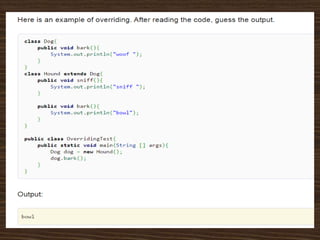
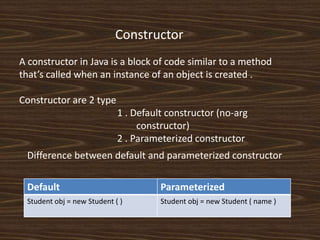
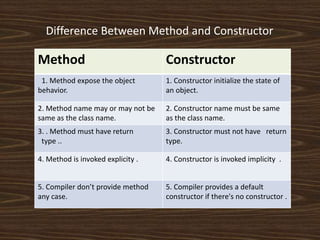
The document provides an introduction to key concepts of Java programming, focusing on object-oriented principles such as inheritance, polymorphism, overloading, overriding, constructors, and encapsulation. It explains how inheritance allows the creation of new classes from existing ones, while polymorphism enables objects to take on multiple forms through method overloading and overriding. Additionally, it covers the importance of constructors and encapsulation in Java, emphasizing how data and methods can be combined into single units.




![EXAMPLE OF SINGLE INHERITANCE
• Class sum //Super class
• {
• int a=10;
• int b=20;
• void show()
• {
• System.out.println(“value of a :-” +a);
• System.out.println(“value of a :-” +b);
• }
• }
• Class sum2 extends sum //base class
• {
• public static void main(String args[])
• {
• Sum2 obj =new sum2();
• Obj.show1();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-170402172637/85/Java-5-320.jpg)












![Abstract class HelloAbstractWorld { }
Class AbstractDemo {
Public static void main (String ar [ ]) {
System.out.println(“Hello World”);
//HelloAbstractWorld obj = new HelloAbstractWorld
}
} /* HelloAbstractWorld is Abstract and cannot be
intantiated */
Simple Abstract Code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/java-170402172637/85/Java-22-320.jpg)