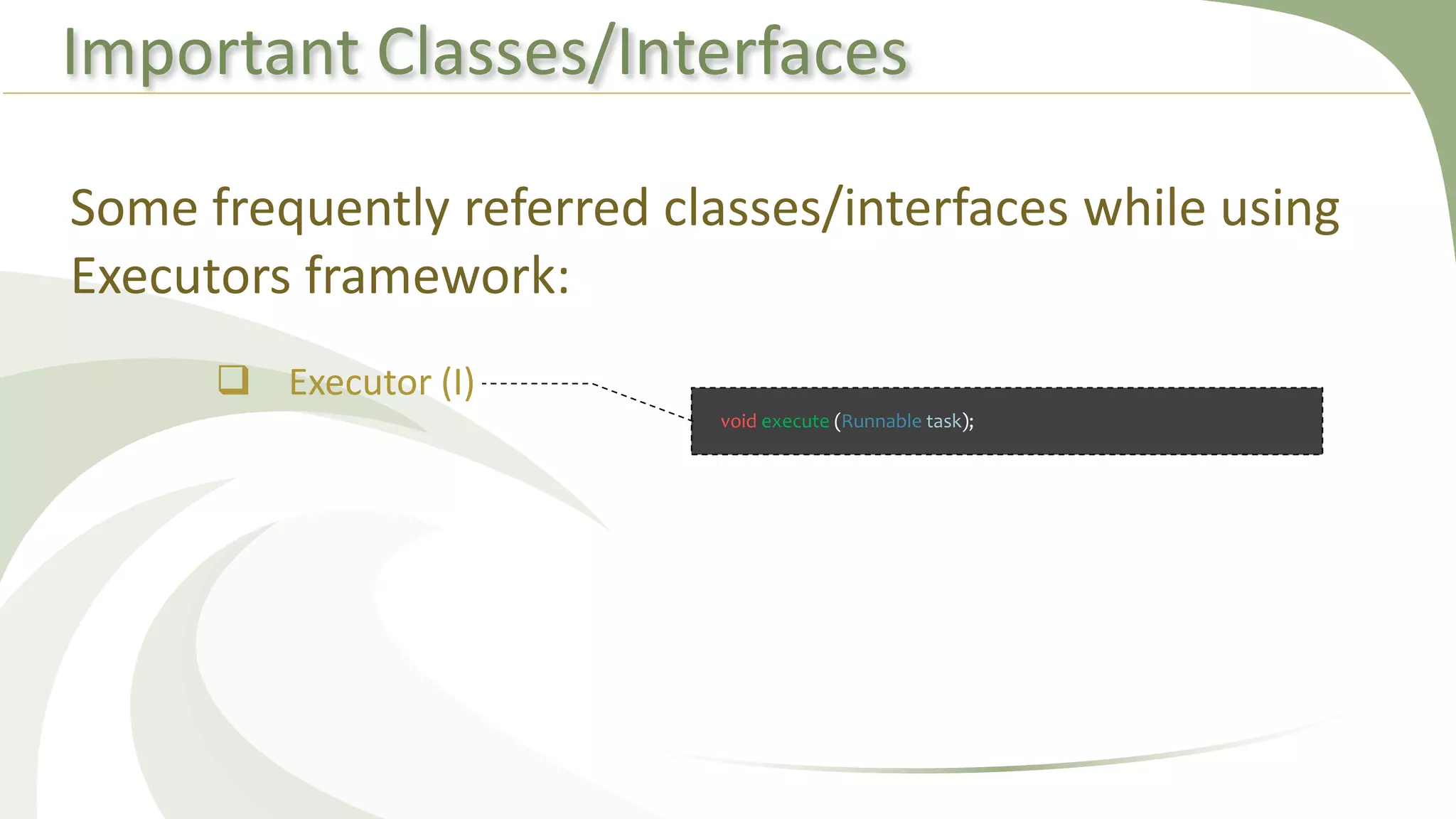
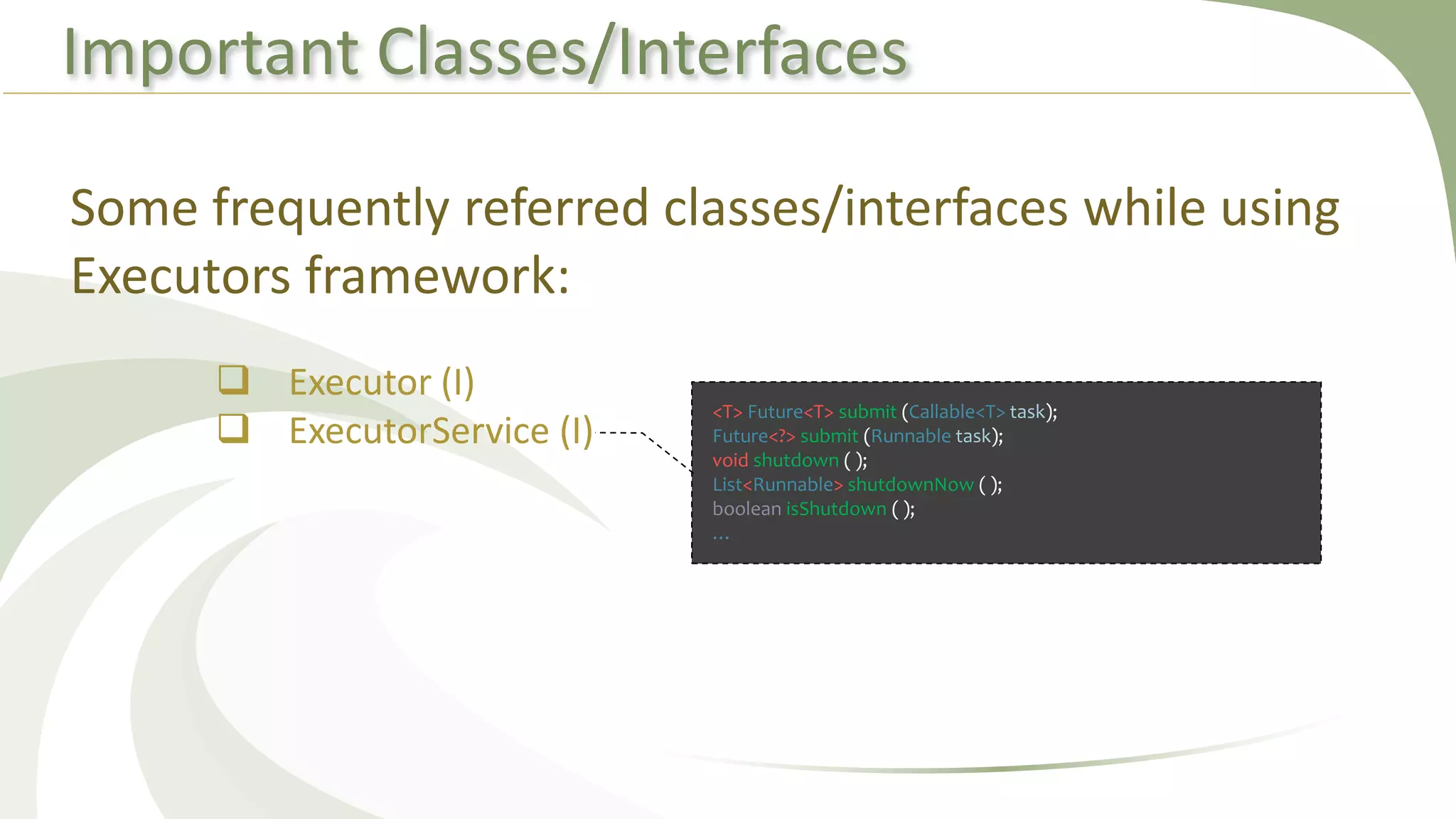
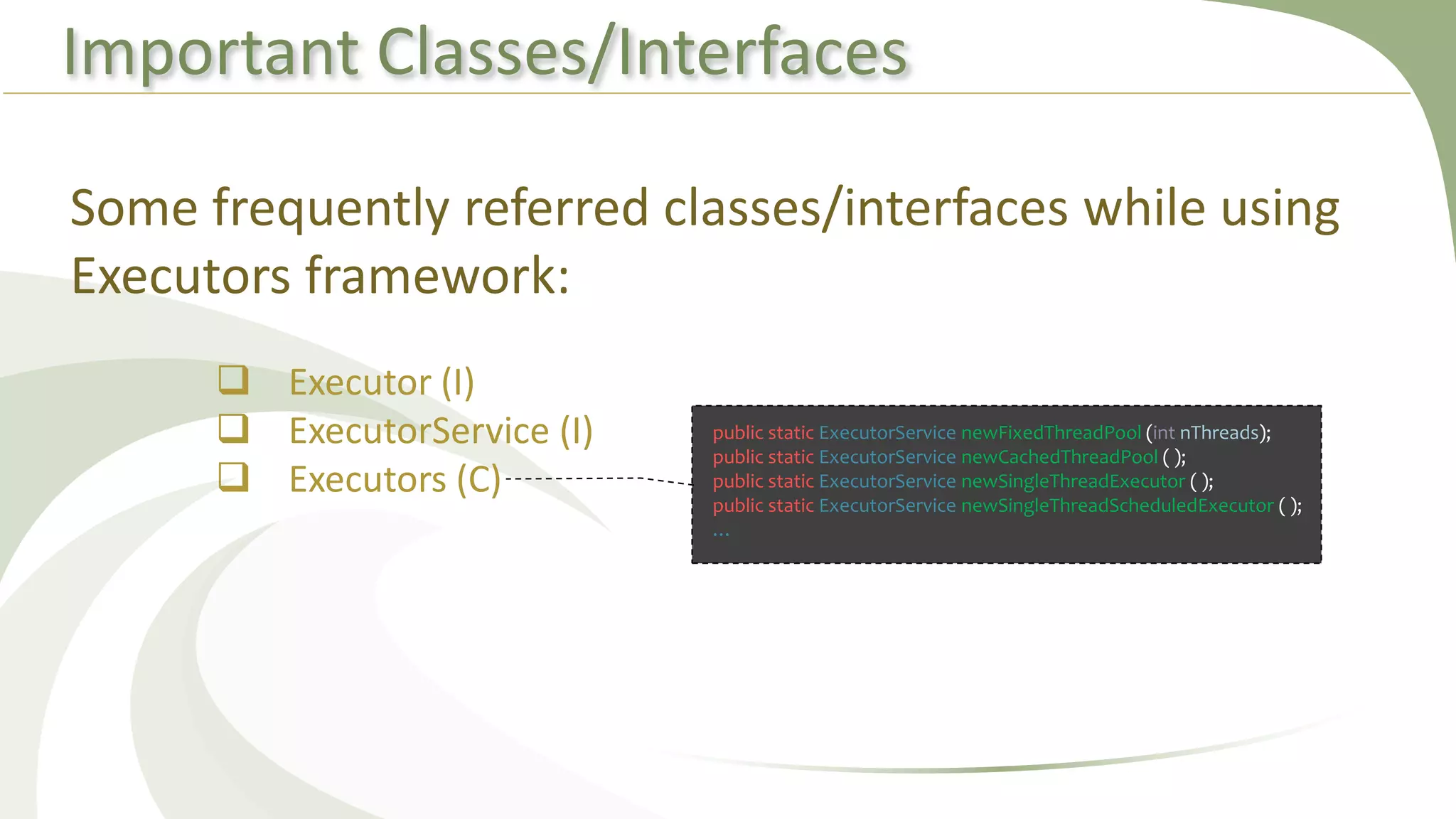
