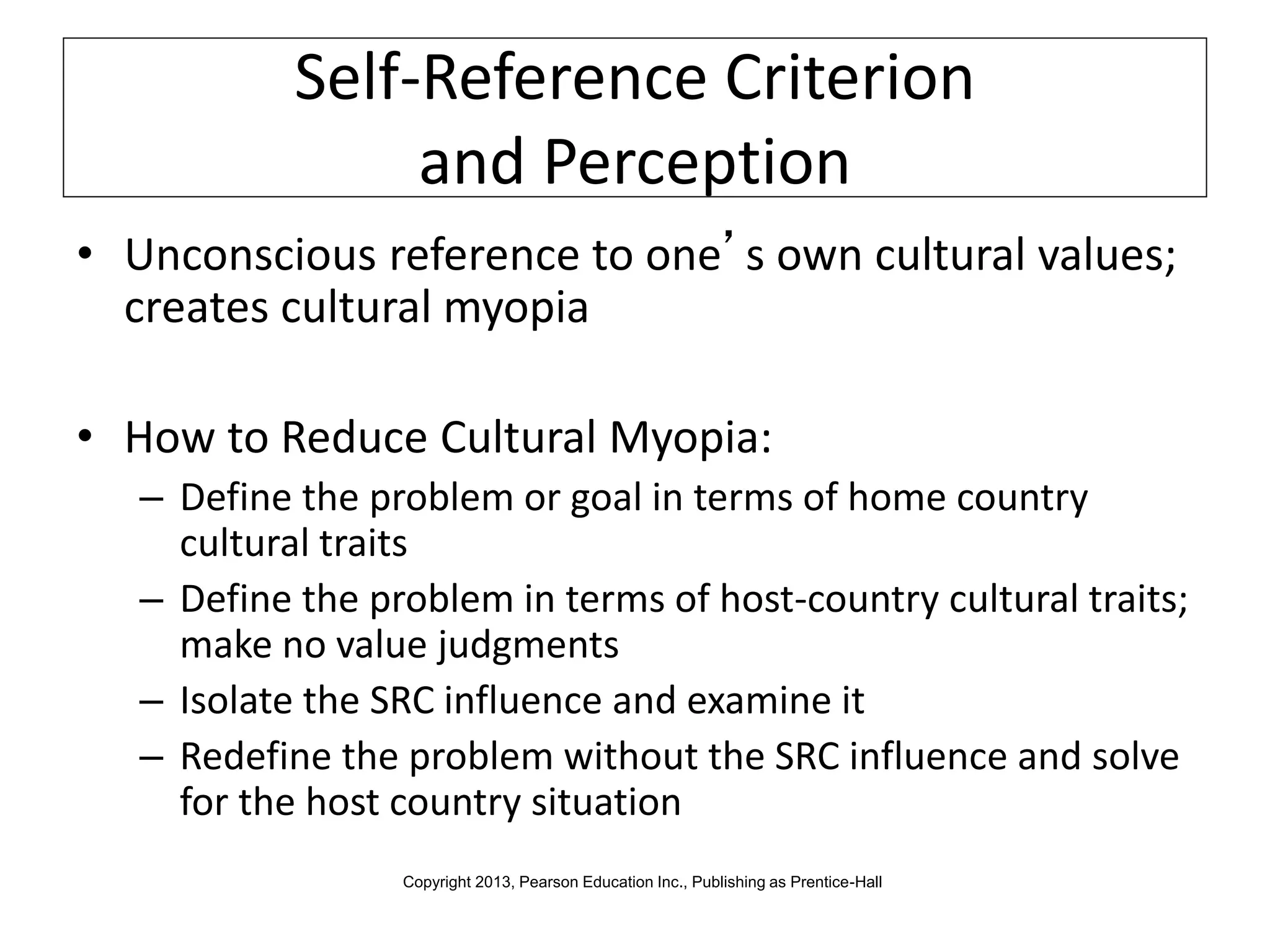
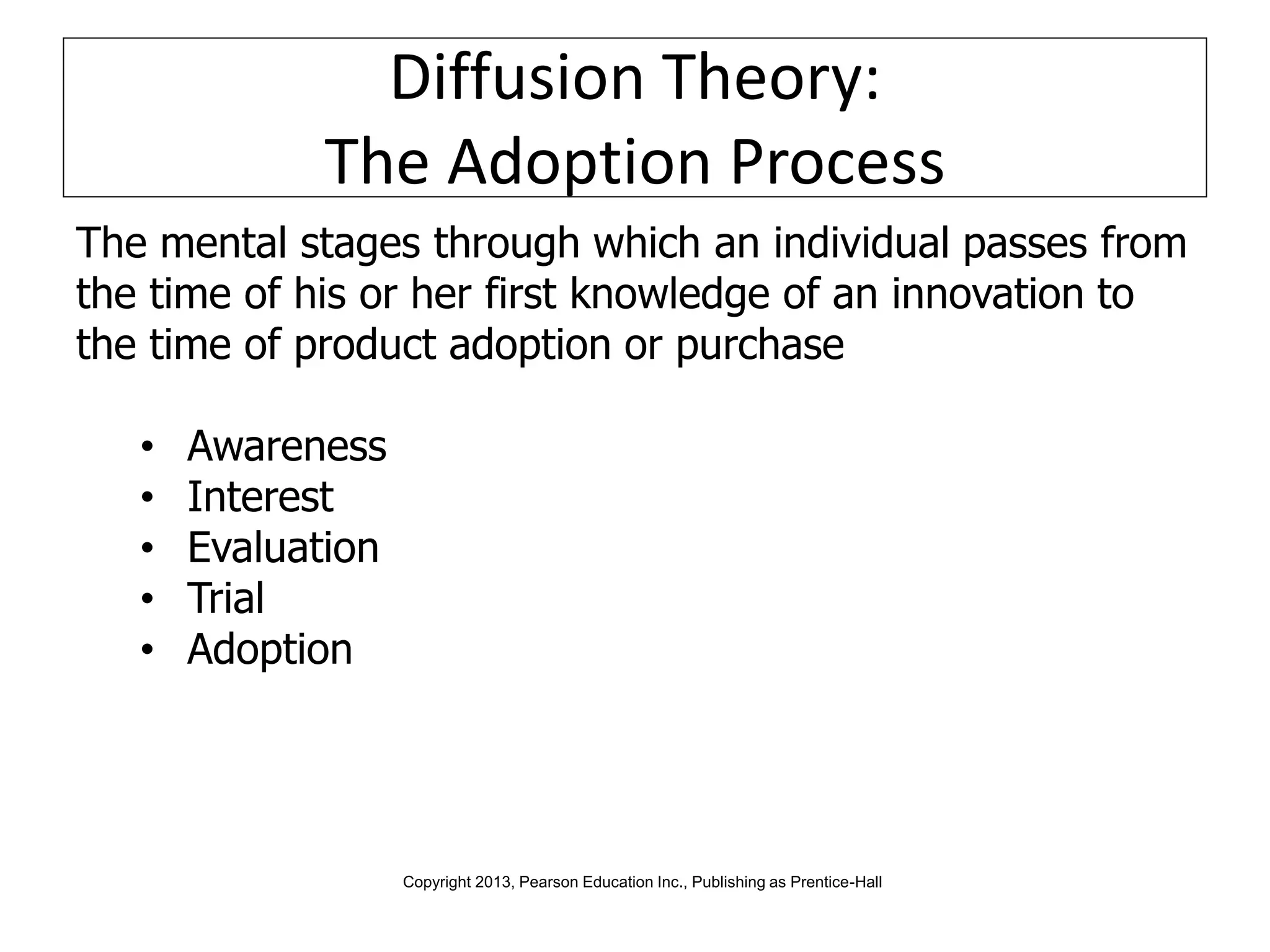
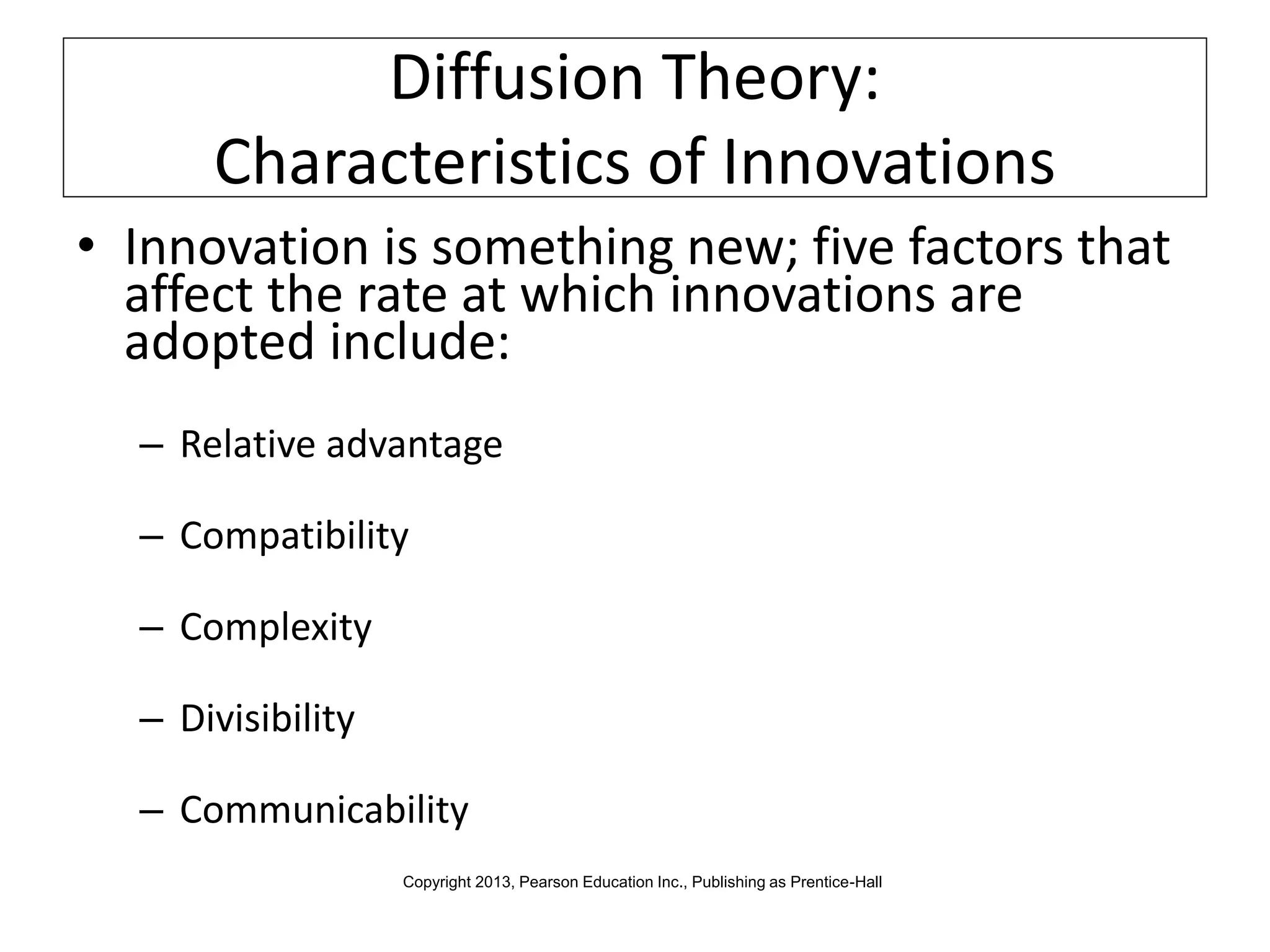
