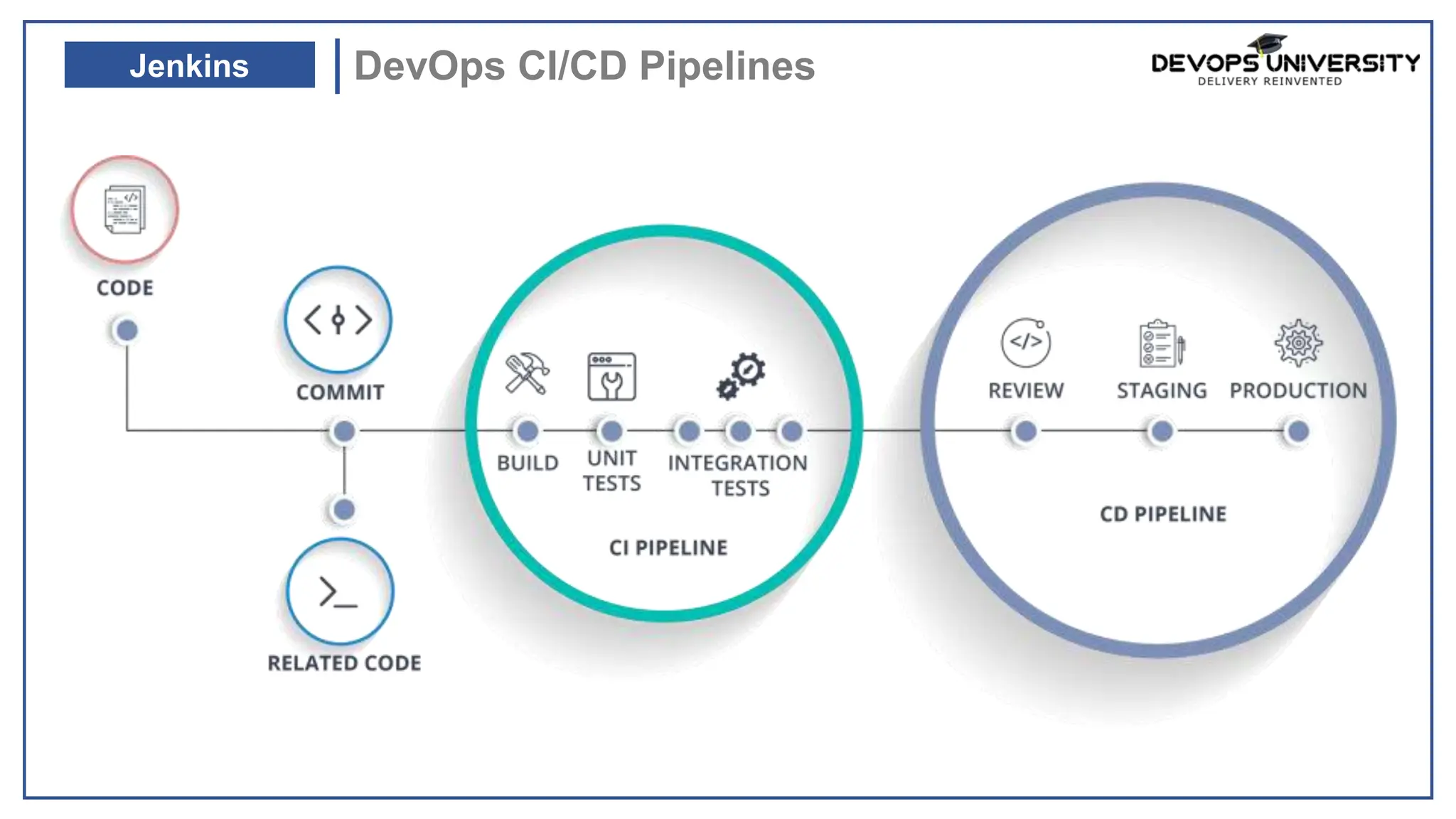
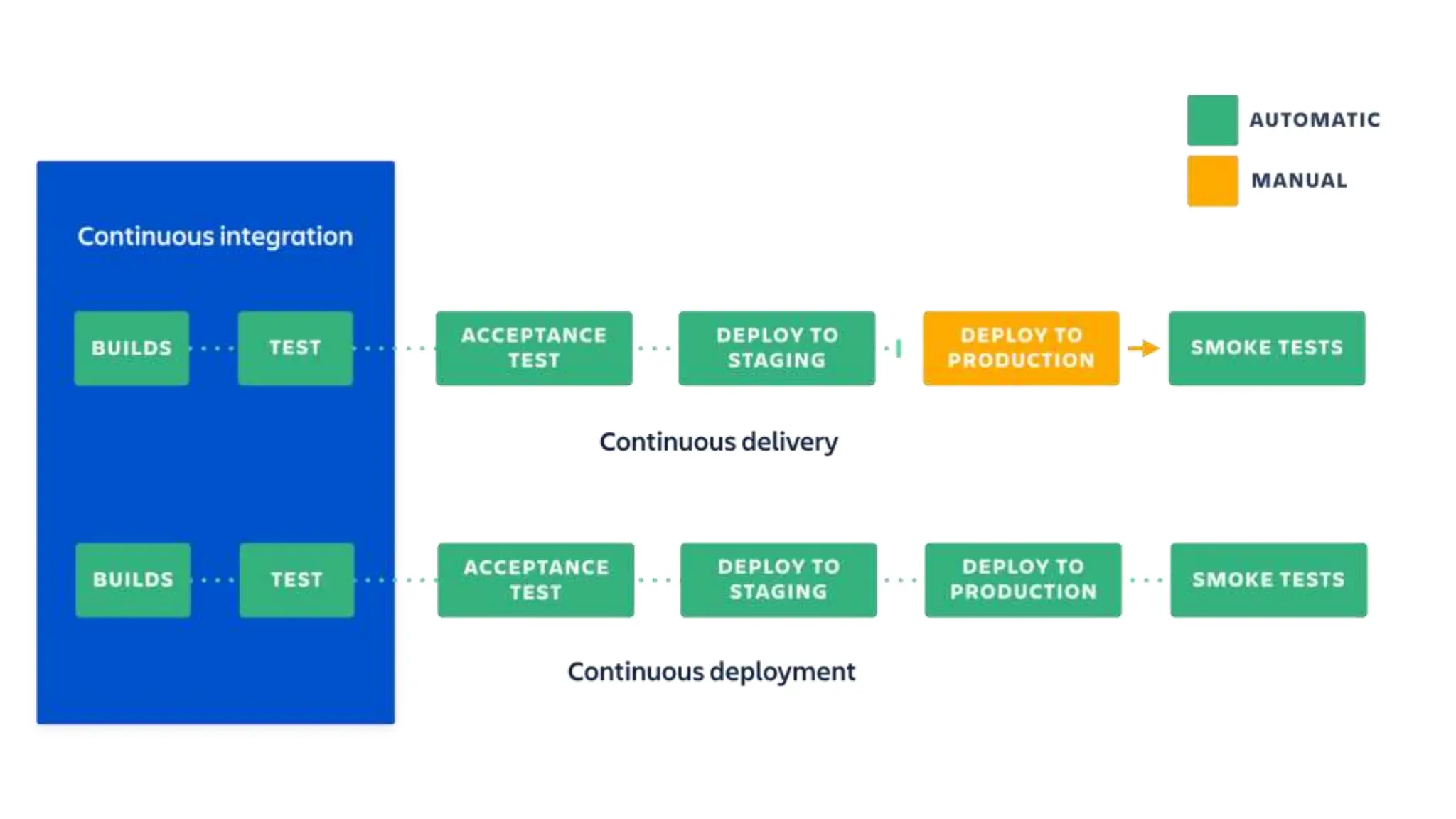
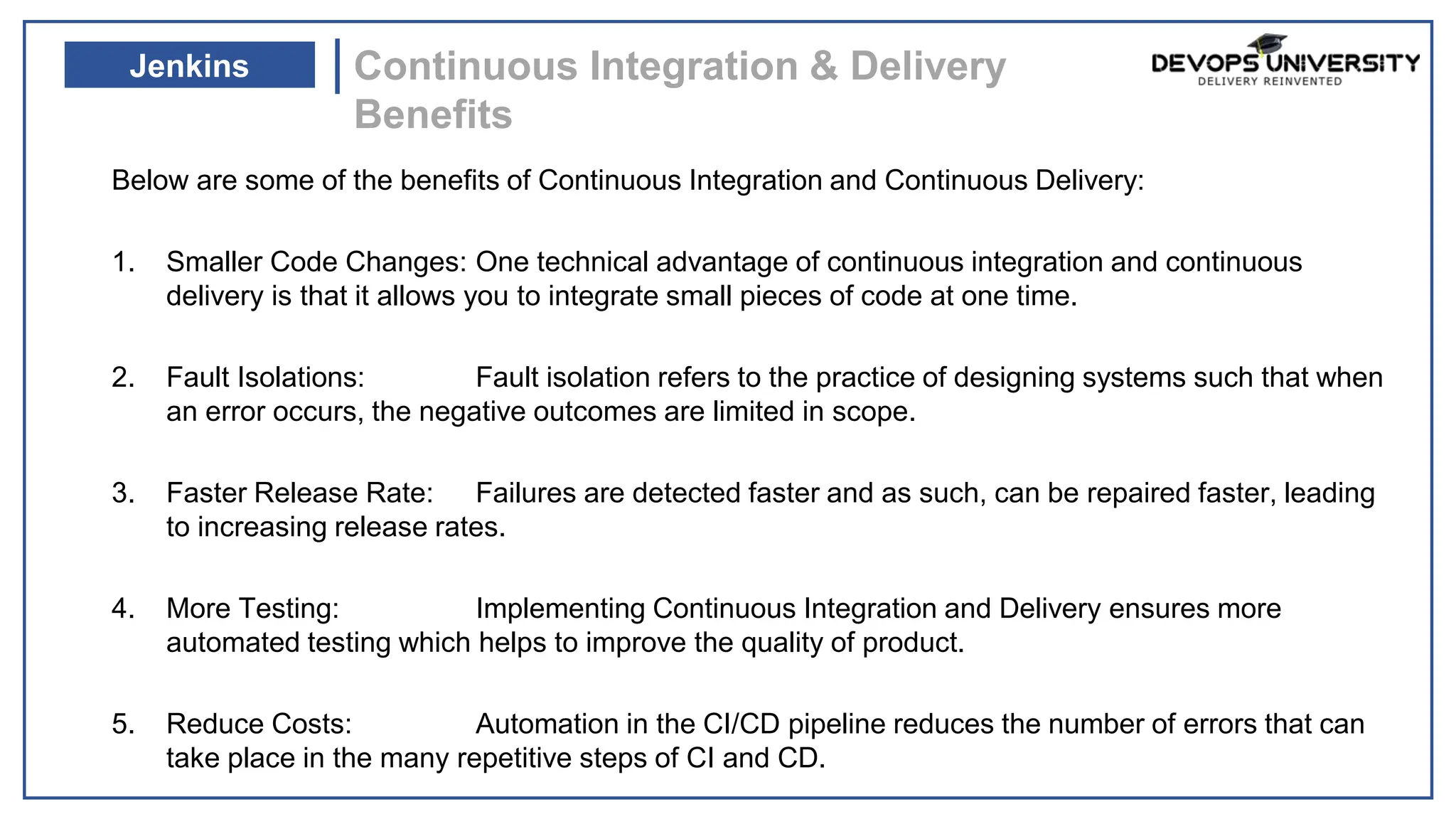
