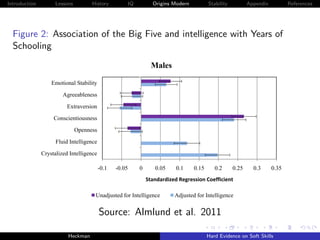
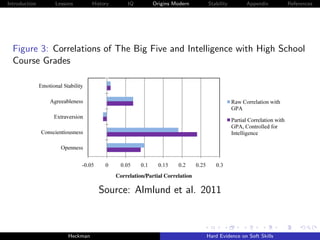
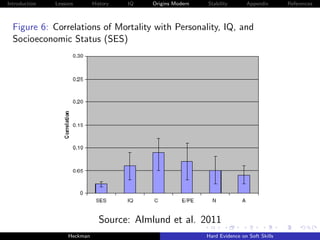
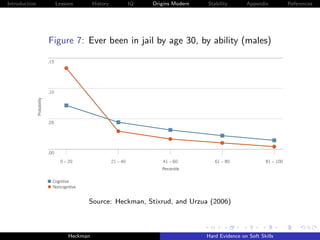
The document discusses the limitations of achievement tests in measuring essential noncognitive skills, or 'soft skills,' which are crucial for success in life. It highlights that personality traits can be quantified and are as important as cognitive abilities in predicting life outcomes. The research emphasizes the need to enhance these traits through education and policy to foster better individual and societal outcomes.











































![Introduction Lessons History IQ Origins Modern Stability Appendix References
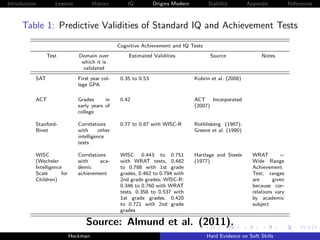
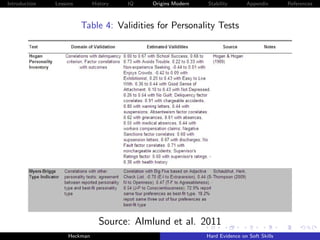
Binet:
“[Success in school] . . .admits of other things than
intelligence; to succeed in his studies, one must have
qualities which depend on attention, will, and character;
for example a certain docility, a regularity of habits, and
especially continuity of effort. A child, even if intelligent,
will learn little in class if he never listens, if he spends his
time in playing tricks, in giggling, in playing truant.”
-Binet (1916, p. 254)
Heckman Hard Evidence on Soft Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-46-320.jpg)



















































![Introduction Lessons History IQ Origins Modern Stability Appendix References
and the authors do not clearly delineate when the measures of personality were taken.
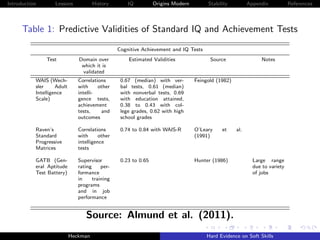
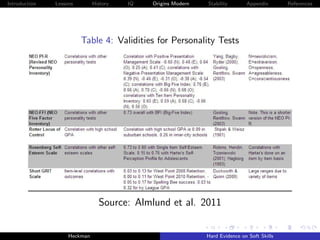
Figure 5: Associations with Job Performance
Figure 14. Associations with Job Performance
Emotional Stability
Agreeableness
Extraversion
Conscientiousness
Openness
Intelligence
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6
Correlation
Note. The values for personality are correlations that were corrected for sampling error, range
restriction, and measurement error. Job performance was based on performance ratings,
productivity data and training proficiency. The authors do report the timing of the measurements
of personality relative to job performance. The value for IQ is a raw correlation.
Source(s): The values reported for personality traits come from a meta-analysis conducted by
Barrick and Mount [1991]. The value for IQ and job performance was reported in Schmidt and
Hunter [2004].
Heckman Hard Evidence on Soft Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-114-320.jpg)

