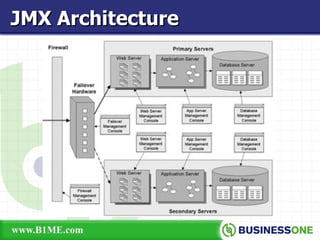
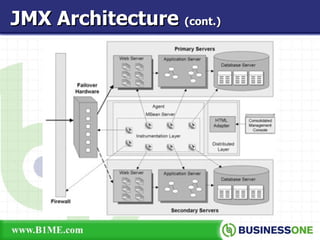
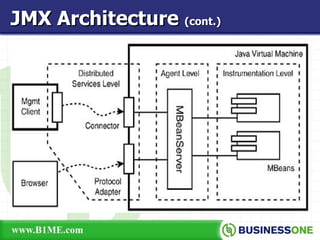
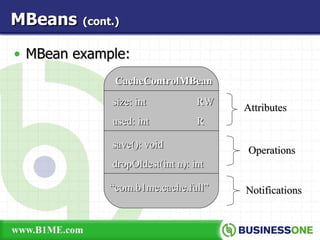
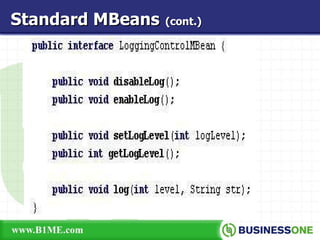
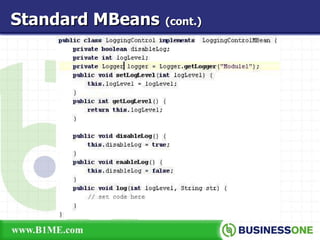
The document provides an overview of Java Management Extension (JMX), which is an API for managing Java applications. It describes key aspects of JMX including its architecture, MBeans, the MBean server, JMX agents, and remote access. It also discusses standard and third-party implementations and tools for JMX.