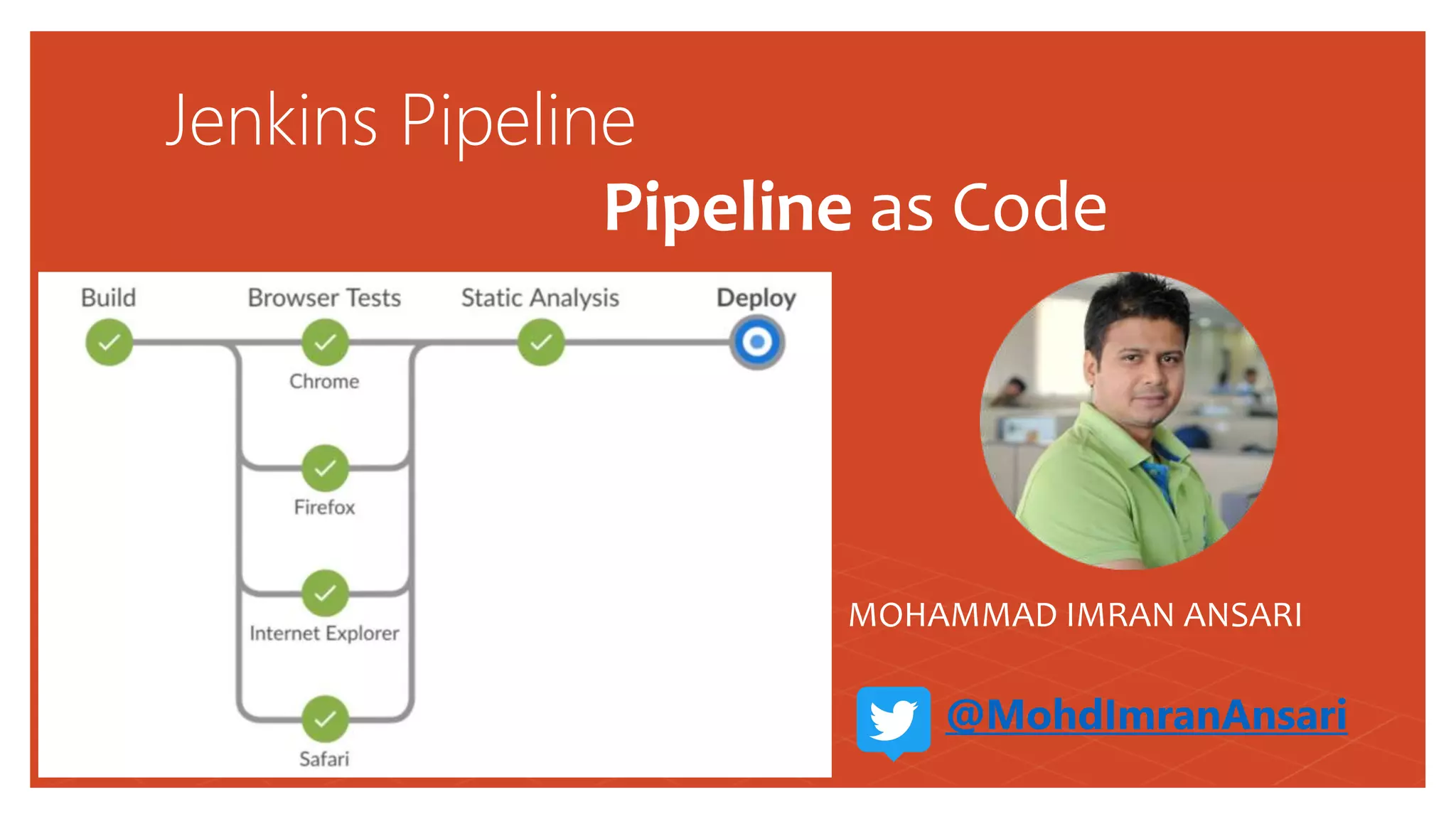
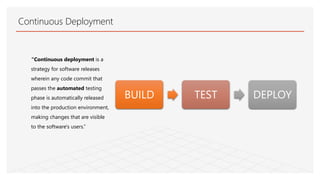
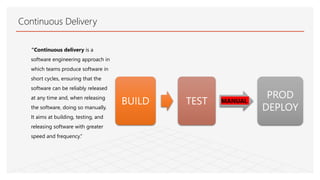
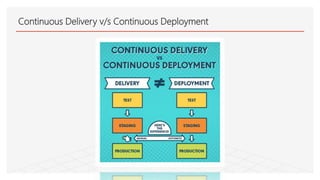
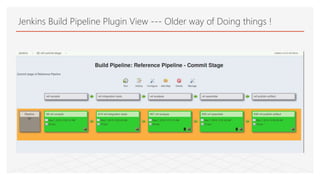
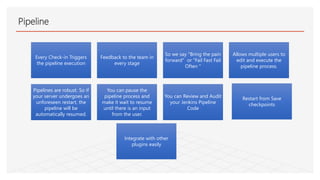
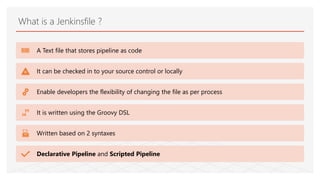
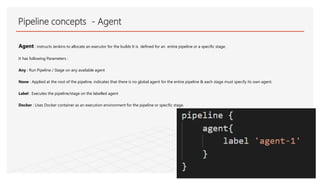
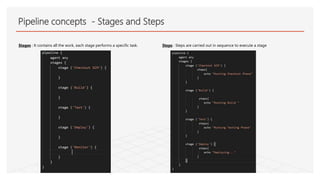
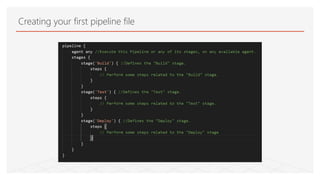
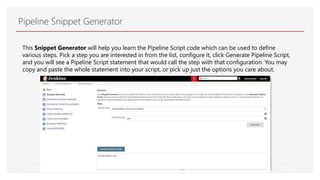
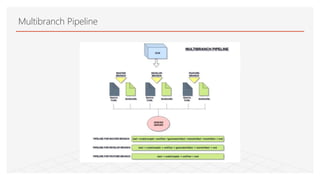
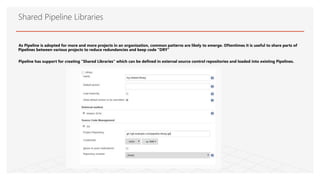
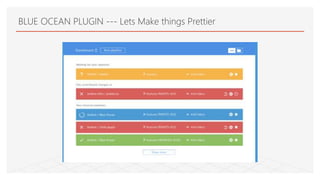
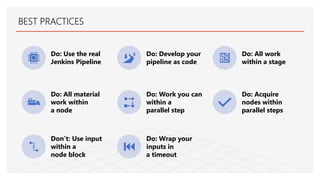
This document discusses Jenkins Pipeline and continuous integration/delivery practices. It defines continuous integration, continuous deployment, and continuous delivery. It also discusses the benefits of using Jenkins Pipeline including open source, plugins, integration with other tools, and treating code as pipeline. Key concepts discussed include Jenkinsfile, declarative vs scripted pipelines, stages, steps, and agents. It demonstrates creating a simple pipeline file and multibranch pipeline.