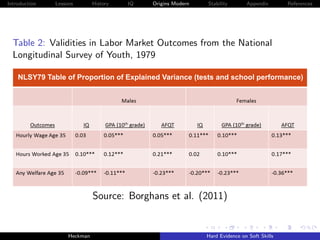
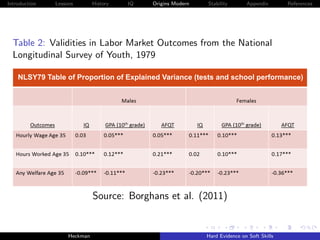
![Introduction Lessons History IQ Origins Modern Stability Appendix References
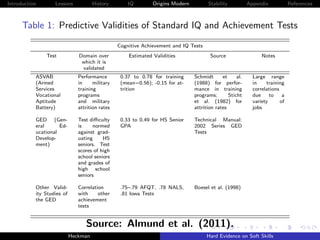
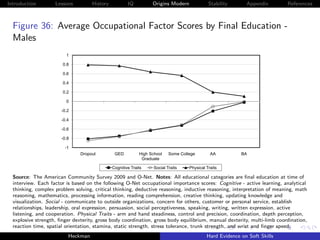
Figure 9: Decomposing Achievement Tests and Grades into IQ and
Personality [NLSY79]
0.60
Achievement Grades
0.50 0.48
0.43
0.40
R-Squared
0.30
0.23
0.20
0.19
0.16
0.10
0.10
0.00
AFQT Grades
IQ, Rosenberg, and Rotter IQ Rosenberg and Rotter
Source: Borghans, Golsteyn, Heckman et al. [2011].
Heckman Hard Evidence on Soft Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-122-320.jpg)
![Introduction Lessons History IQ Origins Modern Stability Appendix References
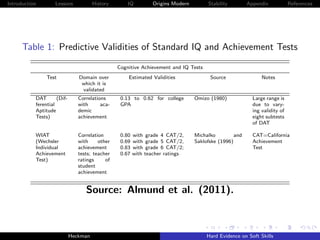
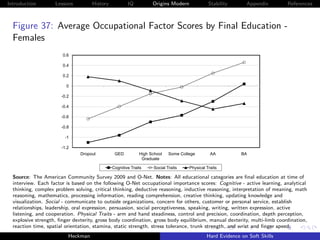
Figure 10: Decomposing Achievement Tests and Grades into IQ and
Personality [Stella Maris]
Source: Borghans, Golsteyn, Heckman et al. [2011].
Heckman Hard Evidence on Soft Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-123-320.jpg)



















