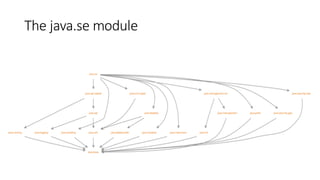
Java 9 introduced modules that provide strong encapsulation and reliable configuration. It also included new APIs like ProcessHandle and private methods in interfaces. Java 10 added local variable type inference with the var keyword and improved support for containerized environments. Java 11 continues enhancements with lambda parameters declared using var and an experimental garbage collector. All future releases will occur every six months with long term support versions every three years.


![ProcessHandle / ProcessHandle.Info
ProcessHandle self = ProcessHandle.current();
long pid = self.getPid();
ProcessHandle.Info info = self.info();
Optional<String[]> args = info.arguments();
Optional<String> cmd = info.commandLine();
Optional<Instant> started = info.startInstant();
Optional<Duration> cpu = info.totalCpuDuration();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java9-10-11-180620131012/85/Java-9-4-320.jpg)

























![What’s In Java 11
• Epsilon: A No-op Garbage Collector (JEP 318)
• Dynamic Class File Constants (JEP 309)
• "seek[s] to reduce the cost and disruption of creating new forms of
materializable class-file constants, which in turn offers language designers and
compiler implementors broader options for expressivity and performance."](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java9-10-11-180620131012/85/Java-9-32-320.jpg)