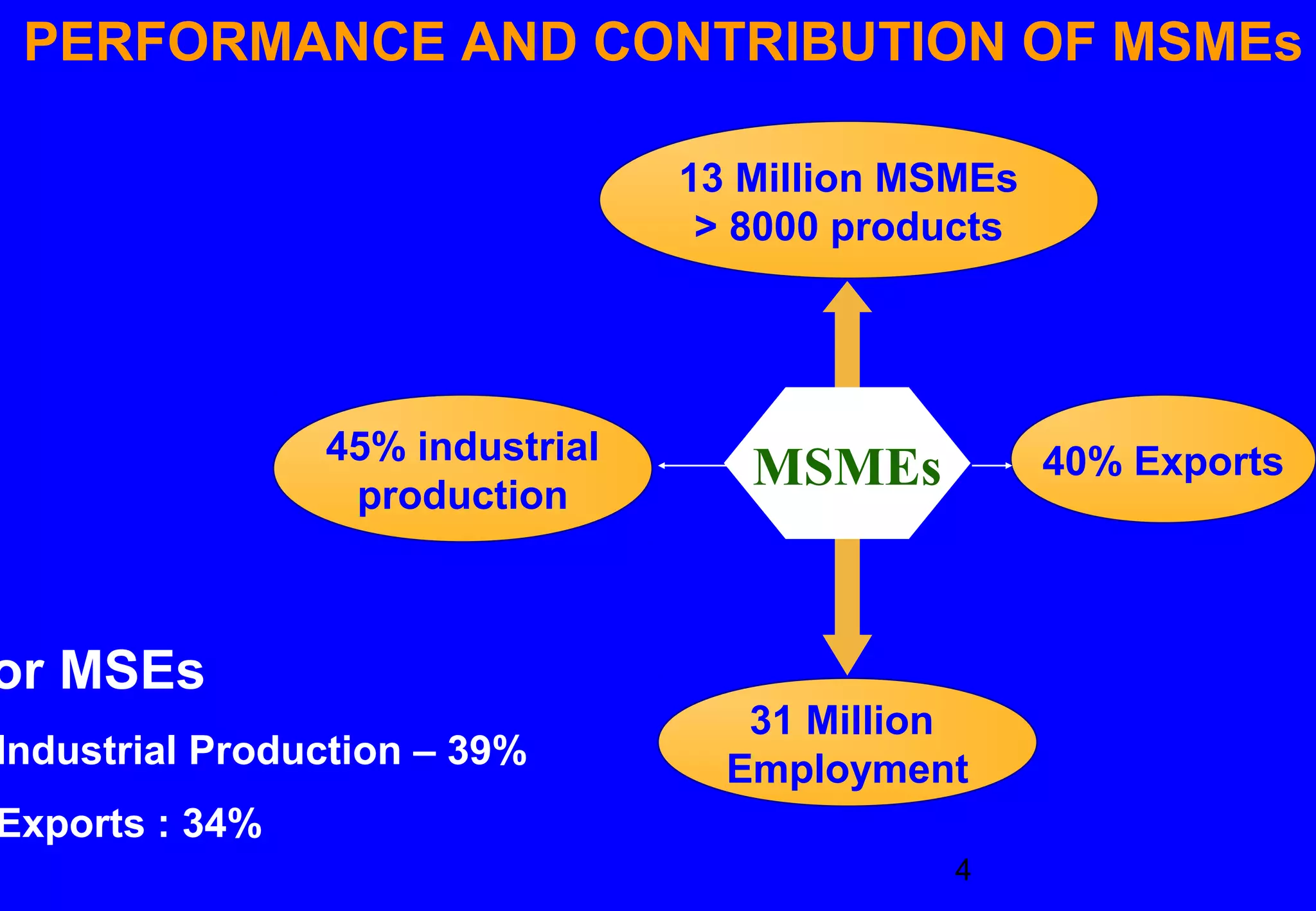
The document discusses the growth and development of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in India. It outlines the government policies that promote MSMEs, including reservations, credit support, fiscal incentives, and infrastructure development. MSMEs contribute significantly to India's economy, accounting for over 30% of GDP, 45% of manufacturing output, 40% of exports, and employment of over 30 million people. The Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development Act of 2006 aims to support MSMEs through registration, credit policies, and payment realization. The government provides various schemes to boost MSMEs, such as credit guarantee funds, technology upgradation subsidies, marketing assistance, cluster development, and entrepreneurship programs