![Introduction Lessons children who
SES History information. Gentle (10.6 points and SD was three distinct Appendix
IQ Origins Modern Stability factors: (a) References
did or did not encouragement, about 9.5 in this sample) formal cognitive processes;
attend nursery easier items after between scores of (b) informational
school were tested
Almlund, Duckworth, Heckman, and Kautz 12/31/2010
items were missed, children in the achievements which reflect
Table 6: Incentives and Performance on Intelligence Tests
at the beginning and so on. optimized vs the content rather than the 83
and end of the year standardconditions The formal properties of
Table 5. Incentives and Performance on Intelligence Tests improved cognition, and (c)
on Stanford-Binet nursery group
Study Sample and Study
Intelligence Test Experimental Effectscores, but only in
their size of incentive Summary
motivational factors which
Design
under either Group (in standard
the standard condition. involve a wide range of
optimized or deviations) personality variables. (p. 2)
Edlund Between subjects
standard M&M candies Experimental group “…a carefully chosen
“…the significant difference
[1972] study. 11 matched
conditions. given for each scored 12 points higher consequence, candy,standard
in improvement in given
pairs of low SES right answer than control group contingent on each occurrence
IQ performance found
children; children during a second testing of correct the nursery and non-
between responses to an IQ
were about one on an alternative form of test, can result inwas
nursery groups a
standard deviation the Stanford Binet significantly solely to
attributable higher IQ
below average in (about 0.8 standard score.”(p. 319)
motivational factors…” (p.
IQ at baseline deviations) 10)
Ayllon &
Breuning Within subjects
Within and Tokens given in as 6.25 points out of aby
Incentives such Scores increased “…test scores often reflect of
“In summary, the promise
KellyZella study. 12 mentally
and between subjects experimental
record albums, possible17 points. Results poor academic skills, but they
about 51 points on individualized incentives
[1972]
[1978] retarded children
study of 485 condition for right Metropolitan Readiness
radios (<$25) given were consistent across may also reflect lack of in
contingent on an increase
Sample 1 (avg IQ 46.8)
special education answers the t = 4.03
for improvement in Test. Otis-Lennon, WISC- motivation to do well (asthe
IQ test performance in
high school exchangeable for
test performance R, and Lorge-Thorndike criterion test…These results,
compared with pretest
students all took IQ prizes tests. obtained from both a in an
performance) resulted
Ayllon & Within then were
tests, subjects Tokens given in t = 5.9 population typically limited in
approximate 17-point
Kelly study 34 urban
randomly assigned experimental skills and in IQ test scores.
increase ability as well as
[1972] fourth graders (avg condition for right
to control or from a group of normal
These increases were equally
Sample 2 IQ = 92.8) groups to answers
incentive childrenacross subtests… The
spread (Experiment II),
retake tests. exchangeable for demonstrate that the use of
incentive condition effects
Subjects were prizes reinforcement procedures
were much less pronounced
Ayllon & below-average in
Within subjects Six weeks of token Experimental group applied to a behaviorpretest
for students having that is
Kelly IQ.
study of 12 reinforcement for scored 3.67 points out of tacitly regarded as “at120 and
IQs between 98 and its
[1972] matched pairs of good academic possible 51 points on a peak” can significantly alter
did not occur for students
Sample 3 mentally retarded performance post-test given under the levelpretest IQs between
having of performance of
children standard conditions that behavior.” (p. 483)
121 and 140.” (p. 225)
Holt and Between and Exp 1-Token higher standard deviation
1.06 than at baseline; “Knowledge of results does
Hobbs within subjects reinforcement for control group dropped
difference between the not appear to be a sufficient
Many other studies (see ADHK).
[1979] study of 80
delinquent boys
correct responses; 2.75 points. On a second
Exp 2 – Tokens
token reinforcement and incentive to significantly
control groups (inferred improve test performance
post-test with incentives,
randomly assigned forfeited for
Heckman from t control groups
exp and= 3.31 for 39 Hard among below-average I.Q.
Evidence on Soft Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-148-320.jpg)












































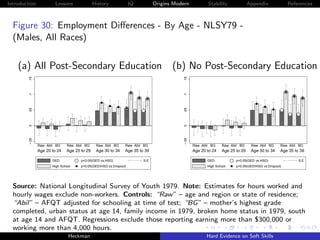
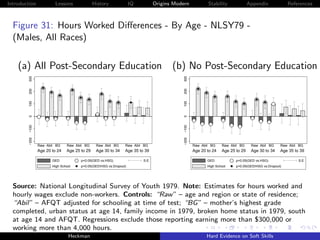
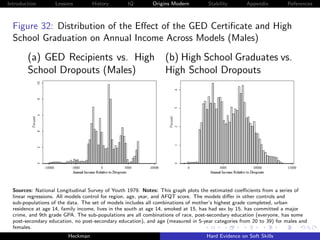
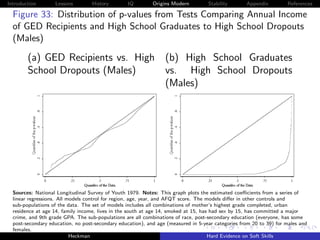




















![Introduction Lessons History IQ Origins Modern Stability Appendix References
Many behavioral economists hold a similar view and appeal to
Mischel as a guiding influence.
“The great contribution to psychology by Walter
Mischel [. . . ] is to show that there is no such thing as
a stable personality trait.”
-Thaler (2008)
Heckman Hard Evidence on Soft Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-250-320.jpg)