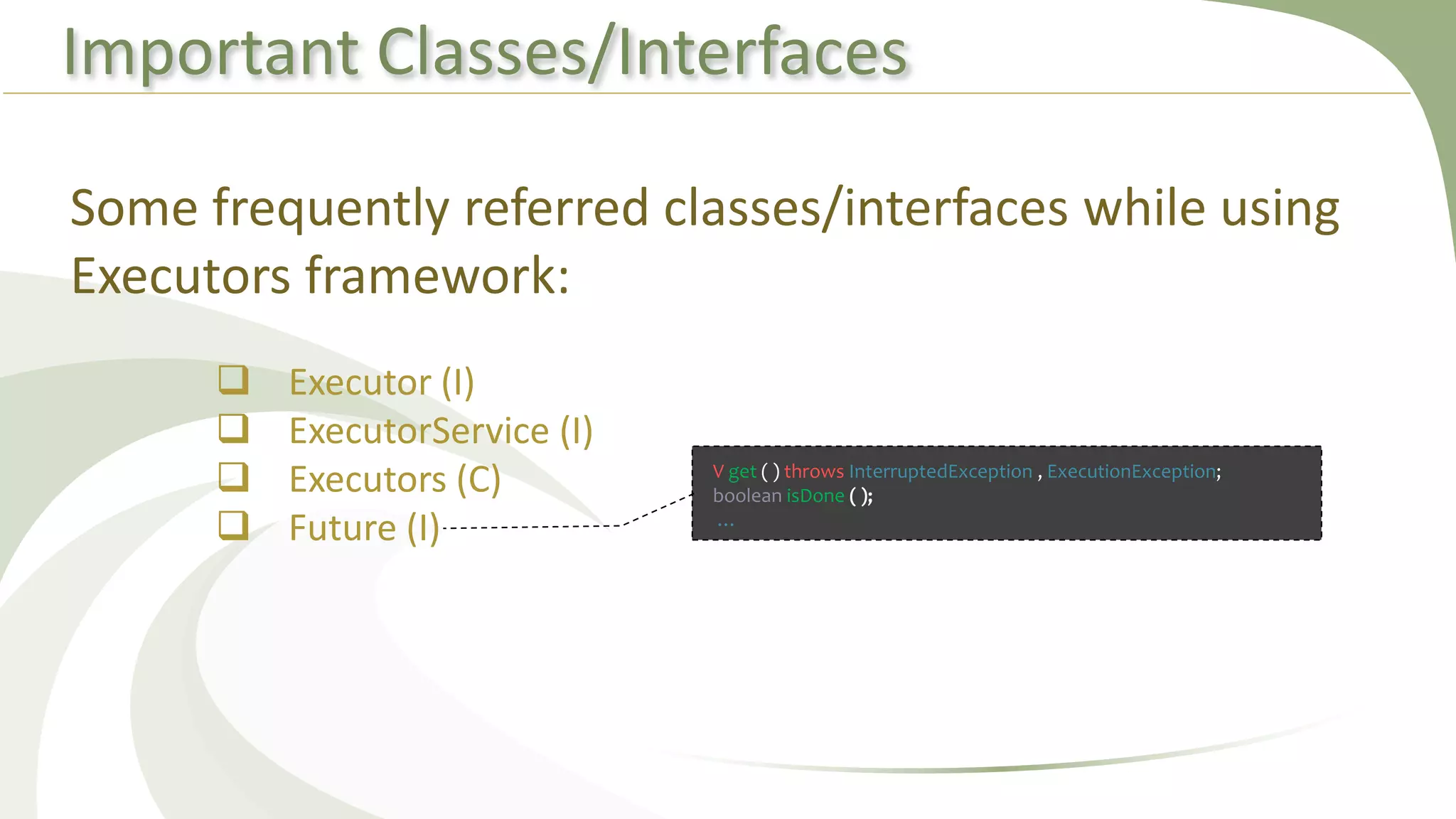
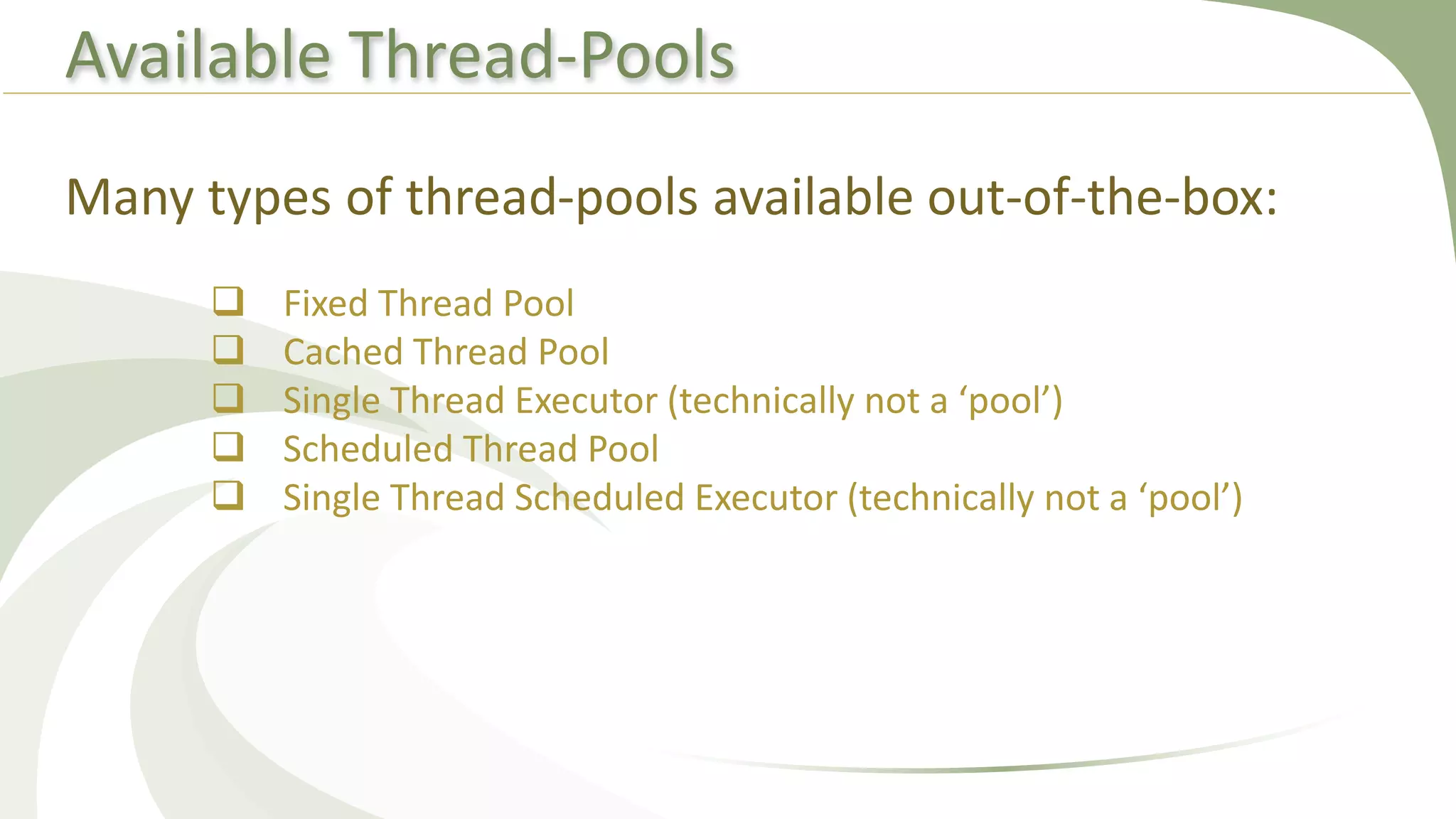
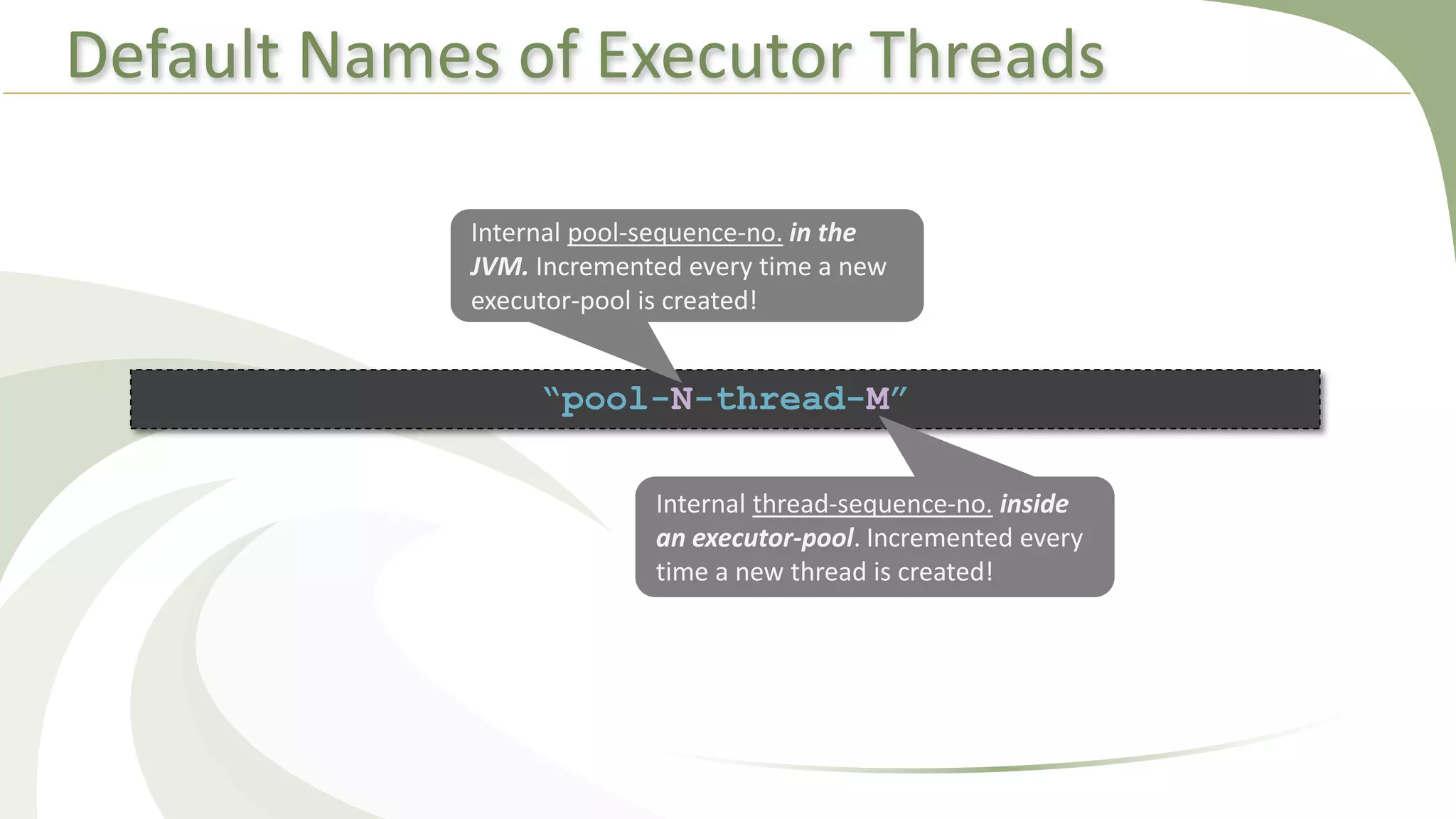
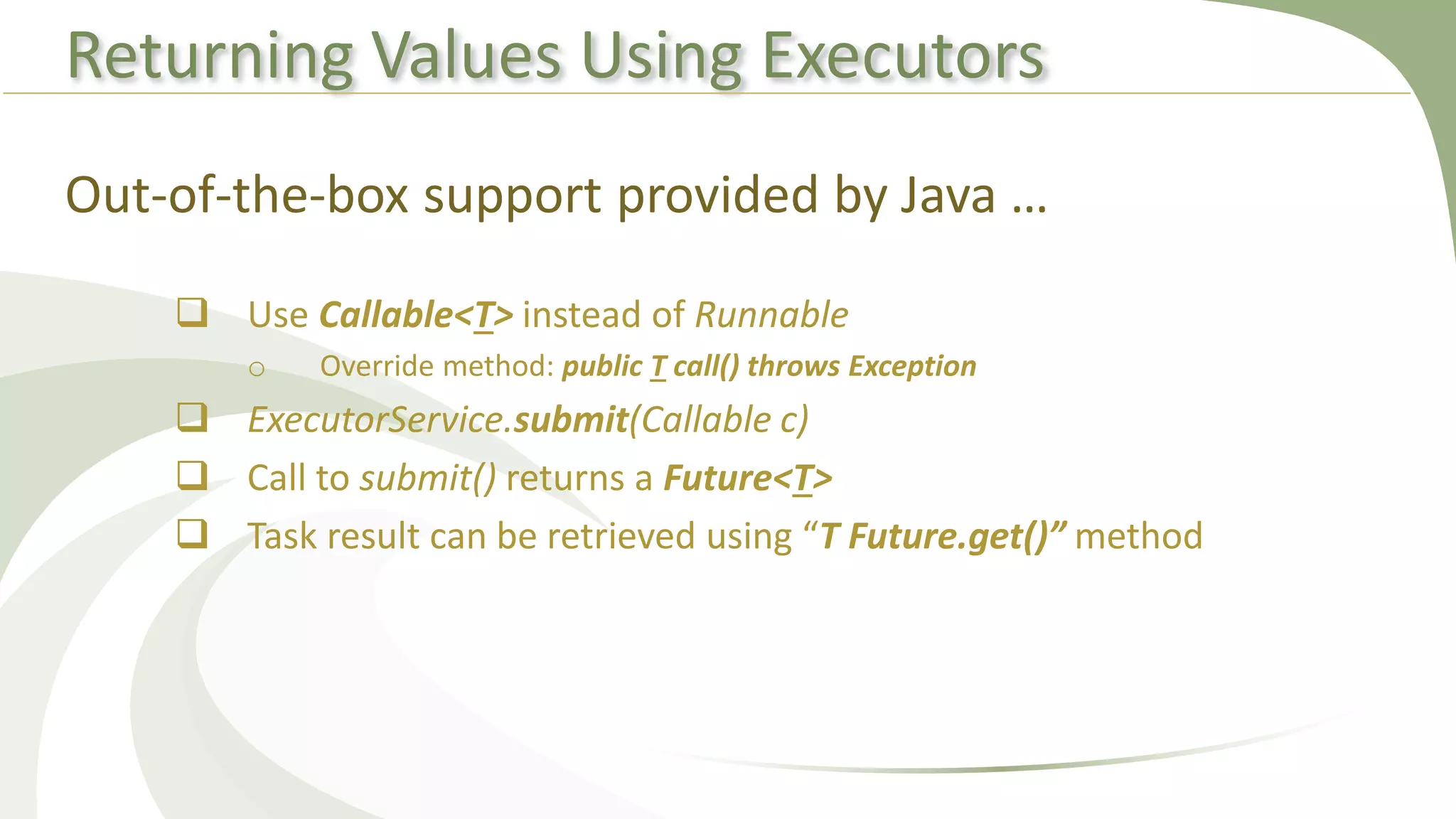
