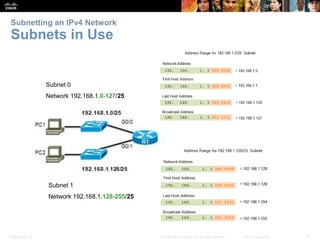
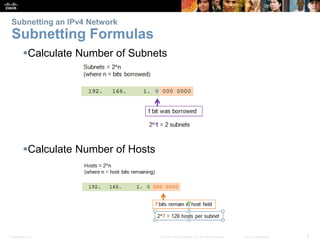
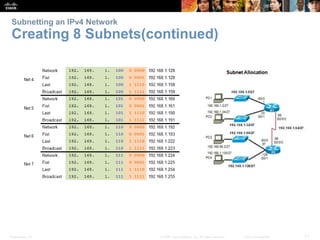
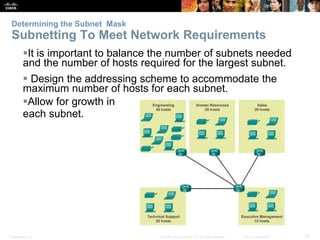
This document discusses subnetting IP networks. It covers reasons for subnetting including network segmentation and traffic control. Subnetting involves dividing a network into smaller subnetworks using a subnet mask. Variable length subnet masking allows for more efficient use of addresses by creating subnets of varying sizes. The document provides examples of subnetting networks and describes considerations for planning IP addressing schemes.