![Introduction Lessons History IQ Origins Modern Stability Appendix References
Figure 40: Cumulative Mean-Level Changes in Personality Across the
Life Cycle
Note: Social vitality and social dominance are aspects of Big Five Extraversion. Cumulative d values represent total lifetime
change in units of standard deviations (“effect sizes”).
Source: Figure taken from Roberts, Walton and Viechtbauer [2006] and Roberts and Mroczek [2008]. Reprinted with
permission of the authors.
Heckman Hard Evidence on Soft Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-256-320.jpg)
![Introduction Lessons History IQ Origins Modern Stability Appendix References
Figure 41: Cumulative Mean-Level Changes in Personality Across the
Life Cycle
Note: Social vitality and social dominance are aspects of Big Five Extraversion. Cumulative d values represent total lifetime
change in units of standard deviations (“effect sizes”).
Source: Figure taken from Roberts, Walton and Viechtbauer [2006] and Roberts and Mroczek [2008]. Reprinted with
permission of the authors.
Heckman Hard Evidence on Soft Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-257-320.jpg)
![Introduction Lessons History IQ Origins Modern Stability Appendix References
Figure 41: Cumulative Mean-Level Changes in Personality Across the
Life Cycle
Note: Social vitality and social dominance are aspects of Big Five Extraversion. Cumulative d values represent total lifetime
change in units of standard deviations (“effect sizes”).
Source: Figure taken from Roberts, Walton and Viechtbauer [2006] and Roberts and Mroczek [2008]. Reprinted with
permission of the authors.
Heckman Hard Evidence on Soft Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-258-320.jpg)
![Introduction Lessons History IQ Origins Modern Stability Appendix References
Figure 41: Cumulative Mean-Level Changes in Personality Across the
Life Cycle
Note: Social vitality and social dominance are aspects of Big Five Extraversion. Cumulative d values represent total lifetime
change in units of standard deviations (“effect sizes”).
Source: Figure taken from Roberts, Walton and Viechtbauer [2006] and Roberts and Mroczek [2008]. Reprinted with
permission of the authors.
Heckman Hard Evidence on Soft Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-259-320.jpg)
![Introduction Lessons History IQ Origins Modern Stability Appendix References
Figure 41: Cumulative Mean-Level Changes in Personality Across the
Life Cycle
Note: Social vitality and social dominance are aspects of Big Five Extraversion. Cumulative d values represent total lifetime
change in units of standard deviations (“effect sizes”).
Source: Figure taken from Roberts, Walton and Viechtbauer [2006] and Roberts and Mroczek [2008]. Reprinted with
permission of the authors.
Heckman Hard Evidence on Soft Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-260-320.jpg)
![Introduction Lessons History IQ Origins Modern Stability Appendix References
Figure 42: Longitudinal Analysis of Cognitive Skills
Notes: T-scores on the y-axis are standardized scores with a mean of 50 and a standard deviation of ten.
Source: Figures taken from Schaie [1994]. Used with permission of the publisher.
Heckman Hard Evidence on Soft Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-261-320.jpg)




























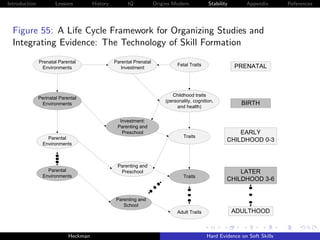
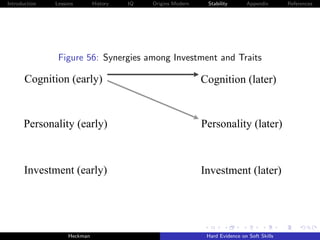
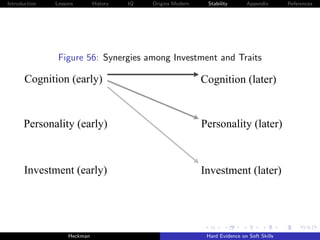
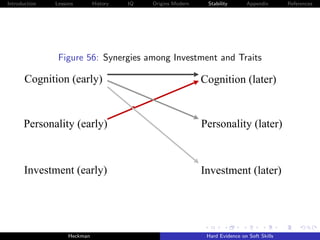
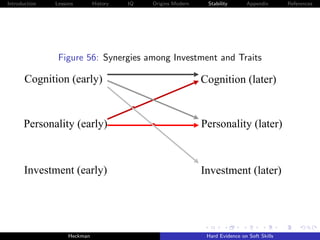
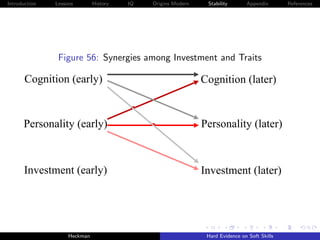

