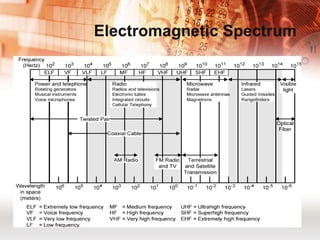
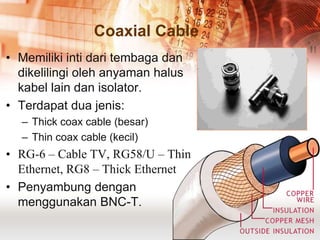
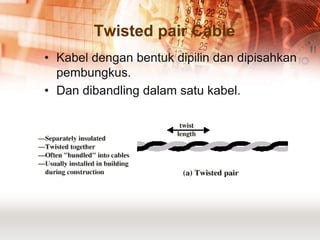
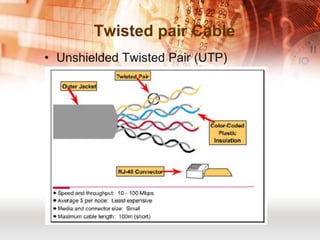
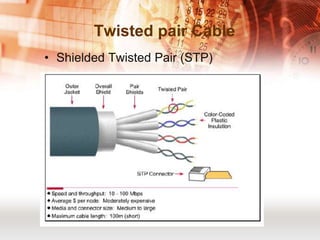
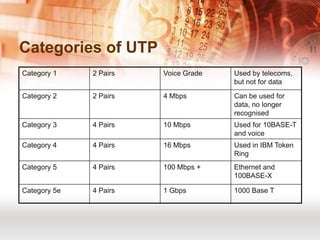
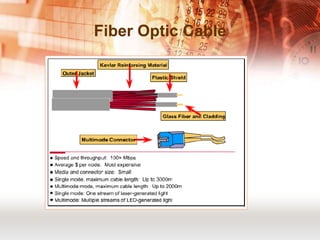
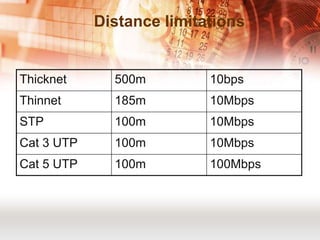
Kabel koaksial dan kabel pasangan berpilin merupakan jenis kabel yang umum digunakan dalam jaringan komputer. Kabel koaksial memiliki inti tembaga yang dikelilingi isolator dan digunakan untuk jaringan Ethernet, sedangkan kabel pasangan berpilin terdiri dari pasangan kabel yang dipilin dan dibungkus. Kabel serat optik juga populer karena mampu mentransmisikan sinyal dalam jarak jauh.