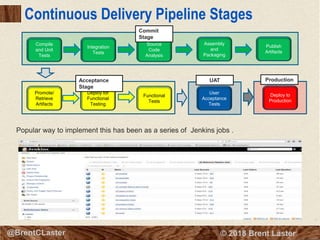
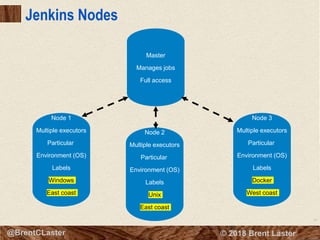
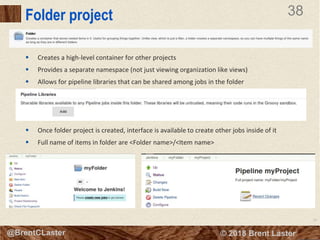
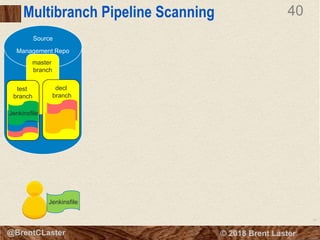
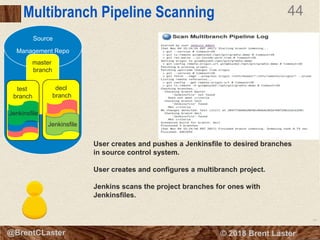
The document presents an overview of Jenkins 2 for automating continuous delivery pipelines, emphasizing key concepts such as continuous integration, delivery, and deployment. It discusses the structure of Jenkins, including its configuration, job management, and the Jenkins DSL for defining pipeline scripts. Additionally, it outlines the features of multibranch pipelines and the benefits of using Jenkins in software development practices.