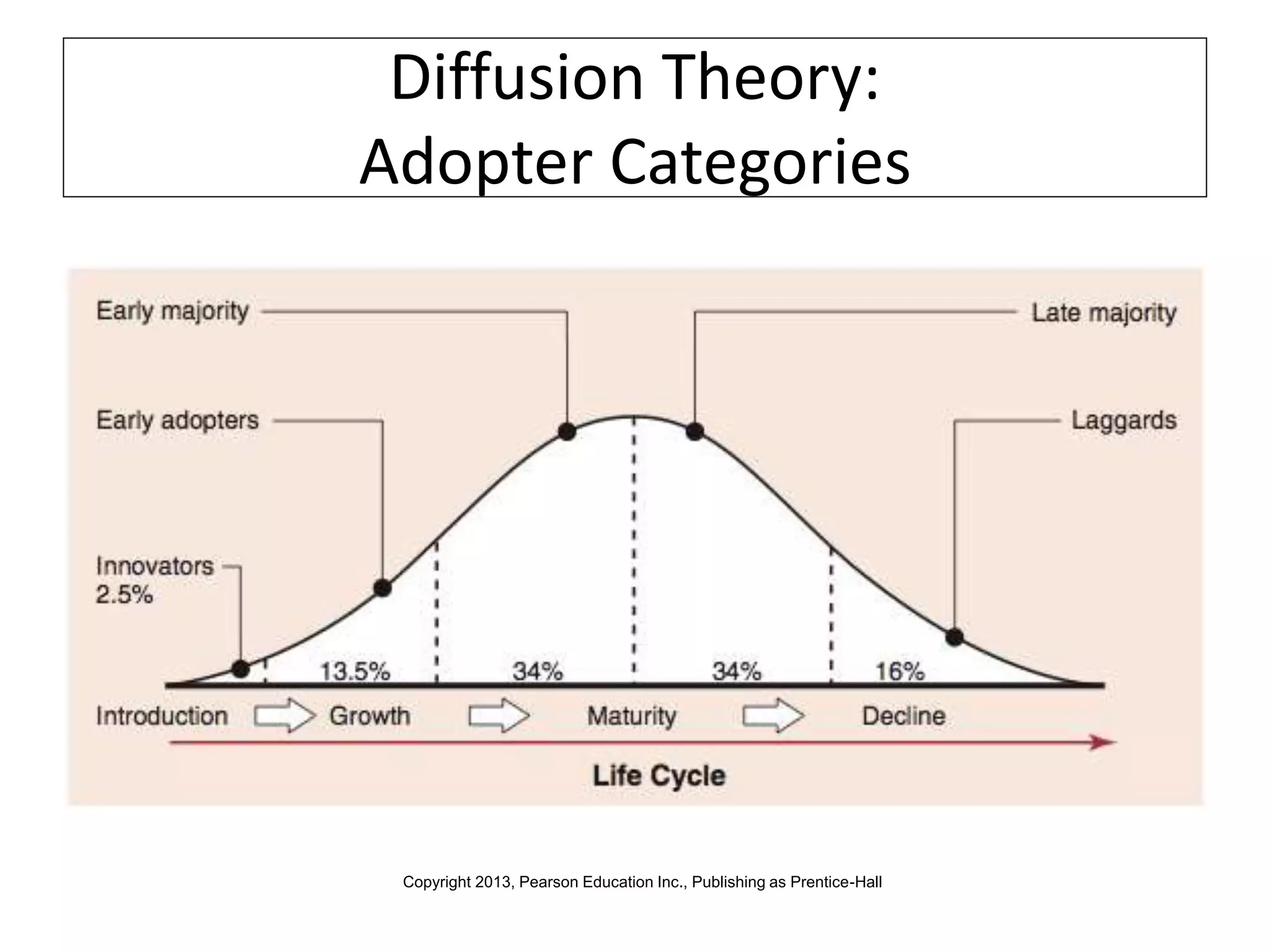
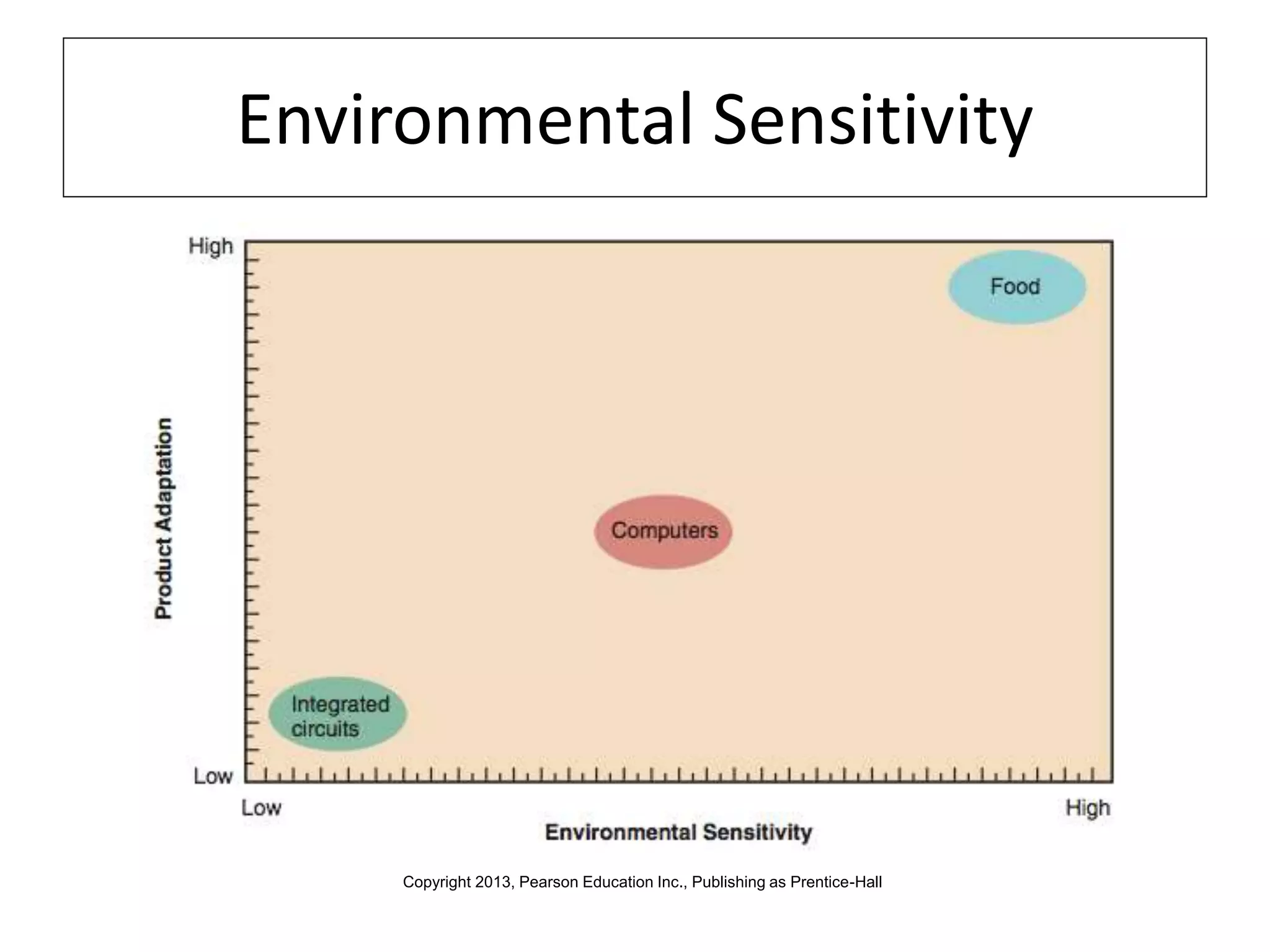
Global marketers must study and understand the cultures of countries where they do business to avoid viewing those cultures through the lens of their own cultural values. Culture is comprised of both physical and nonphysical aspects like customs, religion, and attitudes that are shaped by social institutions and differ across societies. When marketing globally, firms must consider how cultural factors like context, values, aesthetics, language, and traditions can impact whether consumers adopt innovations.