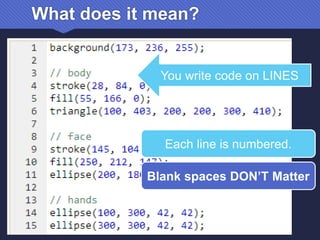
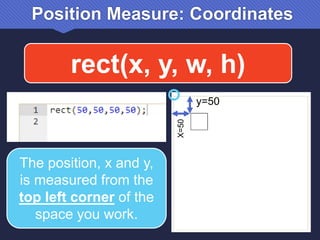
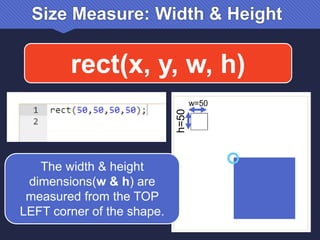
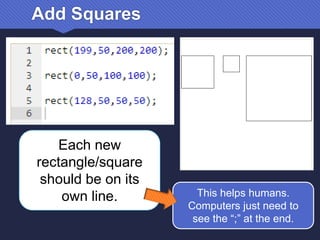
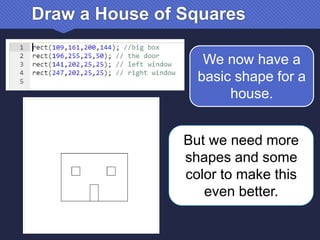
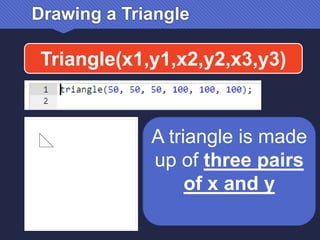
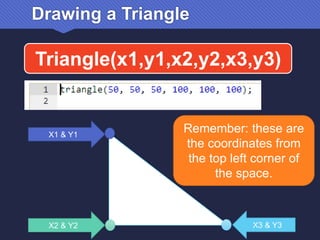
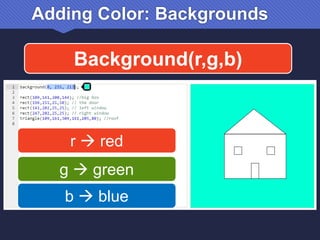
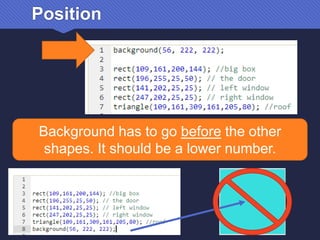
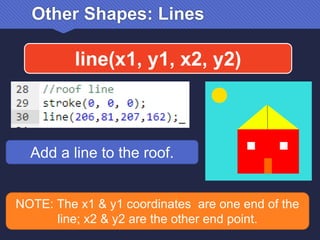
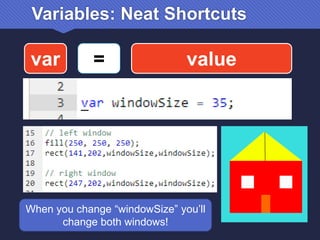
The document provides an introduction to JavaScript, covering its syntax, basic drawing commands, and creation of shapes like squares, triangles, and ellipses. It explains how to use variables, colors, and text in drawings while emphasizing the importance of following specific coding rules. Additionally, it highlights the utility of documentation for programming and the fair use of copyrighted material in educational contexts.