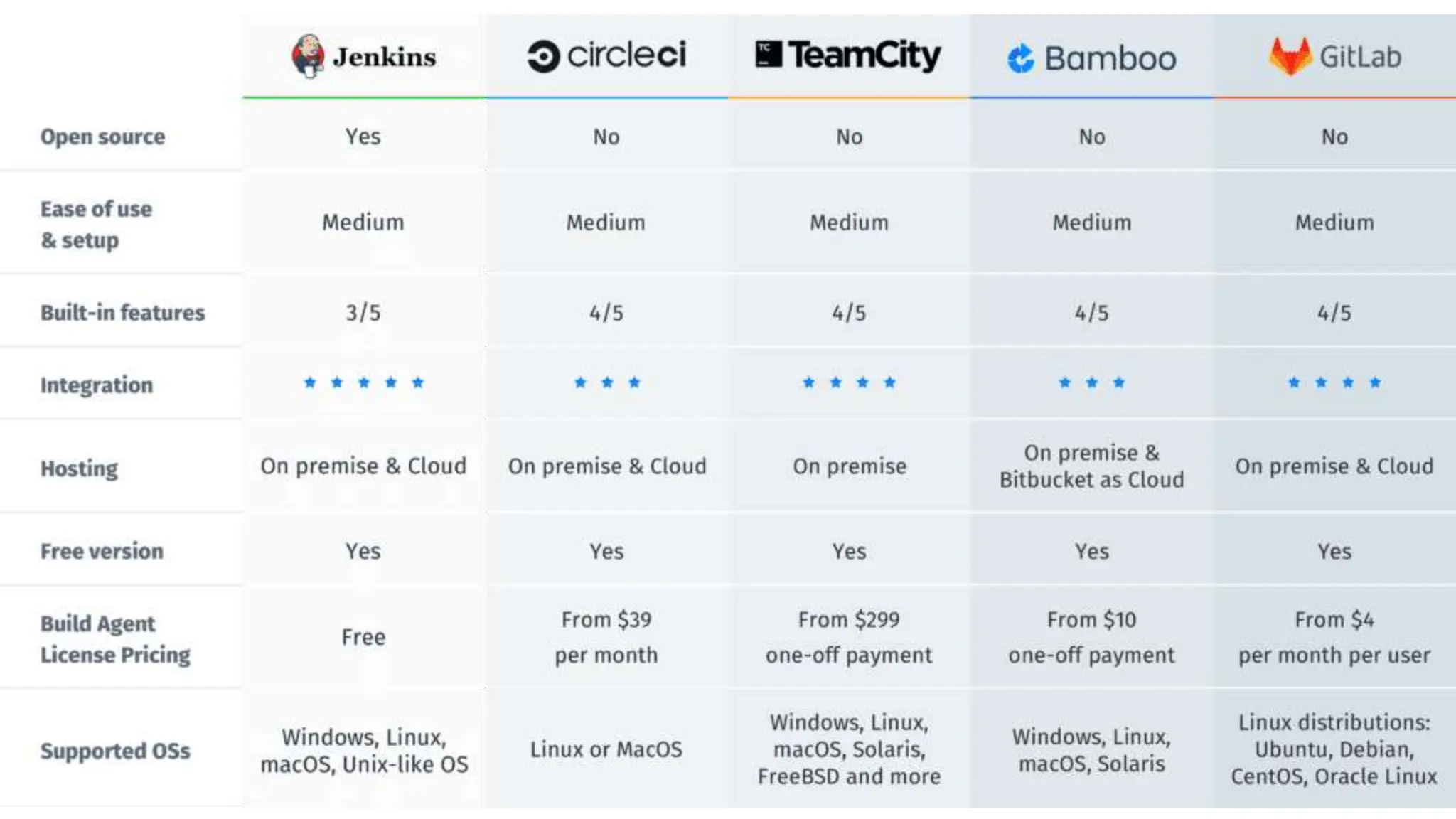
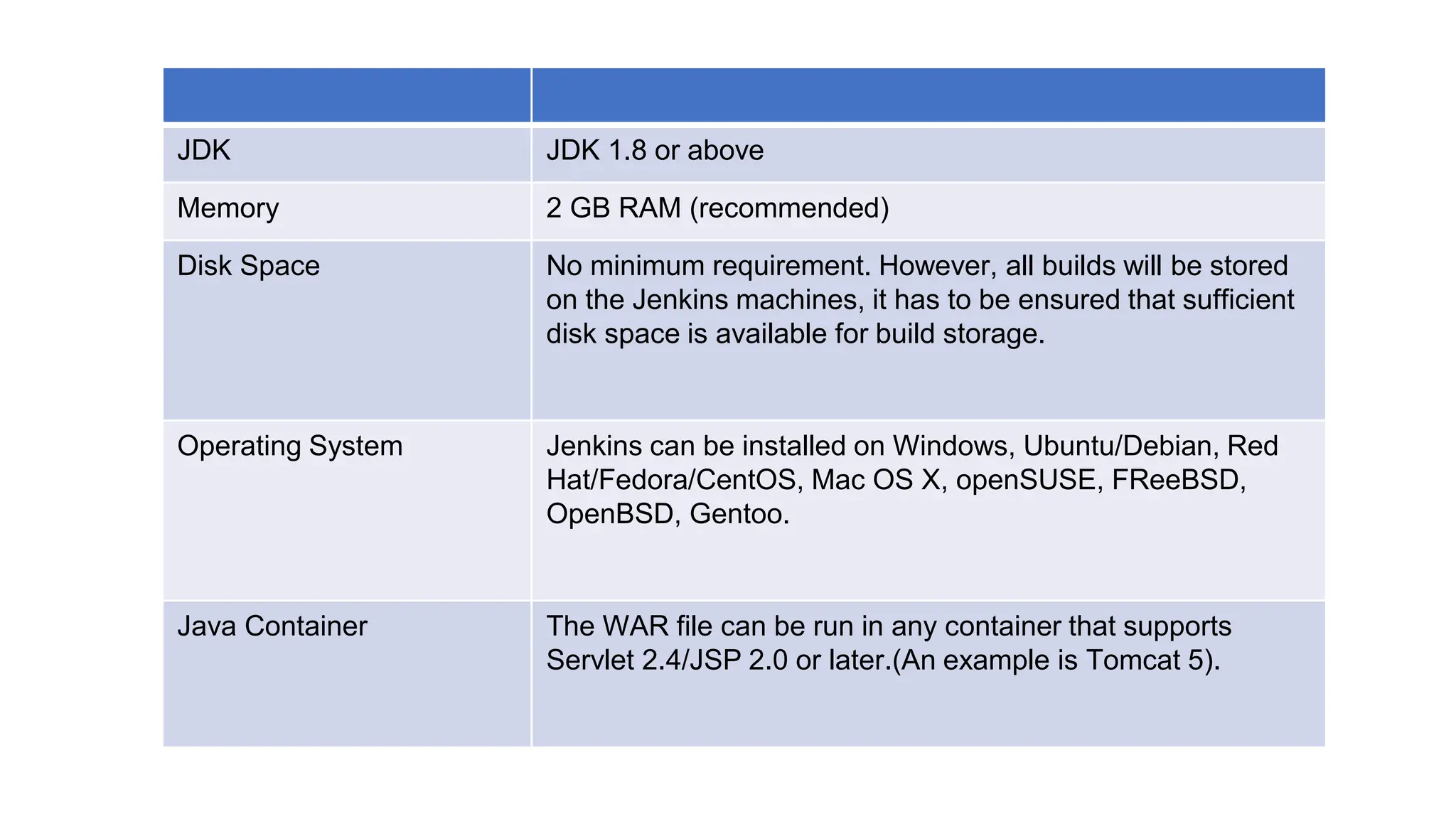
This document provides information about a DevOps University workshop on Continuous Integration. It includes details about topics covered in the workshop such as Maven, Jenkins, continuous integration, continuous delivery, and benefits. It also provides information on installing and configuring Jenkins, managing security in Jenkins, and commonly used Jenkins plugins.