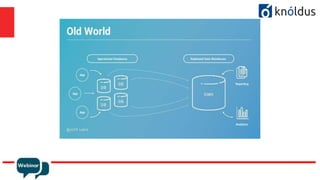
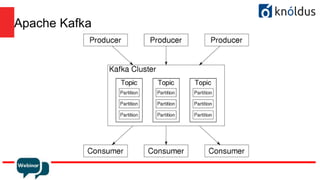
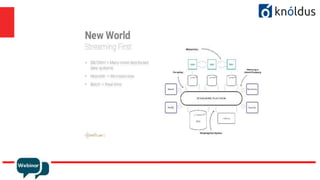
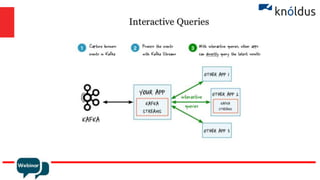
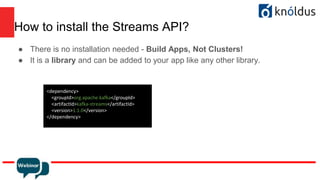
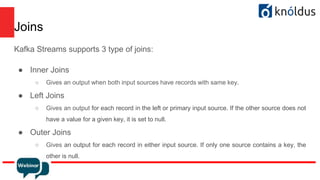
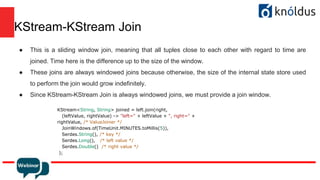
The document provides an introduction to Apache Kafka and its Streams API, discussing how to use the API and the types of join operations available. It details the distinctions between inner, left, outer joins, and various join types including kstream-kstream, ktable-ktable, kstream-ktable, and kstream-globalktable joins. Additionally, it outlines the installation requirements and offers references for further reading.