The document provides information about grammar structures in English, including:
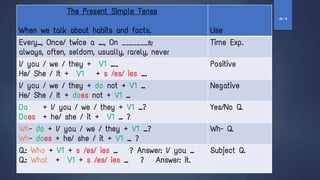
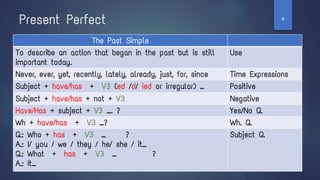
1. It discusses the present simple tense and how it is used to talk about habits and facts, and provides examples of its formation.
2. It explains the use of the verb "to be" in the present simple when describing something as a fact or general truth without an action verb.
3. It covers question formation, negatives, and exceptions in the present simple tense.
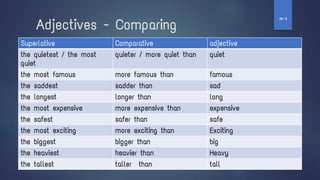
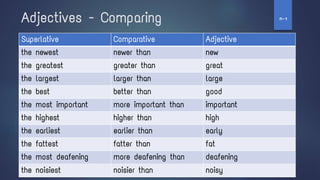
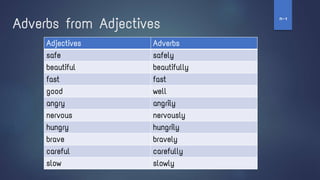
4. It also addresses the present progressive tense, stative verbs, the past simple tense, past progressive tense, adjectives and how to compare them, adverbs, the future simple with "be going to" and "will", modals and