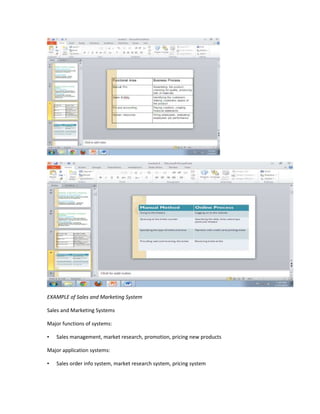
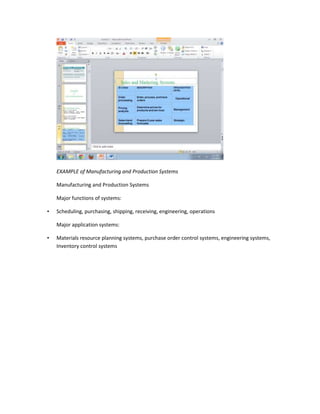
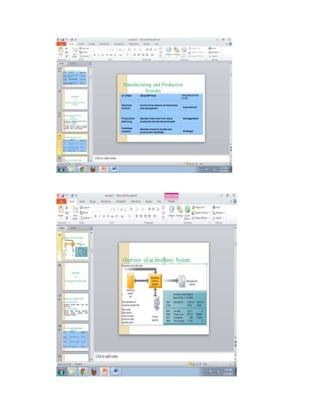
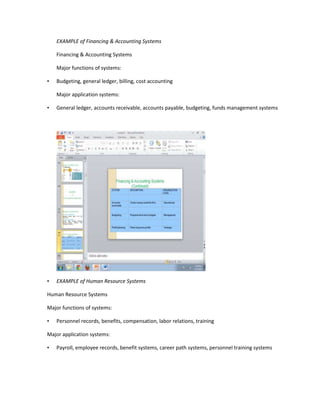
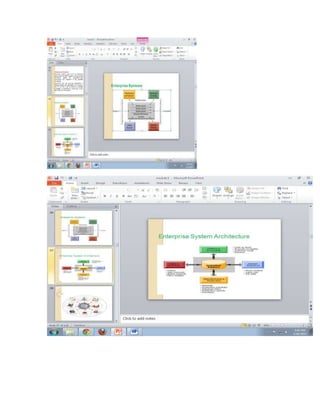
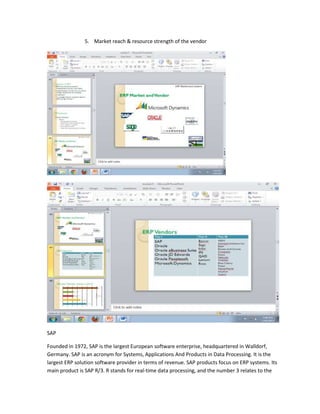
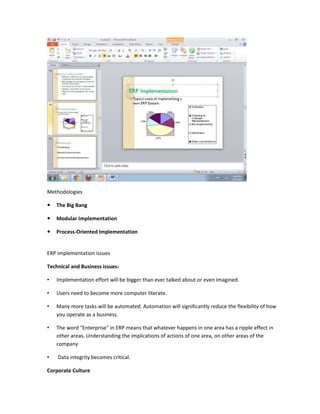
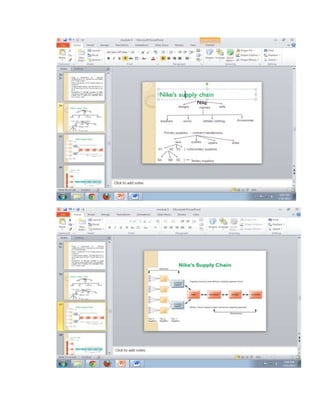
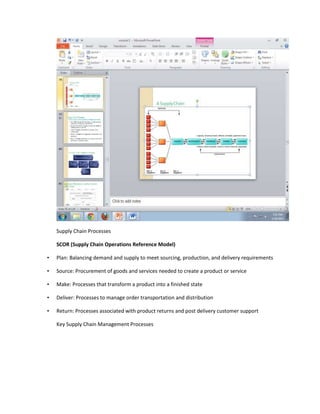
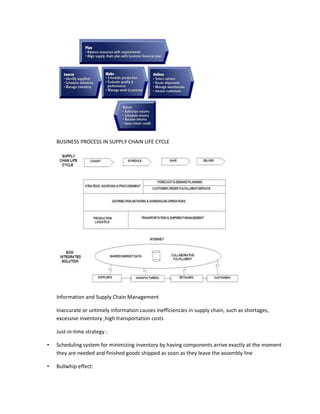
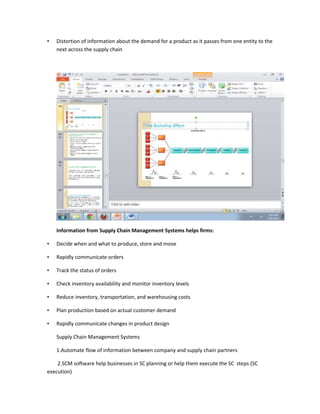
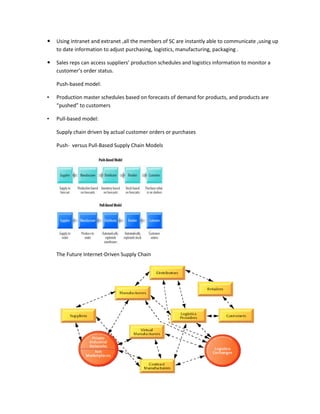
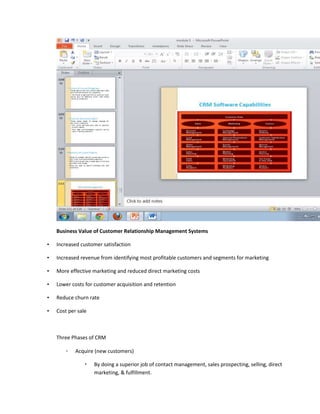
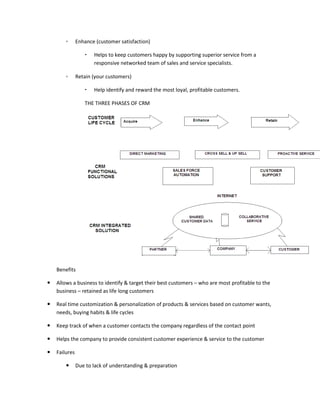
The document provides information on business applications and processes. It discusses business processes and examples like manufacturing, sales and marketing, finance and accounting, and human resources. It then gives examples of information systems that support these processes, such as ERP systems, supply chain management systems, and CRM systems. Finally, it discusses the benefits of enterprise systems for integrating business processes and information flow across an organization.