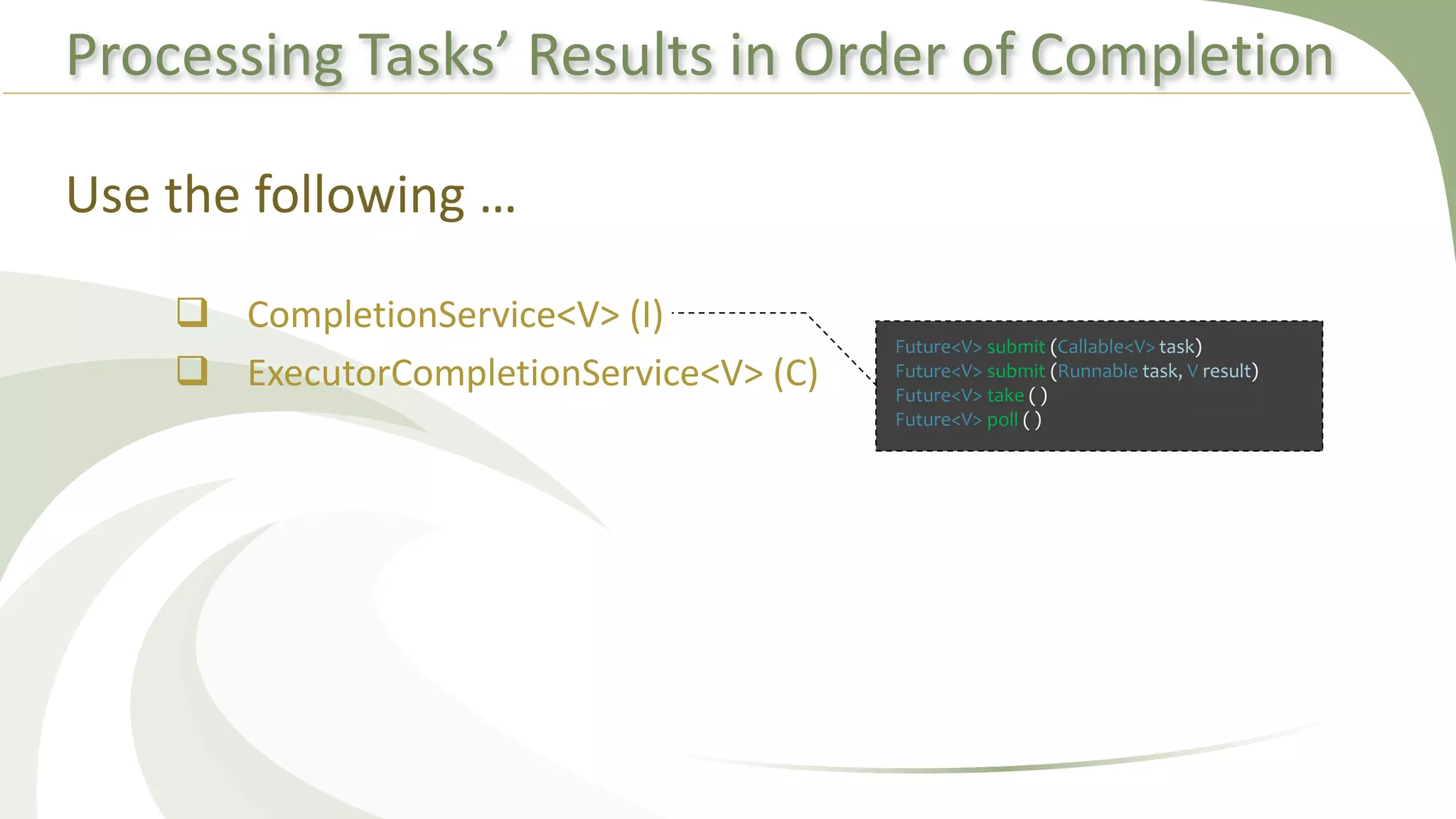
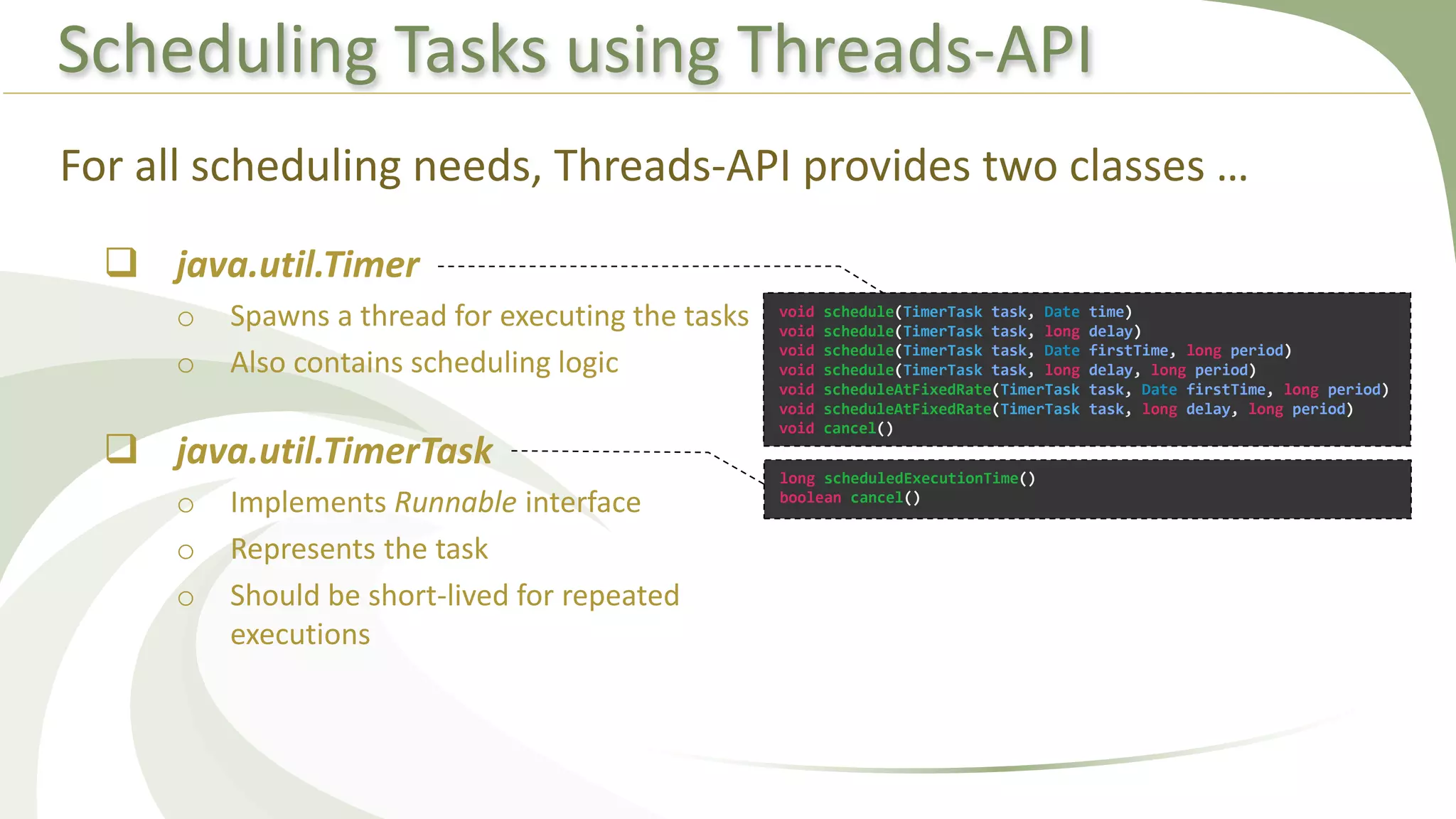
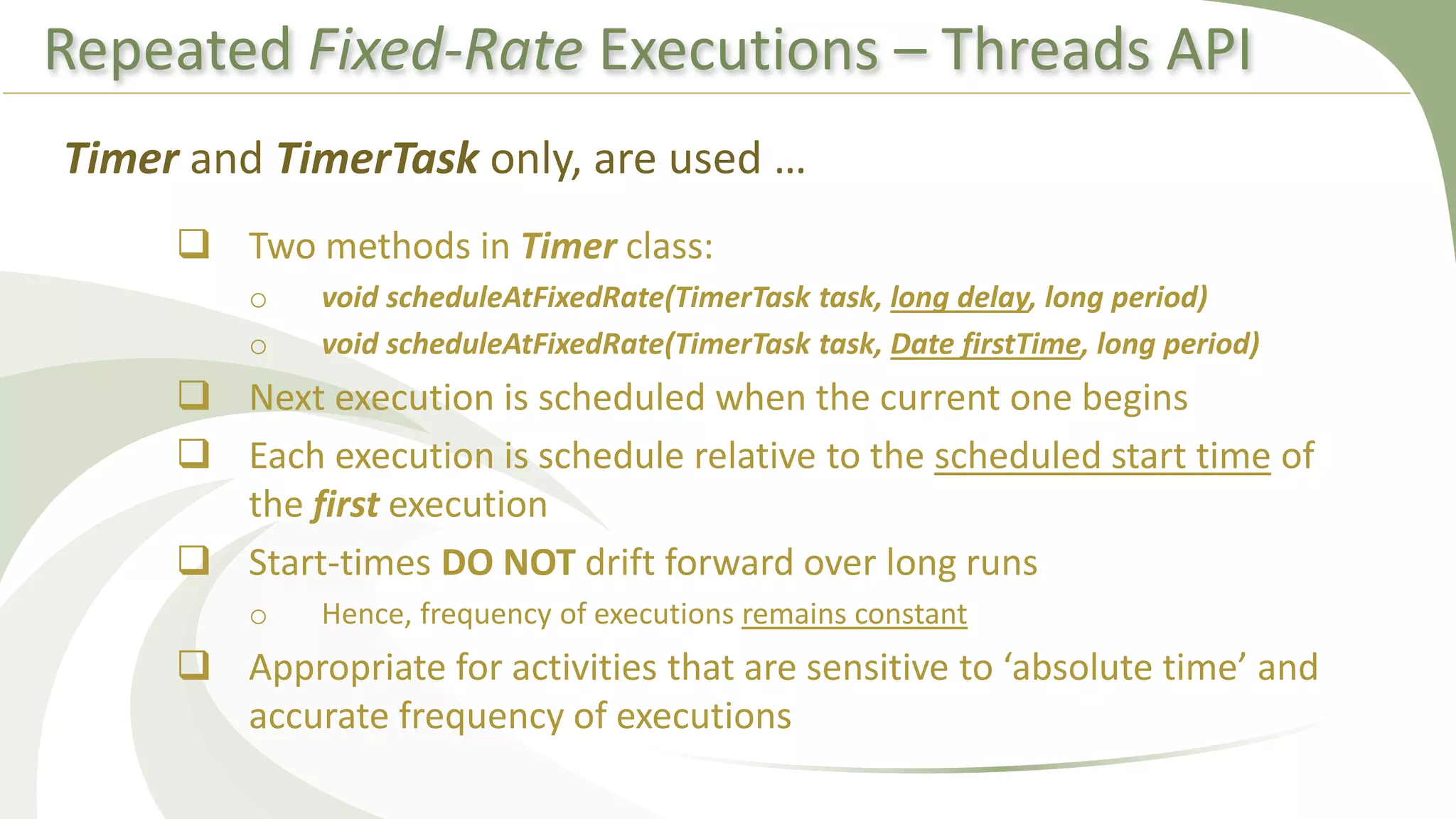