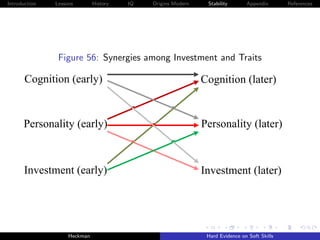
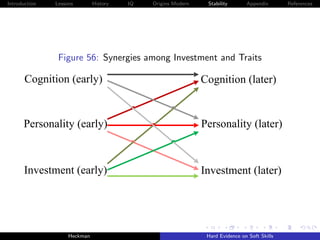
![Introduction Lessons History IQ Origins Modern Stability Appendix References
Cunha, Heckman and Schennach [2010] estimate these
relationships using longitudinal data on the development of
children with rich measures of parental investment and child
traits.
Heckman Hard Evidence on Soft Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-318-320.jpg)
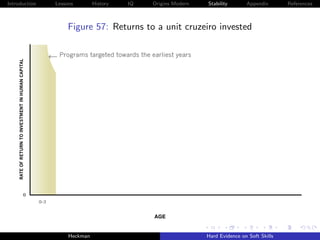
![Introduction Lessons History IQ Origins Modern Stability Appendix References
Cunha, Heckman and Schennach [2010] estimate these
relationships using longitudinal data on the development of
children with rich measures of parental investment and child
traits.
Persistence of traits becomes stronger as children become
older, for both cognitive and noncognitive capabilities.
Heckman Hard Evidence on Soft Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-319-320.jpg)
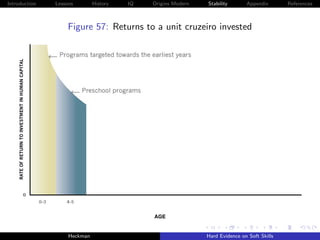
![Introduction Lessons History IQ Origins Modern Stability Appendix References
Cunha, Heckman and Schennach [2010] estimate these
relationships using longitudinal data on the development of
children with rich measures of parental investment and child
traits.
Persistence of traits becomes stronger as children become
older, for both cognitive and noncognitive capabilities.
It is more difficult to compensate for the effects of adverse
environments on cognitive endowments at later ages than it is
at earlier ages.
Heckman Hard Evidence on Soft Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-320-320.jpg)


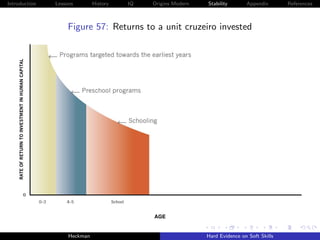
![Introduction Lessons History IQ Origins Modern Stability Appendix References
Explains a large body of evidence on ineffective cognitive
remediation strategies for disadvantaged adolescents.
Personality traits foster the development of cognition but not
vice versa.
It is estimated to be equally easy to substitute at both stages
for personality skills over the life cycle (Cunha, Heckman and
Schennach [2010]).
Heckman Hard Evidence on Soft Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-323-320.jpg)
![Introduction Lessons History IQ Origins Modern Stability Appendix References
Explains a large body of evidence on ineffective cognitive
remediation strategies for disadvantaged adolescents.
Personality traits foster the development of cognition but not
vice versa.
It is estimated to be equally easy to substitute at both stages
for personality skills over the life cycle (Cunha, Heckman and
Schennach [2010]).
Overall, 16% of the variation in educational attainment is
explained by factors extracted from cognitive traits, 12% is due
to factors extracted from personality traits, and 15% is due to
factors extracted from measured parental investments.
Heckman Hard Evidence on Soft Skills](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-324-320.jpg)
































