1) Extreme computing poses major challenges for suppliers related to concurrency, energy usage, data management, and system resiliency as systems increase in size and complexity.
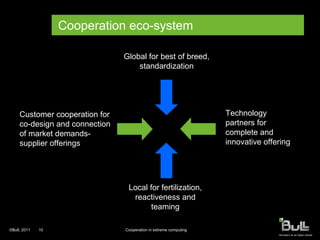
2) International cooperation is necessary to address these challenges as no single organization has a complete solution.
3) Bull promotes cooperation through partnerships, joint R&D labs, co-design with customers, and involvement in European programs like Systematic, Eureka, and FP7 to foster innovation.