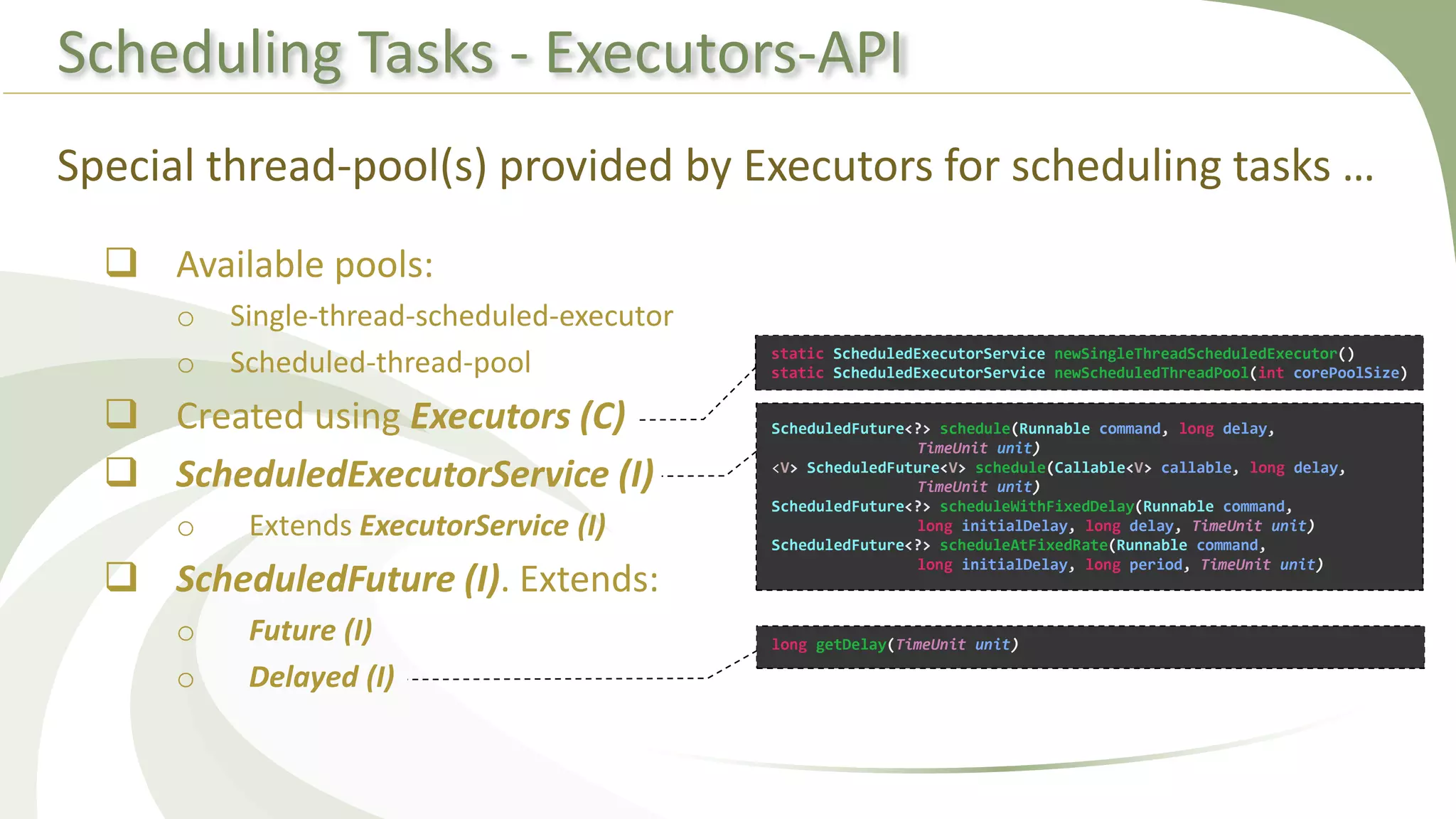
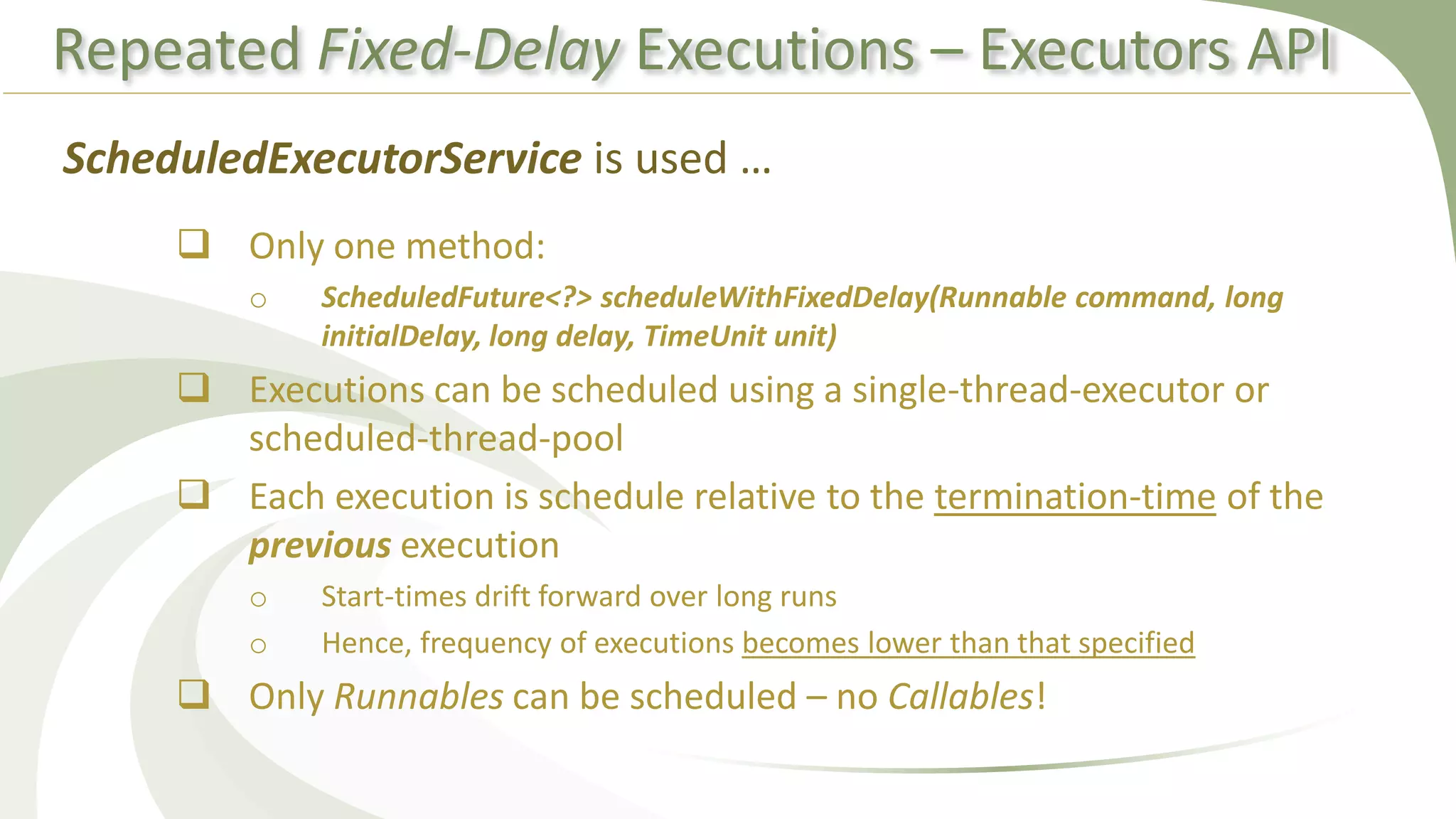
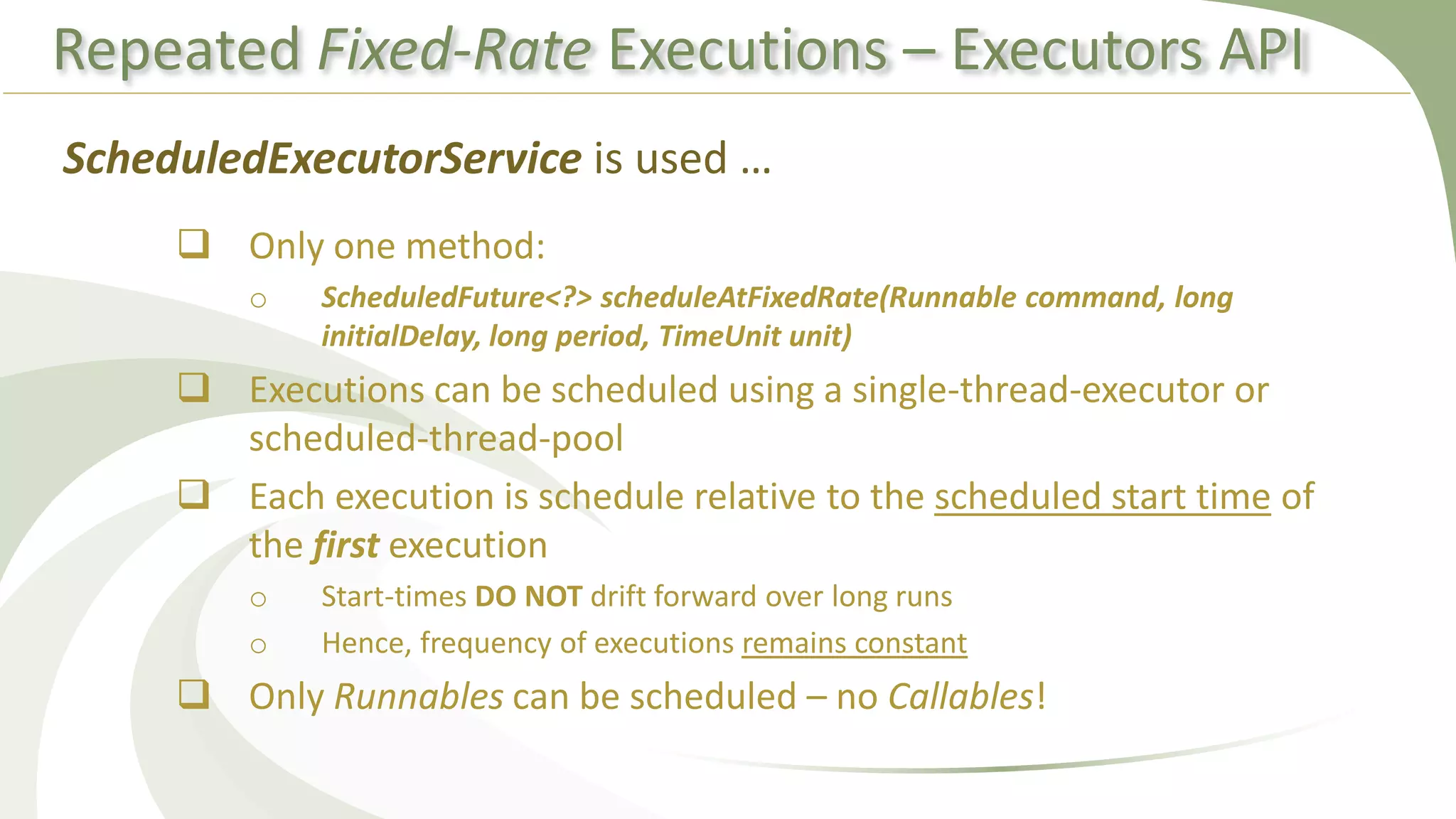
This document provides an overview of using executors to handle multithreading in Java. It discusses key classes and interfaces in the executors framework like Executor, ExecutorService, and Executors. Common thread pools like fixed thread pool and cached thread pool are mentioned. The document also summarizes techniques for naming threads, returning values from threads, creating daemon threads, checking thread status, terminating threads, and handling uncaught exceptions using both the thread and executor APIs. Finally, it covers scheduling tasks using both the timer/timerTask classes and executor service.