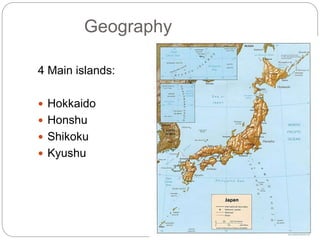
Japan consists of four main islands: Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu. The official language is Japanese and the capital is Tokyo. Traditional Japanese culture has been influenced by Shintoism, Buddhism, and Zen. Japanese cuisine features seafood like sashimi, rice as a staple, and meals are artistically arranged. Customs include bowing for greetings and respecting elders. Sumo wrestling is a popular sport where large wrestlers try to force each other out of a ring.