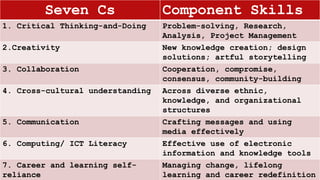
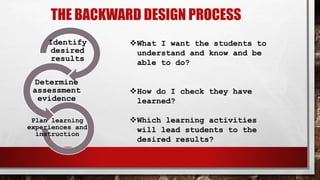
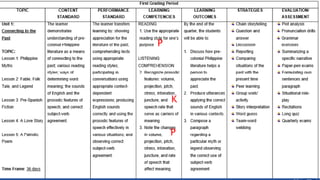
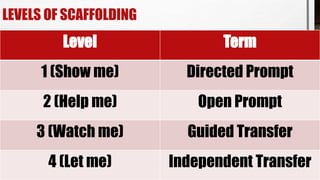
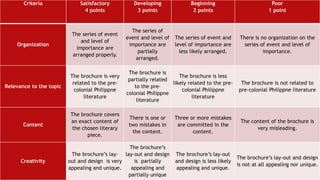
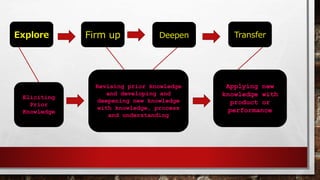
The document outlines the 'Seven Cs' of 21st-century lifelong skills, emphasizing critical thinking, creativity, collaboration, cross-cultural understanding, communication, computing literacy, and career self-reliance. It also details a backward design process for education, which includes identifying desired results, assessment evidence, and planning learning experiences, aimed at fostering students' understanding and application of pre-colonial Philippine literature and related competencies. Additionally, it includes performance tasks and criteria for assessing student outputs in the context of cultural heritage and literature.