![Glossary of Psychology Terms
Definition (American Psychological Association 2007
Psychology Term Dictionary definition in quotes) Example Measures
“Any experience of feeling or emotion, ranging from
suffering to elation, from the simplest to the most complex Positive and Negative Affect Scale (PANAS; (Watson, Clark, &
Affect
sensations of feeing, and from the most normal to the most Tellegen, 1988))
pathological emotional reactions.”
“The tendency to act in a cooperative, unselfish manner,
construed as one end of a dimension of individual
Big Five Agreeableness Agreeableness domain of any Big Five questionnaire.
differences (agreeableness vs. disagreeableness) in the Big
Five personality model.”
“The tendency to be organized, responsible, and
Big Five hardworking, construed as one end of a dimension of
Conscientiousness domain of any Big Five questionnaire
Conscientiousness individual differences (conscientiousness vs. lack of
direction) in the Big Five personality model.”
“An orientation of one’s interests and energies toward the
outer world of people and things rather than the inner world
of subjective experience. Extraversion is a broad personality
Big Five Extraversion Extraversion domain of any Big Five questionnaire.
trait and, like introversion, exists on a continuum of attitudes
and behaviors. Extroverts are relatively more outgoing,
gregarious, sociable, and openly expressive.”
Big Five Neuroticism “One of the dimensions of the…Big Five personality model
characterized by a chronic level of emotional instability and Neuroticism domain of any Big Five questionnaire.
(or Emotional Stability)
proneness to psychological distress.”
Big Five Openness to
Openness domain of any Big Five questionnaire; Typical Intellectual
Experience (or “A dimension of the Big Five personality model that refers Engagement (Goff & Ackerman, 1992)
Intellect) to individual differences in the tendency to be open to new
aesthetic, cultural, or intellectual experiences.”
“A model of the primary dimensions of individual
Big Five personality differences in personality. The dimensions are usually NEO-PI-R (Costa & McCrae, 1992);
model labeled extraversion, neuroticism, agreeableness, Big Five Inventory (John & Srivastava, 1999)
conscientiousness, and openness to experience, though the
labels vary somewhat among researchers.”
A specific mental ability. The tendency to reflect before
Cognitive reflection Cognitive Reflection Test (Frederick, 2005)
taking an intuitive answer as correct.
“Ability to produce original work, theories, techniques or
Creativity thoughts […] Related with imagination, expressiveness, Creative Personality Scale (Gough, 1979)
originality.”
“Forgoing immediate reward in order to obtain a larger or Preschool Delay of Gratification Task (Mischel & Metzner, 1962);
Delay of gratification
more desirable reward in the future” Choice Delay task (Duckworth & Seligman, 2005)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-372-320.jpg)

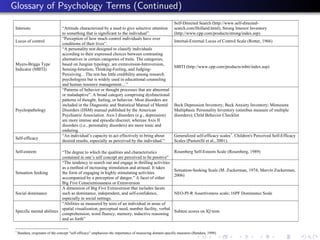
![Glossary of Psychology Terms (Continued)
A dimension of Big Five Extraversion that includes traits California Personality Inventory (CPI)Sociability Scale; NEO-PI-R
Social vitality
such as sociability, positive effect, and gregariousness. Gregariousness and Activity Scales
“Basic foundation of personality, usually assumed to be Children's Behavior Questionnaire
Temperament
biologically determined and present early in life[…] (http://www.bowdoin.edu/~sputnam/rothbart-temperament-
(childhood)
Includes characteristics such as energy level, emotional questionnaires/)
responsiveness, response tempo and willingness to explore”
Type A personality is “a personality pattern characterized by
chronic competitiveness, high levels of achievement
Type A/Type B motivation, and hostility.” Type B personality is “a Jenkins Activity Survey (Jenkins, Zyzanski, & Rosenman, 1971)
personality personality pattern characterized by low levels of
competitiveness and frustration and a relaxed, easy going
approach.”
“A moral, social or aesthetic principle accepted by an
Values in Action Inventory of Strengths (Peterson & Seligman,
Values individual (or society) as a guide to what is good, desirable
2004)
or important.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heckman-111026153410-phpapp01/85/James-Heckman_apresentacao-Seminario-Educacao-para-o-Seculo-21-375-320.jpg)